Abstract
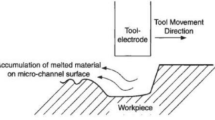
Because of the low surface roughness of three-dimensional (3D) printed microchannels, in some environments, the use requirements cannot be met, and, at the same time, they are difficult to process. Therefore, a surface roughness analysis of 3D printed microchannels and post-processing using abrasive flow technology are proposed. The value of the inner surface roughness of the straight pipe part was calculated by using the least-squares method combined with the definite integral. Using the equal area principle, MATLAB curve fitting was used to numerically calculate the semicircular pipe section, and the relationship between the value of surface roughness and the bending radius of the scanning layer thickness is given. Use MATLAB image processing technology to study the processing area. The roughness of the inner wall of the pipeline was analyzed by laser confocal, stereo, and scanning electron microscopes. The results show that the roughness of the inner surface of the pipe increases with an increase in the thickness of the sweeping layer, an increase in the inclination angle, and a decrease in the radius of curvature. In the case of abrasive flow processing, the longer the processing time, the greater the grinding amount and the greater the amount of grinding outside the pipe wall in each one-way machining; further, the processing has obvious directionality.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, C.; Dai, G.; Hong, Y.: Recent advances in high-strength and elastic hydrogels for 3D printing in biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 95, 50–59 (2019)
Matta, A.K.; Kodali, S.P.; Ivvala, J.; Kumar, P.J.: Metal prototyping the future of automobile industry: a review. Mater. Today: Proc. 5(9), 17597–17601 (2018)
O’Hara, W.J.; Kish, J.M.; Werkheiser, M.J.: Turn-key use of an onboard 3D printer for international space station operations. Addit. Manuf. 24, 560–565 (2018)
Kruth, J.P.; Leu, M.C.; Nakagawa, T.: Progress in additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 47(2), 525–540 (1998)
Wohlers, T.: Future potential of rapid prototyping and manufacturing around the world. Rapid Prototyp. J. 1(1), 4–10 (1995)
Lalehpour, A.; Janeteas, C.; Barari, A.: Surface roughness of FDM parts after post-processing with acetone vapor bath smoothing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 95, 1505–1520 (2017)
Ayrilmis, N.: Effect of layer thickness on surface properties of 3D printed materials produced from wood flour/PLA filament. Polym. Test. 71, 163–166 (2018)
Song, B.; Dong, S.; Zhang, B., et al.: Effects of processing parameters on microstructure and mechanical property of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V. Mater. Des. 35, 120–125 (2012)
Mumtaz, K.; Hopkinson, N.: Top surface and side roughness of Inconel 625 parts processed using selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 15(2), 96–103 (2009)
Bhaduri, D.; Penchev, P.; Batal, A., et al.: Laser polishing of 3D printed mesoscale components. Appl. Surf. Sci. 405, 29–46 (2017)
Zhang, B.; Xiaohua, L.; Bai, J., et al.: Study of selective laser melting (SLM) Inconel 718 part surface improvement by electrochemical polishing. Mater. Des. 116, 531–537 (2017)
Atzeni, E.; Barletta, M.; Calignano, F.: Abrasive fluidized bed (AFB) finishing of AlSi10Mg substrates manufactured by direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). Addit. Manuf. 10, 15–23 (2016)
Uhlmann, E.; Schmiedel, C.; Wendler, J.: CFD Simulation of the abrasive flow machining process. Proc. Cirp 31, 209–214 (2015)
Zhang, J.; Chaudhari, A.; Wang, H.: Surface quality and material removal in magnetic abrasive finishing of selective laser melted 316L stainless steel. J. Manuf. Process. 45(Sep), 710–719 (2019)
Singh, P.; Singh, L.; Sehijpal, S.: Manufacturing and performance analysis of mechanically alloyed magnetic abrasives for magneto abrasive flow finishing. J. Manuf. Process. 50, 161–169 (2020)
Williams, R.E.; Melton, V.L.: Abrasive flow finishing of stereolithography prototypes. Rapid Prototyp. J. 4(2), 56–67 (1998)
Pandey, P.M.; Reddy, N.V.; Dhande, S.G.: Improvement of surface finish by staircase machining in fused deposition modeling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 132(1–3), 323–331 (2003)
Pandey, P.M.; Reddy, N.V.; Dhande, S.G.: Real time adaptive slicing for fused deposition modelling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 43(1), 61–71 (2003)
Thrimurthulu, K.; Pandey, P.M.; Reddy, N.V.: Optimum part deposition orientation in fused deposition modeling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 44(6), 585–594 (2004)
Boschetto, A.; Bottini, L.: Surface improvement of fused deposition modeling parts by barrel finishing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 21(6), 686–696 (2015)
Jain, R.K.; Jain, V.K.: Stochastic simulation of active grain density in abrasive flow machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 152(1), 17–22 (2003)
Gorana, V.K.; Jain, V.K.; Lal, G.K.: Experimental investigation into cutting forces and active grain density during abrasive flow machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 44(2), 201–211 (2003)
Gorana, V.K.; Jain, V.K.; Lal, G.K.: Forces prediction during material deformation in abrasive flow machining. Wear 260(1), 128–139 (2004)
Jain, R.K.; Jain, V.K.: Specific energy and temperature determination in abrasive flow machining process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 41(12), 1689–1704 (2001)
Kumar, S.S.; Hiremath, S.S.: A review on abrasive flow machining (AFM). Proc. Technol. 25, 1297–1304 (2016)
Finnie, I.: Some observations on the erosion of ductile metals. Wear 19(1), 81–90 (1972)
Jain, V.K.: Magnetic field assisted abrasive based micro-/nano-finishing. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 209(20), 6022–6038 (2009)
Jayswal, S.C.; Jain, V.K.; Dixit, P.M.: Modeling and simulation of magnetic abrasive finishing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 26(5–6), 477–490 (2005)
Khitun, A.; Bao, M.; Wang, K.L.: Magnetic cellular nonlinear network with spin wave bus for image processing. Superlattices Microstruct. 47(3), 464–483 (2010)
Mora, C.; Kwan, A.: Sphericity, shape factor, and convexity measurement of coarse aggregate for concrete using digital image processing. Cem. Concr. Res. 30(3), 351–358 (2000)
Szmaja, W.: Digital image processing system for magnetic domain observation in SEM. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 189(3), 353–365 (1998)
Acknowledgements
The authors are also grateful for the financial aids from the National key R&D Project (Grant No: 2017YFB1104601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jian, Y., Shi, Y., Liu, J. et al. Surface Roughness Analysis of 3D Printed Microchannels and Processing Characteristics of Abrasive Flow Finishing. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 801–812 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05260-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05260-5