Abstract—
The topic of the present study is combining a dynamic model of a protoplanetary disk with the computations of radiation transfer for obtaining synthetic spectra and disk images suitable for immediate comparison of the model with observations. Evolution of the disk was computed using the FEOSAD hydrodynamic model, which includes a self-consistent calculation of the dynamics of dust and gas in the 2D thin disk approximation. Radiation transfer was simulated by the open code RADMC-3D. Three phases of disk evolution were considered: a young gravitationally unstable disk, a disk during an accretion luminosity burst, and an evolved disk. For these stages, the influence of various processes upon the disk’s thermal structure was analyzed, as well as the differences between the temperatures obtained in the initial dynamic model and in the model with a detailed calculation of the radiation transfer. It is shown that viscous heating in the inner regions and adiabatic heating in the disk spirals can be important sources of heating. On the basis of the calculated spectral energy distributions, using SED-fitter software package used for the observations, physical parameters of the model disks were reconstructed. A significant spread between reconstructed parameters and initial characteristics of the disk indicates verification necessity of the models within the framework of spatially resolved observations of disks in the different spectral ranges.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
www.ita.uni-heidelberg.de/~dullemond/software/radmc-3d
REFERENCES
J. B. Pollack, O. Hubickyj, P. Bodenheimer, J. J. Lissauer, M. Podolak, and Y. Greenzweig, Icarus 124, 62 (1996).
A. P. Boss, Astrophys. J. 599, 577 (2003).
E. I. Vorobyov, Astron. Astrophys. 552, A129 (2013); arXiv: 1302.1892 [astro-ph.EP].
S. Nayakshin, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 408, L36 (2010); arXiv: 1007.4159 [astro-ph.EP].
A. C. Boley, T. Hayfield, L. Mayer, and R. H. Durisen, Icarus 207, 509 (2010); arXiv: 0909.4543 [astro-ph.EP].
J. P. Williams and L. A. Cieza, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 49, 67 (2011); arXiv: 1103.0556 [astro-ph.GA].
J. R. Najita, S. E. Strom, and J. Muzerolle, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 378, 369 (2007); arXiv: 0704.1681 [astro-ph].
L. A. Cieza, M. R. Schreiber, G. A. Romero, M. D. Mora, et al., Astrophys. J. 712, 925 (2010); arXiv: 1001.4825 [astro-ph.GA].
C. J. Lada, in Star Forming Regions, Ed. by M. Peimbert and J. Jugaku, IAU Symp. 115, 1 (1987).
S. V. W. Beckwith, A. I. Sargent, R. S. Chini, and R. Guesten, Astron. J. 99, 924 (1990).
E. I. Chiang and P. Goldreich, Astrophys. J. 490, 368 (1997); arXiv: astro-ph/9706042.
P. Woitke, in Proceedings of the Summer School on Protoplanetary Disks: Theory and Modeling Meet Observations, Ed. by I. Kamp, P. Woitke, and J. D. Ilee, EPJ Web of Conf. 102, 00007 (2015).
C. R. O’Dell and Z. Wen, Astrophys. J. 436, 194 (1994).
H. Avenhaus, S. P. Quanz, A. Garufi, S. Pérez, et al., Astrophys. J. 863, 44 (2018); arXiv: 1803.10882 [astro-ph.SR].
A. Dutrey, S. Guilloteau, G. Duvert, L. Prato, M. Simon, K. Schuster, and F. Menard, Astron. Astrophys. 309, 493 (1996).
S. M. Andrews, J. Huang, L. M. Pérez, A. Isella, et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 869, L41 (2018); arXiv: 1812.04040 [astro-ph.SR].
M. Flock, J. P. Ruge, N. Dzyurkevich, T. Henning, H. Klahr, and S. Wolf, Astron. Astrophys. 574, A68 (2015); arXiv: 1411.2736 [astro-ph.EP].
R. Dong, Z. Zhu, and B. Whitney, Astrophys. J. 809, 93 (2015); arXiv: 1411.6063 [astro-ph.EP].
P. Woitke, I. Kamp, S. Antonellini, F. Anthonioz, et al., Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 131, 064301 (2019); arXiv: 1812.02741 [astro-ph.EP].
E. I. Vorobyov, V. Akimkin, O. Stoyanovskaya, Y. Pav-lyuchenkov, and H. B. Liu, Astron. Astrophys. 614, A98 (2018); arXiv: 1801.06898 [astro-ph.EP].
E. I. Vorobyov and S. Basu, Astrophys. J. 650, 956 (2006); arXiv: astro-ph/0607118.
E. I. Vorobyov and V. G. Elbakyan, Astron. Astrophys. 631, A1 (2019); arXiv: 1908.10589 [astro-ph.SR].
E. I. Vorobyov, A. M. Skliarevskii, V. G. Elbakyan, Y. Pavlyuchenkov, V. Akimkin, and M. Guedel, Astron. Astrophys. 627, A154 (2019); arXiv: 1905.11335 [astro-ph.EP].
V. G. Elbakyan, A. Johansen, M. Lambrechts, V. Akimkin, and E. I. Vorobyov, Astron. Astrophys. 637, A5 (2020); arXiv: 2004.00126 [astro-ph.EP].
G. Lodato, New Astron. Rev. 52, 21 (2008).
E. I. Vorobyov and Y. N. Pavlyuchenkov, Astron. Astrophys. 606, A5 (2017); arXiv: 1706.00401 [astro-ph.GA].
K. Kornet, T. F. Stepinski, and M. Różyczka, Astron. Astrophys. 378, 180 (2001).
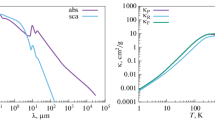
D. Semenov, T. Henning, C. Helling, M. Ilgner, and E. Sedlmayr, Astron. Astrophys. 410, 611 (2003); arXiv: astro-ph/0308344.
R. Dong, E. Vorobyov, Y. Pavlyuchenkov, E. Chiang, and H. B. Liu, Astrophys. J. 823, 141 (2016); arXiv: 1603.01618 [astro-ph.SR].
S. M. Andrews, K. A. Rosenfeld, A. L. Kraus, and D. J. Wilner, Astrophys. J. 771, 129 (2013); arXiv: 1305.5262 [astro-ph.SR].
T. P. Robitaille, B. A. Whitney, R. Indebetouw, and K. Wood, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 169, 328 (2007); arXiv: astro-ph/0612690.
D. An, S. V. Ramírez, K. Sellgren, R. G. Arendt, et al., Astrophys. J. 736, 133 (2011); arXiv: 1104.4788 [astro-ph.GA].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was supported by Russian Foundation for Basic Research (contract No. 19-32-50146). E.V. acknowledges support by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Russian Federation (state science assignment to Southern Federal University VnGr /2020-03-IF, 2020).
Additional information
Translated by L. Yungelson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skliarevskii, A.M., Pavlyuchenkov, Y.N. & Vorobyov, E.I. Restoration of the Parameters of a Gas-Dust Disk Based on Its Synthetic Images. Astron. Rep. 65, 170–183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063772921030045
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063772921030045