Abstract
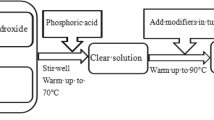
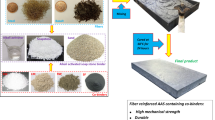
This paper has developed a new compound curing agent powder for a modified phosphate binder (3 wt% of raw sand). This combination can be self-cured and achieve relatively high bonding strength. The optimal composition ratio of curing agent powder is fused magnesia powder:silica fume:sodium polyacrylate at a ratio of 6:6:5, respectively. In this case, the tensile strength of phosphate binder sand sample at 4 h and 24 h is 0.65 MPa and 1.27 MPa, respectively. Infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy were utilized to analyze the variation of functional groups and the morphology of bonding bridge fracture of phosphate bonded sand samples after the addition of curing agent (fused magnesia powder, silica fume and sodium polyacrylate). The result shows that fused magnesia powder, silica fume and sodium polyacrylate all participate in the polymerization and curing reaction of phosphate binder; furthermore, sodium polyacrylate can effectively mitigate the propagation of cracks on bonding film.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Allen, F.S. Cannon, C. Nieto-Delgado et al., Full-Scale Air Emissions Monitoring and Casting Quality Demonstration of a Hybrid Hydrolyzed Collagen-Alkali Silicate Core Binder. Int. J Metalcast. 10, 172–189 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0021-y
J. Zych, Behavior of Chemically Bonded Molding Sands in Dry Air. Int. J. Metalcast. 3, 17–27 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355445
H. Iao, X. Du, Y. Sun et al., Effect of Powder Breakdown Additives on Properties of Ester-Hardened Sodium Silicate Bonded Ceramic Sand. Int. J. Metalcast. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00517-z
L. Xia, Y.S. Zhang, J. Huang, A New Compound Phosphate Heat-Cured Foundry Binder[J]. Adv. Mater. Res. 97–101, 979–982 (2010)
S.M. Dobosz, P. Jelinek, K. Major-Gabry, Development tendencies of moulding and core sands. China Foundry 8(04), 438–446 (2011)
T.S. Wang, W.H. Liu, Y.M. Li, Research on preparation of phosphate-modified animal glue binder for foundry use[J]. R. Soc. Open Sci. 5(3), 171795 (2018)
D. He, L. Xia, J. Huang et al., Study of Environmentally Friendly Phosphate-Bonded No-Bake Sand[J]. Adv. Mater. Res. 602–604, 1161–1164 (2013)
Z. Youshou, X. Yiyu, H. Jin et al., Mechanism of Strength Loss of No-bake Phosphate Bonded Sand Mold/Core[J]. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Mater. Sci. Ed.) 24(01), 9–12 (2009)
W. Zhengyue, X. Mingxia, L. Hui et al., Studies on the Curing Mechanism of Aluminum-Chromium-Phosphate Binder[J]. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 37(1), 565–568 (2008)
J. Weise, J. Hilbers, F. Handels et al., New Core Technology for Light Metal Casting[J]. Adv. Eng. Mater. 21, 1800608 (2019)
A. Khamkongkaeo, A. Bootchanont, W. Klysubun et al., Effect of Phosphate Compound on Physical and Mechanical Properties of SiO2 Ceramic [J]. Ceram. Int. 45(1), 1356–1362 (2019)
L. Zihao, W. Mingchao, G. Anrang et al., Effect of Nano CuO on Water Resistance of Phosphate Adhesive[J]. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 403(02), 197–201 (2020). (In Chinese)
Xu. Yuan, Study on A Kind of No-Bake Phosphate Binder Used for Foundry [D] (Shenyang University of Technology, China, 2014). (In Chinese)
W. Shouwu, D. Yingmiao, Z. Xueting et al., Study on Synthesis and Performance of Sodium Polyacrylate[J]. Advances in Fine Petrochemicals 11(5), 42–43 (2010). (In Chinese)
D. Jianguo, Study on Synthesis Method of Low Molecular Weight Sodium Polyacrylate and Application [D] (Guangdong University of Technology, Guangdong, 2014). (In Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Song, L. The Development of a New Compound Curing Agent for a Modified Self-Cured Phosphate Foundry Binder. Inter Metalcast 16, 204–211 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00588-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00588-6