Abstract
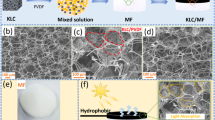
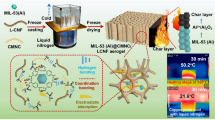
In this paper, we employed a facile approach to prepare flexible and porous metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) containing cellulose nanofiber (CNF) aerogels (MNCAs) through freeze-drying MOF-containing cellulose nanofiber suspensions. After coating with methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS) by chemical vapor deposition, recycled and hydrophobic MTMS-coated MNCAs (MMNCAs) were obtained. Due to the low density (0.009 g/cm3), high porosity (97%) and good mechanical properties of the aerogel, the adsorption capacity of MMNCAs reached up to 210 g/g, which was nearly 3–5 times that of pure CNF aerogels. These prepared aerogels showed excellent oil/water selectivity and high capacity to adsorb oil and organic solvents. This kind of cellulose-based aerogel may be applicable in the field of environmental protection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vibhute A M, Muvvala V, Sureshan K M. A sugar-based gelator for marine oil-spill recovery. Angewandte Chemie, 2016, 128(27): 7913–7916
Chapman H, Purnell K, Law R J, Kirby M F. The use of chemical dispersants to combat oil spills at sea: a review of practice and research needs in Europe. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 54(7): 827–838
Kuyukina M S, Ivshina I B, Ritchkova M I, Philp J C, Cunningham C J, Christofi N. Bioremediation of crude oil-contaminated soil using slurry-phase biological treatment and land farming techniques. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 2003, 12(1): 85–99
Angelova D, Uzunov I, Uzunova S, Gigova A, Minchev L. Kinetics of oil and oil products adsorption by carbonized rice husks. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 172(1): 306–311
Sabir S. Approach of cost-effective adsorbents for oil removal from oily water. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2015, 45(17): 1916–1945
Maleki H. Recent advances in aerogels for environmental remediation applications: a review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 300: 98–118
Wang C H, Kim J, Tang J, Na J, Kang Y M, Kim M, Lim H, Bando Y, Li J, Yamauchi Y. Large-scale synthesis of MOF-derived superporous carbon aerogels with extraordinary adsorption capacity for organic solvents. Angewandte Chemie, 2020, 59(5): 2066–2070
Muhd Julkapli N, Bagheri S. Nanocellulose as a green and sustainable emerging material in energy applications: a review. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2017, 28(12): 1583–1594
Timo H, Fan Z, Tobias R, Andreas W, Rolf M. Nanocellulose aerogels for supporting iron catalysts and in situ formation of polyethylene nanocomposites. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(11): 1605586
Li Y L, Liu Y S, Liu Y, Lai W C, Huang F, Ou A P, Qin R, Liu X Y, Wang X. Ester crosslinking enhanced hydrophilic cellulose nanofibrils aerogel. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(9): 11979–11988
Wu Z Y, Liang H W, Chen L F, Hu B C, Yu S H. Bacterial cellulose: a robust platform for design of three dimensional carbon-based functional nanomaterials. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2016, 49 (1): 96–105
Phanthong P, Reubroycharoen P, Kongparakul S, Samart C, Wang Z D, Hao X G, Abudula A, Guan G Q. Fabrication and evaluation of nanocellulose sponge for oil/water separation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 190: 184–189
Huang S, Wang D Y. A simple nanocellulose coating for self-cleaning upon water action: molecular design of stable surface hydrophilicity. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56 (31): 9053–9057
Jin H, Kettunen M, Laiho A, Pynnonen H, Paltakari J, Marmur A, Ikkala O, Ras H A. Superhydrophobic and superoleophobic nanocellulose aerogel membranes as bioinspired cargo carriers on water and oil. Langmuir, 2011, 27(5): 1930–1934
Korhonen J T, Kettunen M, Ras R H A, Ikkala O. Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2011, 3(6): 1813–1816
Liu H Z, Geng B Y, Chen Y F, Wang H Y. Review on the aerogel-type oil sorbents derived from nanocellulose. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(1): 49–66
Todd H, Cranston E D. Review of hydrogels and aerogels containing nanocellulose. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(11): 4609–4631
Zanini M, Lavoratti A, Lazzari L K, Galiotto D, Pagnocelli M, Baldasso C, Zattera A J. Producing aerogels from silanized cellulose nanofiber suspension. Cellulose, 2017, 24(2): 769–779
Zhang W N, Lu G, Cui C L, Liu Y Y, Li S Z, Yan W J, Xing C, Chi Y R, Yang Y H, Huo F G. A family of metal-organic frameworks exhibiting size-selective catalysis with encapsulated noble-metal nanoparticles. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(24): 4056–4060
Kaneti Y V, Dutta S, Hossain M S A, Shiddiky M J A, Tung K L, Shieh F K, Tsung C K, Wu K C W, Yamauchi Y. Strategies for improving the functionality of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks: tailoring nanoarchitectures for functional applications. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(38): 1700213
Jiang J, Yaghi O M. Brønsted acidity in metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(14): 6966–6997
Howarth A J, Liu Y Y, Li P, Li Z Y, Wang T C, Hupp J T, Farha O K. Chemical, thermal and mechanical stabilities of metal-organic frameworks. Nature Reviews. Materials, 2016, 1(3): 15018
Sun L, Campbell M G, Dincă M. Electrically conductive porous metal-organic frameworks. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(11): 3566–3579
Wang C H, Kaneti Y V, Bando Y, Lin J J, Liu C, Li J S, Yamauchi Y. Metal-organic framework-derived one-dimensional porous or hollow carbon-based nanofibers for energy storage and conversion. Materials Horizons, 2018, 5(3): 394–407
Kaneti Y V, Zhang J, He Y B, Wang Z J, Tanaka S, Hossain M S A, Pan Z Z, Xiang B, Yang Q H, Yamauchi Y. Fabrication of an MOF-derived heteroatom-doped Co/CoO/carbon hybrid with superior sodium storage performance for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2017, 5(29): 15356–15366
Li H L, Eddaoudi M M, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi O M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature, 1999, 402(6759): 276–279
Wang C H, Kim J, Tang J, Kim M, Lim H, Malgras V, You J, Xu Q, Li J S, Yamauchi Y. New strategies for novel MOF-derived carbon materials based on nanoarchitectures. Chem, 2020, 6(1): 19–40
Hmadeh M, Lu Z, Liu Z, Gándara F, Furukawa H, Wan S, Augustyn V, Chang R, Liao L, Zhou F, et al. New porous crystals of extended metal-catecholates. Chemistry of Materials, 2012, 24(18): 3511–3513
Ma X T, Lou Y, Chen X B, Shi Z, Xu Y. Multifunctional flexible composite aerogels constructed through in-situ growth of metal-organic framework nanoparticles on bacterial cellulose. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 356: 227–235
Matsumoto M, Kitaoka T. Ultraselective gas separation by nanoporous metal-organic frameworks embedded in gas-barrier nanocellulose films. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(9): 1765–1769
Li L, Chen Q, Niu Z G, Zhou X H, Yang T, Huang W. Lanthanide metal-organic frameworks assembled from a fluorene-based ligand: selective sensing of Pb2+ and Fe3+ ions. Journal of Materials Chemistry. C, Materials for Optical and Electronic Devices, 2016, 4 (9): 1900–1905
Li B Y, Dong X G, Wang H, Ma D X, Tan K, Jensen S, Deibert B J, Butler J, Cure J, Shi Z, et al. Capture of organic iodides from nuclear waste by metal-organic framework-based molecular traps. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 485
Cavka J H, Jakobsen S, Olsbye U, Guillou N, Lamberti C, Bordiga S, Lillerud K P. A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(42): 13850–13851
Gilang G, Yusuf V K, Joel H, Sauvik C, Jongbeom N, Brian Y, Nugraha N. General synthesis of hierarchical sheet/plate-like M-BDC (M = Cu, Mn, Ni, and Zr) metal-organic frameworks for electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Chemical Science, 2020, 14: 3644–3655
Lee J Y, Farha O K, Roberts J, Scheidt K A, Nguyen S T, Hupp J T. Metal-organic framework materials as catalysts. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(5): 1450
Kandiah M, Nilsen M H, Usseglio S, Jakobsen S, Olsbye U, Tilset M, Larabi C, Quadrelli E A, Bonino F, Lillerud K P. Synthesis and stability of tagged UiO-66 Zr-MOFs. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(24): 6632–6640
Abe K, Iwamoto S, Yano H. Obtaining cellulose nanofibers with a uniform width of 15 nm from wood. Biomacromolecules, 2007, 8 (10): 3276–3278
Zhou S K, You T T, Zhang X M, Xu F. Superhydrophobic cellulose nanofiber-assembled aerogels for highly efficient water-in-oil emulsions separation. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2018, 1(5): 2095–2103
Aghajanzadeh M, Zamani M, Molavi H, Khieri Manjili H, Danafar H, Shojaei A. Preparation of metal-organic frameworks UiO-66 for sdsorptive removal of methotrexate from aqueous solution. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2018, 28 (1): 177–186
Xu Z Y, Zhou H, Jiang X D, Li J Y, Huang F. Facile synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/trimethyl chlorosilane-coated cellulose nanofibres aerogel for oil absorption. IET Nanobiotechnology, 2017, 11(8): 929–934
Xu Z Y, Jiang X D, Zhou H, Li J Y. Preparation of magnetic hydrophobic polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-cellulose nanofiber (CNF) aerogels as effective oil absorbents. Cellulose, 2018, 25(2): 1217–1227
Xu Z Y, Jiang X D, Tan S C, Wu W B, Shi J T, Zhou H, Chen P. Preparation and characterisation of CNF/MWCNT carbon aerogel as efficient adsorbents. IET Nanobiotechnology, 2018, 12(4): 500–504
Zhao W, Jia W P, Xu M Z, Wang J X, Li Y M, Zhang Z Y, Wang Y N, Zheng L, Li Q, Yun J N, Yan J, Wang X, Liu Z. Facile synthesis of oil adsorbent carbon microtubes by pyrolysis of plant tissues. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(13): 9352–9361
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. SWZ-ZD201906) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31770607). The authors thank the Advanced Analysis & Testing Center of Nanjing Forestry University for its help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhai, S., Wu, W. et al. Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels with high loading of metal-organic framework particles as floating and reusable oil absorbents. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 15, 1158–1168 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-2021-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-2021-z