Abstract
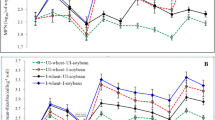
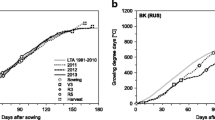
The performance of the soybean (Glycine max) inoculated with Bradyrhizobium is influenced by cropping history. However, re-inoculation with elite strains of Bradyrhizobium generally provides increases in soybean grain yield. The Amazonian savanna has an agricultural frontier area where soybeans have recently been introduced. In this study, we evaluated soybean nodulation, N accumulation, N2 fixation, and grain yield responses to inoculation with the commercial Bradyrhizobium strains SEMIA 587 and SEMIA 5019 of B. elkanii, SEMIA 5079 of B. japonicum, and SEMIA 5080 of B. diazoefficiens. Four field experiments were performed in areas with or without previous cropping with inoculated soybean that contained preexisting bradyrhizobia populations of ≥ 103 or < 102 cells g−1 soil, respectively. Inoculation of soybean in first-year cropping areas resulted in increases in several parameters compared to those in non-inoculated soybean; as expected, these effects were less pronounced when areas had been previously cropped with soybean. Despite no statistical differences, re-inoculation provided average increases in grain yield of 12 to 18% compared to that in the non-inoculated control. A dose of 200 kg ha−1 of N-fertilizer impaired the nodulation and did not increase grain yields when compared with the inoculation. Estimates obtained with the 15 N natural abundance technique confirmed the high contribution of N2 fixation in inoculated plants, ranging from 84 to 90%. Although soybean cropping increases the soil bradyrhizobia population size, annual inoculation is important to guarantee host infection by efficient strains of soybean Bradyrhizobium and their persistence in savanna soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albareda M, Rodríguez-Navarro DN, Temprano FJ (2009) Soybean inoculation: dose, N fertilizer supplementation and rhizobia persistence in soil. Field Crops Res 113:352–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2009.05.013
Alves BJR, Boddey RM, Urquiaga S (2003) The success of BNF in soybean in Brazil. Plant Soil 252:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024191913296
Alves BJR, Zotarelli L, Fernandes FM, Heckler JC, Macedo RAT, Boddey RM, Jantalia CP, Urquiaga S (2006) Biological nitrogen fixation and nitrogen fertilizer on the nitrogen balance of soybean, maize and cotton. Pesq Agropec Bras 41:449–456. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2006000300011 ([in Portuguese with English abstract])
Ambrosini VG, Fontoura SM, de Moraes RP, Tamagno S, Ciampitti IA, Bayer C (2019) Soybean yield response to Bradyrhizobium strains in fields with inoculation history in Southern Brazil. J Plant Nutr 42:1941–1951. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2019.1648680
Barbosa RI, Campos C, Pinto F, Fearnside PM (2007) The “Lavrados” of Roraima: biodiversity and conservation of Brazil’s Amazonian savannas. Funct Ecosyst Communities 1:29–41
Barcellos FG, Menna P, Batista JSS, Hungria M (2007) Evidence of horizontal transfer of symbiotic genes from a Bradyrhizobium japonicum inoculant strain to indigenous diazotrophs Sinorhizobium (Ensifer) fredii and Bradyrhizobium elkanii in a Brazilian Savannah soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2635–2643. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01823-06
Batista JSS, Hungria M, Barcellos FG, Ferreira MC, Mendes IC (2007) Variability in Bradyrhizobium japonicum and B. elkanii seven years after introduction of both the exotic microsymbiont and the soybean host in a Cerrados soil. Microb Ecol 53:270–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-006-9149-2
Bergersen FJ, Peoples MB, Turner GL (1988) Isotopic discriminations during the accumulation of nitrogen by soybeans. Aust J Plant Physiol 15:407–420. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP9880407
Brasil. Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento (2012) Plano setorial de mitigação e de adaptação às mudanças climáticas para a consolidação de uma economia de baixa emissão de carbono na agricultura: plano ABC (Agricultura de Baixa Emissão de Carbono)/Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento, Ministério do Desenvolvimento Agrário, coordenação da Casa Civil da Presidência da República.–Brasília: MAPA/ACS, 173p. Available on: http://www.agricultura.gov.br/assuntos/sustentabilidade/planoabc/arquivo-publicacoes-plano-abc/download.pdf
Boddey RM, Peoples MB, Palmer B, Dart PJ (2000) Use of the 15N natural abundance technique to quantify biological nitrogen fixation by woody perennials. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 57:235–270. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009890514844
Brockwell J, Roughley RJ, Herridge DF (1987) Population dynamics of Rhizobium japonicum strains used to inoculate three successive crops of soybean. Aust J Agric Res 38:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR9870061
Chalk PM, Inácio CT, Balieiro FC, Rouws JR (2016) Do techniques based on 15N enrichment and 15N natural abundance give consistent estimates of the symbiotic dependence of N2-fixing plants? Plant Soil 399:415–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2689-9
Chibeba AM, Kyei-Boahen S, Guimarães MF, Nogueira MA, Hungria M (2018) Feasibility of transference of inoculation-related technologies: a case study of evaluation of soybean rhizobial strains under the agro-climatic conditions of Brazil and Mozambique. Agric Ecosyst Environ 261:230–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2017.06.037
Ciampitti IA, Salvagiotti F (2018) New insights into soybean biological nitrogen fixation. Agron J 110:1185–1196. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2017.06.0348
Collino DJ, Salvagiotti F, Perticari A, Piccinetti C, Ovando G, Urquiaga S, Racca RW (2015) Biological nitrogen fixation in soybean in Argentina: relationships with crop, soil, and meteorological factors. Plant Soil 392:239–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2459-8
CONAB. Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento (2020) Acompanhamento da safra brasileira de grãos, v. 7 - Safra 2019/20 - Quarto levantamento, Brasília, 104p. Janeiro 2020. Available on: https://www.conab.gov.br/info-agro/safras/graos/boletim-da-safra-de-graos, Accessed 06 April 2020
De Bruin JL, Pedersen P, Conley SP, Gaska JM, Naeve SL, Kurle JE, Elmore W, Giesler LJ, Abendroth LJ (2010) Probability of yield response to inoculants in fields with a history of soybean. Crop Sci 50:265–272. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2009.04.0185
Delamuta JRM, Ribeiro RA, Ormeño-Orrilho E, Melo IS, Martínez-Romero E, Hungria M (2013) Polyphasic evidence supporting the reclassification of Bradyrhizobium japonicum group Ia strains as Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3342–3351. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.049130-0
Ferreira DF (2011) Sisvar: a computer statistical analysis system. Ciênc Agrotec 35:1039–1042. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542011000600001
Ferreira MC, Andrade DDS, Chueire LMDO, Takemura SM, Hungria M (2000) Tillage method and crop rotation effects on the population sizes and diversity of bradyrhizobia nodulating soybean. Soil Biol Biochem 32:627–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00189-3
Galli-Terasawa LV, Glienke-Blanco C, Hungria M (2003) Diversity of a soybean rhizobial population adapted to a Cerrados soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:933–939. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WIBI.0000007324.50022.c0
Gianluppi D, Smiderle OJ (2005) O cultivo da soja nos cerrados de Roraima. In: Barbosa RI, Xaud HAM, Costa e Souza JM (eds) Savanas de Roraima: etnoecologia, biodiversidade e potencialidades agrossilvipastoris. FEMACT-RR, Boa Vista, pp 177–182
Hungria M, Araujo RS, Júnior S, Barbosa E, Zilli JÉ (2017) Inoculum rate effects on the soybean symbiosis in new or old fields under tropical conditions. Agron J 109:1106–1112. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2016.11.0641
Hungria M, Campo RJ, Mendes IC, Graham PH (2006a) Contribution of biological nitrogen fixation to the N nutrition of grain crops in the tropics: the success of soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) in South America. In: Singh RP, Shankar N, Jaiwal PK (eds) Nitrogen nutrition and sustainable plant productivity. Studium Press, LLC Houston, pp 43–93
Hungria M, Franchini JC, Campo RJ, Crispino CC, Moraes JZ, Sibaldelli RNR, Mendes IC, Arihara J (2006b) Nitrogen nutrition of soybean in Brazil: contributions of biological N2 fixation and N fertilizer to grain yield. Can J Plant Sci 86:927–939. https://doi.org/10.4141/P05-098
Hungria M, Mendes IC (2015) Nitrogen fixation with soybean: the perfect symbiosis? In: de Bruijn FJ (ed) Biological nitrogen fixation. John Wiley, New Jersey, pp 1005–1019. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119053095.ch99
Hungria M, Vargas MAT (2000) Environmental factors affecting N2 fixation in grain legumes in the tropics, with an emphasis on Brazil. Field Crops Res 65:151–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(99)00084-2
IBGE. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (2019) Base cartográfica continua do Brasil. Rio de Janeiro, 2019. Available on: https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/cartas-e-mapas/bases-cartograficas-continuas, Accessed 02 May 2020
Kaschuk G, Nogueira MA, Luca MJ, Hungria M (2016) Response of determinate and indeterminate soybean cultivars to basal and topdressing N fertilization compared to sole inoculation with Bradyrhizobium. Field Crop Res 195:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.05.010
Leggett M, Diaz-Zorita M, Koivunen M, Bowman R, Pesek R, Stevenson C, Leister T (2017) Soybean response to inoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum in the United States and Argentina. Agron J 109:1031–1038. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2016.04.0214
Liao CFH (1981) Devarda’s alloy method for total nitrogen determination. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45:852–855. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1981.03615995004500050005x
Loureiro MF, Kaschuk G, Alberton O, Hungria M (2007) Soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] rhizobial diversity in Brazilian Oxisols under various soil, cropping, and inoculation managements. Biol Fertil Soils 43:665–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-006-0146-x
MAPA. Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento (2011) ANEXO à IN SDA 13, de 25/03/2011: protocolo oficial para avaliação da viabilidade e eficiência agronômica de cepas, inoculantes e tecnologias relacionado ao processo de fixação biológica do nitrogênio em leguminosas. Retrieved from: http://www.agricultura.gov.br/assuntos/insumos-agropecuarios/insumos-agricolas/fertilizantes/legislacao/in-sda–13-de–24–03–2011-inoculantes.pdf
Mason S, Galusha T, Kmail Z (2016) Soybean yield and nodulation response to crop history and inoculation. Agron J 108:309–312. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2015.0245
Mendes IC, Hungria M, Vargas MAT (2003) Soybean response to starter nitrogen and Bradyrhizobium inoculation on a Cerrado Oxisol under no-tillage and conventional tillage systems. R Bras Ci Solo 27:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832003000100009
Mendes IC, Hungria M, Vargas MAT (2004) Establishment of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and B. elkanii strains in a Brazilian Cerrado Oxisol. Biol Fertil Soils 40:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0739-1
Moretti LG, Crusciol CA, Kuramae EE, Bossolani JW, Moreira A, Costa NR, Alves CJ, Pascoaloto IM, Rondina ABL, Hungria M (2020) Effects of growth-promoting bacteria on soybean root activity, plant development, and yield. Agron J 112:418–428. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.20010
Moretti LG, Lazarini E, Bossolani JW, Parente TL, Caioni S, Araujo RS, Hungria M (2018) Can additional inoculations increase soybean nodulation and grain yield? Agron J 110:715–721. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2017.09.0540
Narożna D, Pudełko K, Króliczak J, Golińska B, Sugawara M, Mądrzak CJ, Sadowsky MJ (2015) Survival and competitiveness of Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains 20 years after introduction into field locations in Poland. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:5552–5559. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01399-15
Nepstad D, Schwartzman S, Bamberger B, Santilli M, Ray D, Schlesinger P, Lefebvre P, Alencar A, Prinz E, Fiske G, Rolla A (2006) Inhibition of Amazon deforestation and fire by parks and indigenous lands. Conserv Biol 20:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2006.00351.x
Nishi CYM, Hungria M (1996) Effects of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] inoculation in a soil with established population of Bradyrhizobium with strains SEMIA 566, 586, 587, 5019, 5079 e 5080. Pesq Agropec Bras 31:359–368 ([in Portuguese with English abstract])
Norris DO, Date RA (1976) Legume bacteriology. In: Shaw NH, Bryan WW (eds) Tropical pasture research: principles and methods. Commonwealth Bureau Pastures & Field Crops Bulletin No. 51, Pennsylvania, pp 134–74
RELARE. Rede de Laboratórios para Recomendação, Padronização e Difusão de Tecnologia de Inoculantes Microbianos de Interesse Agrícola (2004) Retrieved from: http://www.relare.org.br
Santachiara G, Salvagiotti F, Rotundo JL (2019) Nutritional and environmental effects on biological nitrogen fixation in soybean: a meta-analysis. Field Crops Res 240:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.05.006
Santos MA, Vargas MA, Hungria M (1999) Characterization of soybean Bradyrhizobium strains adapted to the Brazilian savannas. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.1999.tb00654.x
Santos MS, Nogueira MA, Hungria M (2019) Microbial inoculants: reviewing the past, discussing the present and previewing an outstanding future for the use of beneficial bacteria in agriculture. AMB Expr 9:205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0932-0
Saturno DF, Cerezini P, Moreira da Silva P, Oliveira ABD, Oliveira MCND, Hungria M, Nogueira MA (2017) Mineral nitrogen impairs the biological nitrogen fixation in soybean of determinate and indeterminate growth types. J Plant Nutr 40:1690–1701. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2017.1310890
Shearer G, Kohl DH (1986) N2-fixation in field settings: estimations based on natural 15N abundance. Aust J Plant Physiol 13:699–756. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP9860699c
Smiderle OJ (2019) Cultivo de soja no Cerrado de Roraima. Embrapa Roraima, Sistemas de Produção, 6. Boa Vista, Roraima, 146p. Retrieved from: https://www.embrapa.br/RORAIMA
Somasegaran P, Hoben HJ (1994) Methods in legume-Rhizobium technology. In: Garber RC (ed) Handbook for rhizobia. Springer, New York
Thies JE, Singleton PW, Bohlool BB (1991) Modeling symbiotic performance of introduced rhizobia in the field by use of indices of indigenous population size and nitrogen status of the soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:29–37
Thies JE, Woomer PL, Singleton PW (1995) Enrichment of Bradyrhizobium spp populations in soil due to cropping of the homologous host legume. Soil Biol Biochem 27:633–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(95)98643-3
Thilakarathna MS, Raizada MN (2017) A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of diverse rhizobia inoculants on soybean traits under field conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 105:177–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.11.022
Torabian S, Farhangi-Abriz S, Denton MD (2019) Do tillage systems influence nitrogen fixation in legumes? A review. Soil Tillage Res 185:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.09.006
Unkovich M, Herridge D, Peoples M, Cadisch G, Boddey R, Giller K, Alves BJR, Chalk P (2008) Measuring plant‐associated nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Canberra, Australia: ACIAR. Retrieved from: http://www.aciar.gov.au/publication/MN136
Zilli JÉ, Alves BJR, Rouws LFM, Simões-Araujo JL, Soares LHB, Cassán F, Castellanos MO, O’Hara G (2019) The importance of denitrification performed by nitrogen-fixing bacteria used as inoculants in South America. Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04187-7
Zilli JÉ, Campo RJ, Hungria M (2010) Effectiveness of Bradyrhizobium inoculation at pre-sowing of soybean. Pesq Agropec Bras 45:335–337. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2010000300015 ([In Portuguese with English abstract])
Zilli JÉ, Marson LC, Marson BF, Gianluppi V, Campo RJ, Hungria M (2008) Soybean inoculation by spraying Bradyrhizobium over plants. Pesq Agropec Bras 43:541–544. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2008000400014 ([In Portuguese with English abstract])
Zilli JÉ, Pereira GMD, França Júnior I, Silva KD, Hungria M, Rouws JRC (2013) Dynamic of rhizobia in the soil during the dry season in Cerrado of Roraima. Acta Amaz 43:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0044-59672013000200004
Zilli JÉ, Ribeiro KG, Campo RJ, Hungria M (2009) Influence of fungicide seed treatment on soybean nodulation and grain yield. R Bras Ci Solo 33:917–923. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832009000400016
Acknowledgements
Authors J.É. Zilli, O.J. Smiderle, S. Urquiaga and M. Hungria gratefully acknowledge "Research Productivity" fellowships from National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), and R.S. Pacheco a research grant from the Foundation for Research Support of the Rio de Janeiro State (FAPERJ). We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
Financial research support from INCT–Plant-Growth Promoting Microorganisms for Agricultural Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility (CNPq 465133/2014–2, Fundação Araucária-STI-043/2019, CAPES) and Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (Embrapa).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zilli, J.É., Pacheco, R.S., Gianluppi, V. et al. Biological N2 fixation and yield performance of soybean inoculated with Bradyrhizobium. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 119, 323–336 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10128-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10128-7