Abstract
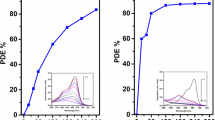
TiO2 is one of the most used materials in the photocatalysis of organic pollutants. It can be prepared by different techniques including electrochemical methods. The influence of the structure of TiO2 films grown electrochemically using plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) was investigated in terms of the photocatalytic activity. The film microstructure and morphology were analyzed and its influence in photocatalytic response was evaluated by photodegradation of ciprofloxacin (CIP). A strong influence of the synthesis temperature on the structural properties (pore diameter and crystallite size) was observed, which could be correlated with the photocatalytic activity change of the synthesized materials. To correlate the structural to the photocatalytic activity, besides Pareto graphs and analysis, a variable called microstructure ratio-SR (pore diameter/crystallite size) was evaluated. Results have shown the F2020005 film (20 mA cm−2, 20 °C and 0.05 mol L−1) presented the highest photocatalytic activity. As a complementary study, ecotoxicity tests were realized using Lactuca sativa L. seeds and the macrophyte Lemna minor. In these experiments, it was observed that the effluents of the photocatalysis carried out with the materials synthesized by PEO presented lower toxicity, compared to the CIP solution without any treatment. The best results for the degradation of CIP were obtained using films synthesized at higher temperatures. CIP photocatalytic degradation using TiO2 films grown by PEO was effective, generating byproducts of low toxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon request.
References
An T, Yang H, Li G et al (2010) Kinetics and mechanism of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in degradation of ciprofloxacin in water. Appl Catal B Environ 94:288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.12.002
de Brito CR, de Melo IP, Neto J (2012) Tratabilidade química e biológica de efluente farmacêutico contendo ciprofloxacino. REA—Rev Estud Ambient 14:6–16. https://doi.org/10.7867/1983-1501.2012v14n3p6-16
de Oliveira M, Frihling BEF, Velasques J et al (2020) Pharmaceuticals residues and xenobiotics contaminants: occurrence, analytical techniques and sustainable alternatives for wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 705:135568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135568
Ebele AJ, Abou-Elwafa Abdallah M, Harrad S (2017) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment. Emerg Contam 3:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2016.12.004
Fawzi Suleiman Khasawneh O, Palaniandy P (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals using TiO2 based nanocomposite catalyst-review. Civ Environ Eng Rep 29:1–33. https://doi.org/10.2478/ceer-2019-0021
Ferreira CH, Nunes SC, Santos VAQ et al (2018) Plasma electrolytic titanium oxide applied for pathogenic bacteria inactivation. Environ Technol 41:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1491641
Gad-Allah TA, Ali MEM, Badawy MI (2011) Photocatalytic oxidation of ciprofloxacin under simulated sunlight. J Hazard Mater 186:751–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.066
Guo Q, Ma Z, Zhou C et al (2019) Single molecule photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces. Chem Rev 119:11020–11041. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00226
Gusain R, Gupta K, Joshi P, Khatri OP (2019) Adsorptive removal and photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using metal oxides and their composites: a comprehensive review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 272:102009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2019.102009
Halling-Sorensen B (2000) Environmental risk assessment of antibiotics: comparison of mecillinam, trimethoprim and ciprofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother 46:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/46.suppl_1.53
Hassanzadeh S, Mashhadi R, Yousefi M et al (2017) Frequency of efflux pump genes mediating ciprofloxacin and antiseptic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Microb Pathog 111:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.08.026
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1972) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Agricultural Experiment Station, California
Khan RHU, Yerokhin AL, Matthews A (2008) Structural characteristics and residual stresses in oxide films produced on Ti by pulsed unipolar plasma electrolytic oxidation. Philos Mag 88:795–807. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786430801968603
Kuang D, Zhang J, Xu X et al (2018) Emerging high-level ciprofloxacin resistance and molecular basis of resistance in Salmonella enterica from humans, food and animals. Int J Food Microbiol 280:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.05.001
Kümmerer K (2009) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—a review—part I. Chemosphere 75:417–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.086
Kunz A, Peralta-Zamora P, de Moraes SG, Durán N (2002) Novas tendências no tratamento de efluentes têxteis. Quim Nova 25:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422002000100014
Malakootian M, Nasiri A, Amiri Gharaghani M (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin antibiotic by TiO2 nanoparticles immobilized on a glass plate. Chem Eng Commun 207:56–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2019.1573168
Mirzaei R, Mesdaghinia A, Hoseini SS, Yunesian M (2019) Antibiotics in urban wastewater and rivers of Tehran, Iran: consumption, mass load, occurrence, and ecological risk. Chemosphere 221:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.187
Montagner C, Sodré F, Acayaba R et al (2018) Ten years-snapshot of the occurrence of emerging contaminants in drinking, surface and ground waters and wastewaters from São Paulo State, Brazil. J Braz Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180232
Montañés MT, García-Gabaldón M, Roca-Pérez L et al (2020) Analysis of norfloxacin ecotoxicity and the relation with its degradation by means of electrochemical oxidation using different anodes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 188:109923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109923
Mustapha S, Ndamitso MM, Abdulkareem AS et al (2020) Application of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles immobilized on clay in wastewater treatment: a review. Appl Water Sci 10:49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1138-y
Nogueira RFP, Jardim WF (1998) A fotocatálise heterogênea e sua aplicação ambiental. Quim Nova 2:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40421998000100011
Novo A, André S, Viana P et al (2013) Antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial residues and bacterial community composition in urban wastewater. Water Res 47:1875–1887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.01.010
de Oliveira GAR, Leme DM, de Lapuente J et al (2018) A test battery for assessing the ecotoxic effects of textile dyes. Chem Biol Interact 291:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.06.026
Schneider J, Matsuoka M, Takeuchi M et al (2014) Understanding TiO2 Photocatalysis: mechanisms and Materials. Chem Rev 114:9919–9986. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr5001892
Shetty R, Chavan VB, Kulkarni PS et al (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals pollutants using N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst: identification of CFX degradation intermediates. Indian Chem Eng 59:177–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00194506.2016.1150794
Sikora MS, Rosario AV, Pereira EC, Paiva-Santos CO (2011) Influence of the morphology and microstructure on the photocatalytic properties of titanium oxide films obtained by sparking anodization in H3PO4. Electrochim Acta 56:3122–3127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.01.068
Torres NH, Américo JH, Ferreira LFR et al (2012) Fármacos no ambiente—revisão. Rev Estud Ambient 14:67–75. https://doi.org/10.7867/1983-1501.2012v14n4p67-75
Van Doorslaer X, Dewulf J, Van Langenhove H, Demeestere K (2014) Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: an emerging class of environmental micropollutants. Sci Total Environ 500–501:250–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.075
Xing X, Du Z, Zhuang J, Wang D (2018) Removal of ciprofloxacin from water by nitrogen doped TiO2 immobilized on glass spheres: rapid screening of degradation products. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 359:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.026
Zavala MÁL, Reynoso-Cuevas L (2015) Simultaneous extraction and determination of four different groups of pharmaceuticals in compost using optimized ultrasonic extraction and ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1423:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.10.051
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Wang X et al (2017) Siderophores in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae promote ciprofloxacin resistance by inhibiting the oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 491:855–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.108
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to LIEC-UFSCar and the Analysis Center of UTFPR-PB.
Funding
This work was supported by FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo) (Grant: #2008/00180–0, #2013/07296–2, #2014/50249–8, #2017/11986–5) and CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, Brazil) (Grant: 408250/2016–0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: R. Saravanan.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, A.S., Rocha, R.D.C., Pereira, E.C. et al. Photodegradation of Ciprofloxacin antibiotic over TiO2 grown by PEO: ecotoxicity response in Lactuca sativa L. and Lemna minor. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 2771–2780 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03239-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03239-9