Abstract
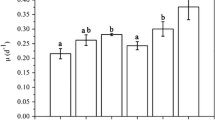
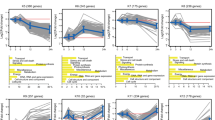
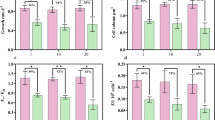
With atmospheric CO2 increasing, a large amount of CO2 is absorbed by oceans and lakes, which changes the carbonate system and affects the survival of aquatic plants, especially microalgae. The main aim of our study was to explore the responses of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyceae) to elevated CO2 by combined transcriptome and metabolome analysis under three different scenarios: control (CK, 400 ppm), short-term elevated CO2 (ST, 1000 ppm), and long-term elevated CO2 (LT, 1000 ppm). The transcriptomic data showed moderate changes between ST and CK. However, metabolic analysis indicated that fatty acids (FAs) and partial amino acids (AAs) were increased under ST. There was a global downregulation of genes involved in photosynthesis, glycolysis, lipid metabolism, and nitrogen metabolism but increase in the TCA cycle and β-oxidation under LT. Integrated transcriptome and metabolome analyses demonstrated that the nutritional constituents (FAs, AAs) under LT were poor compared with CK, and most genes and metabolites involved in C and N metabolism were significantly downregulated. However, the growth and photosynthesis of cells under LT increased significantly. Thus, C. reinhardtii could form a specific adaptive evolution to elevated CO2, affecting future biogeochemical cycles.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CK:
-
Control
- ST:
-
Short-term acidification
- LT:
-
Long-term acidification
- Ppm:
-
Parts per million
- LC:
-
Low concentrations of CO2
- HC:
-
High concentrations of CO2
- UPLC-Q-TOF-MS:
-
Ultra-performance liquid chromatograph coupled to quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry
- CCM:
-
CO2 concentrating mechanism
- FPKM:
-
Fragments per kilobase million mapped reads
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genomes
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PLS-DA:
-
Partial least squares-discriminant analysis
- OPLS-DA:
-
Orthogonal projections for latent structures-discriminant analysis
- DEG:
-
Differentially expressed gene
- SDM:
-
Significantly different metabolite
- VIP:
-
Variable importance for the projection
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- FA:
-
Fatty acid
- AA:
-
Amino acid
References
Alberts AW, Vagelos PR (1968) Acetyl CoA carboxylase. i. Requirement for two protein fractions. Pro Natl Acad Sci USA 59:561–568
Allen AE, Ward BB, Song B (2005) Characterization of diatom (Bacillariophyceae) nitrate reductase genes and their detection in marine phytoplankton communities. J Phycol 41:95–104
Bailly J, Coleman JR (1988) Effect of CO2 concentration on protein biosynthesis and carbonic anhydrase expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 87:833–840
Blatti JL, Michaud J, Burkart MD (2013) Engineering fatty acid biosynthesis in microalgae for sustainable biodiesel. Curr Opin Chem Biol 17:496–505
Bogaert KA, Perez E, Rumin J, Giltay A, Carone M, Coosemans N, Radoux M, Eppe G, Levine RD, Remacle F, Remacle C (2019) Metabolic, physiological, and transcriptomics analysis of batch cultures of the green microalga Chlamydomonas grown on different acetate concentrations. Cells 8:1367
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Bowler C, Vardi A, Allen AE (2010) Oceanographic and biogeochemical insights from diatom genomes. Annu Rev Mar Sci 2:333–365
Brennan G, Collins S (2015) Growth responses of a green alga to multiple environmental drivers. Nat Clim Chang 5:892–897
Cheng J, Li K, Zhu Y, Yang W, Zhou J, Cen K (2017) Transcriptome sequencing and metabolic pathways of astaxanthin accumulated in Haematococcus pluvialis mutant under 15% CO2. Bioresour Technol 228:99–105
Chiu SY, Kao CY, Tsai MT, Ong SC, Chen CH, Lin CS (2009) Lipid accumulation and CO2 utilization of Nannochloropsis oculata in response to CO2 aeration. Bioresour Technol 100:833–838
Choi SP, Nguyen MT, Sim SJ (2010) Enzymatic pretreatment of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii biomass for ethanol production. Bioresour Technol 101:5330–5336
Collins S, Bell G (2004) Phenotypic consequences of 1,000 generations of selection at elevated CO2 in a green alga. Nature 431:566
Collins S, Sultemeyer D, Bell G (2006) Changes in C uptake in populations of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii selected at high CO2. Plant Cell Environ 29:1812–1819
Davis M, Fiehn O, Durnford DG (2013) Metabolic acclimation to excess light intensity in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Environ 36:1391–1405
Devi MP, Mohan SV (2012) CO2 supplementation to domestic wastewater enhances microalgae lipid accumulation under mixotrophic microenvironment: effect of sparging period and interval. Bioresour Technol 112:116–123
Dong T, Han R, Yu J, Zhu M, Zhang Y, Gong Y, Li Z (2019) Anthocyanins accumulation and molecular analysis of correlated genes by metabolome and transcriptome in green and purple asparaguses (Asparagus officinalis, L.). Food Chem 271:18–28
Driver T, Trivedi DK, McIntosh OA, Dean AP, Goodacre R, Pittman JK (2017) Two glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenases from Chlamydomonas have distinct roles in lipid metabolism. Plant Physiol 174:2083–2097
Eriksson M, Villand P, Gardeström P, Samuelsson G (1998) Induction and regulation of expression of a low-CO2-induced mitochondrial carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 116:637–641
Fan J, Xu H, Li Y (2016) Transcriptome-based global analysis of gene expression in response to carbon dioxide deprivation in the green algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Algal Res 16:12–19
Fan J, Xu H, Luo Y, Wan M, Huang J, Wang W, Li Y (2015) Impacts of CO2 concentration on growth, lipid accumulation, and carbon-concentrating-mechanism-related gene expression in oleaginous Chlorella. Appl Microbiol and Biotechnol 99:2451–2462
Fernie AR, Carrari F, Sweetlove LJ (2004) Respiratory metabolism: glycolysis, the TCA cycle and mitochondrial electron transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:254–261
Genty B, Briantais JM, Baker NR (1989) The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta-Gen Subjects 990:87–92
Hasler CT, Jeffrey JD, Schneider EVC, Hannan KD, Tix JA, Suski CD (2017) Biological consequences of weak acidification caused by elevated carbon dioxide in freshwater ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 806:1–12
Hauke J, Kossowski T (2011) Comparison of values of Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlation coefficients on the same sets of data. Quaest Geogr 30:87–93
Hockin NL, Mock T, Mulholland F, Kopriva S, Malin G (2012) The response of diatom central carbon metabolism to nitrogen starvation is different from that of green algae and higher plants. Plant Physiol 158:299–312
Ibáñez AM, Martinelli F, Reagan RL, Uratsu SL, Vo A, Tinoco MA, Phu ML, Chen Y, Rocke DM, Dandekar AM (2014) Transcriptome and metabolome analysis of citrus fruit to elucidate puffing disorder. Plant Sci 217–218:87–98
Jin J, Zhang H, Zhang J, Liu P, Chen X, Li Z, Xu Y, Lu P, Cao P (2017) Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis to characterize cold stress responses in Nicotiana tabacum. BMC Genomics 18:496
Jose S, Suraishkumar GK (2016) High carbon (CO2) supply leads to elevated intracellular acetyl CoA levels and increased lipid accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris. Algal Res 19:307–315
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2015) HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 12:357–360
Kim MS, Baek JS, Yun YS, Sim SJ, Park S, Kim SC (2006) Hydrogen production from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii biomass using a two-step conversion process: anaerobic conversion and photosynthetic fermentation. Int J Hydrog Energy 31:812–816
Kong QX, Li L, Martinez B, Chen P, Ruan R (2010) Culture of microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in wastewater for biomass feedstock production. Appl Biochem and Biotechnol 160:9–18
Li F, Beardall J, Collins S, Gao K (2017) Decreased photosynthesis and growth with reduced respiration in the model diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum grown under elevated CO2 over 1800 generations. Glob Change Biol 23:127–137
Li J, Han D, Wang D, Ning K, Jia J, Wei L, Jing X, Huang S, Chen J, Li Y, Hu Q, Xu J (2014) Choreography of transcriptomes and lipidomes of Nannochloropsis reveals the mechanisms of oil synthesis in microalgae. Plant Cell 26:1645–1665
Liang C, Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Zhang X, Ye N (2020) The effects of elevated CO2 concentrations on changes in fatty acids and amino acids of three species of microalgae. Phycologia 59:208–217
Mehta K, Jaiswal D, Nayak M, Prasannan CB, Wangikar PP, Srivastava S (2019) Elevated carbon dioxide levels lead to proteome-wide alterations for optimal growth of a fast-growing cyanobacterium, Synechococcus elongatus PCC 11801. Sci Rep 9:6257
Morin N, Cescut J, Beopoulos A, Lelandais G, Berre VL, Uribelarrea JL, Molina-Jouve C, Nicaud JM (2011) Transcriptomic analyses during the transition from biomass production to lipid accumulation in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. PLoS One 6:e27966
Noguchi K, Watanabe CK, Terashima I (2015) Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on primary metabolite levels in Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 leaves: an examination of metabolome data. Plant Cell Physiol 56:2069–2078
Peng H, Wei D, Chen G, Chen F (2016) Transcriptome analysis reveals global regulation in response to CO2 supplementation in oleaginous microalga Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C-169. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:151
Polturak G, Heinig U, Grossman N, Battat M, Leshkowitz D, Malitsky S, Rogachev I, Aharoni A (2018) Transcriptome and metabolic profiling provides insights into betalain biosynthesis and evolution in Mirabilis jalapa. Mol Plant 11:189–204
Ramanathan V (1988) The greenhouse theory of climate change: a test by an inadvertent global experiment. Science 240:293–299
Raven JA, Girard-Bascou J (2002) Algal model systems and the elucidation of photosynthetic metabolism. J Phycol 37:943–950
Rismani-Yazdi H, Haznedaroglu BZ, Hsin C, Peccia J (2012) Transcriptomic analysis of the oleaginous microalga Neochloris oleoabundans reveals metabolic insights into triacylglyceride accumulation. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:74
Ruocco M, Musacchia F, Olive I, Costa MM, Barrote I, Santos R, Sanges R, Procaccini G, Silva J (2017) Genomewide transcriptional reprogramming in the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa under experimental ocean acidification. Mol Ecol 26:4241–4259
Ryall K, Harper JT, Keeling PJ (2003) Plastid-derived Type II fatty acid biosynthetic enzymes in chromists. Gene 313:139–148
Salie MJ, Thelen JJ (2016) Regulation and structure of the heteromeric acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1861:1207–1213
Spalding MH (1989) Photosynthesis and photorespiration in freshwater green algae. Aquat Bot 34:181–209
Stets EG, Butman D, McDonald CP, Stackpoole SM, DeGrandpre MD, Striegl RG (2017) Carbonate buffering and metabolic controls on carbon dioxide in rivers. Glob Biogeochem Cycle 31:663–677
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Sun Z, Chen YF, Du J (2016) Elevated CO2 improves lipid accumulation by increasing carbon metabolism in Chlorella sorokiniana. Plant Biotechnol J 14:557–566
Sweetlove LJ, Beard KFM, Nunes-Nesi A, Fernie AR, Ratcliffe RG (2010) Not just a circle: flux modes in the plant TCA cycle. Trends Plant Sci 15:462–470
Wagner GP, Kin K, Lynch VJ (2012) Measurement of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data: RPKM measure is inconsistent among samples. Theory Biosci 131:281–285
Waite M, Wakil SJ (1962) Studies on the mechanism of fatty acid synthesis. XII. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. J Biol Chem 237:2750–2757
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang X (2010) DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 26:36–138
Wang N, Qian Z, Luo M, Fan S, Zhang X, Zhang L (2018) Identification of salt stress responding genes using transcriptome analysis in green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Int J Mol Sci 19:3359
Xia JR, Gao KS (2005) Impacts of elevated CO2 concentration on biochemical composition, carbonic anhydrase, and nitrate reductase activity of freshwater green algae. J Integr Plant Biol 47:668–675
Yang Y, Gao K (2003) Effects of CO2 concentrations on the freshwater microalgae, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus (Chlorophyta). J Appl Phycol 15:379–389
Yang Y, Gao K, Xia J (2001) Effects of doubled atmospheric CO2 concentration on the growth and photosynthesis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Volvocales, Chlorophyceae). Phycol Res 49:299–303
Yoo C, Jun SY, Lee JY, Ahn CY, Oh HM (2010) Selection of microalgae for lipid production under high levels carbon dioxide. Bioresour Technol 101:S71–S74
Zhou P, Li Q, Liu G, Xu N, Yang Y, Zeng W, Chen A, Wang S (2018) Integrated analysis of transcriptomic and metabolomic data reveals critical metabolic pathways involved in polyphenol biosynthesis in Nicotiana tabacum under chilling stress. Funct Plant Biol 46:30–43
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant numbers 2018YFD0900703), Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development Program under contract 2019JZZY020706, National Natural Science Foundation of China grant (31770393), Financial Fund of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, P. R. of China (NFZX2018), China Agriculture Research System (CARS-50), and Taishan Scholars Funding of Shandong Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.W.L. and N.H.Y. designed the project. Y.F.Z., Z.P.G., Y.D.R., L.W., and J.Z. performed the research. Y.F.Z., C.W.L., S.Y.T., D.X., X.W.Z., and Y.T.W. analyzed the data. Y.F.Z. and C.W.L. wrote the first draft. All authors contributed to interpreting the data and writing the manuscript. The manuscript is approved by all authors for publications. This work is the original works of the authors, and the manuscript was not previously submitted to this journal.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Gu, Z., Ren, Y. et al. Integrating Transcriptomics and Metabolomics to Characterize Metabolic Regulation to Elevated CO2 in Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii. Mar Biotechnol 23, 255–275 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-021-10021-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-021-10021-y