Abstract
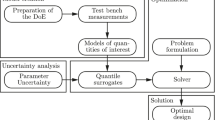
To enhance the calibration efficiency, reduce the fuel consumption and improve the emission performance of the engine, a calibration method using Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) is proposed in this work. First, the design of experiment (DoE) is constructed by using the Space-filling method, and the engine bench sampling test is implemented according to results of DoE. Then, the square exponential covariance function is selected through the comparison of four covariance functions, and the corresponding hyper-parameters are optimized by using Newton gradient algorithm. Finally, the GPR model of the engine is established and its calibration performance is validated by the experimental data. The comparison shows that the performance of the developed GPR model is superior to the Polynomial model and Neural Network model, whose coefficient of determination (R2) of Fuel Consumption (FC), NOx emission (NOx) and Soot emission (Soot) are up to 0.9980, 0.9326 and 0.9247. The case study demonstrates that the virtual calibration optimization based on GPR model improves the fuel consumption performance greatly, while taking NOx and Soot emission indicators into account.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DoE:
-
design of experiment
- NN:
-
neural network
- SVM:
-
support vector machine
- GPR:
-
gaussian process regression
- GP:
-
gaussian process
- SGD:
-
stochastic gradient descent
- RMSE:
-
root mean square error
- MAE:
-
mean absolute error
- ECU:
-
engine control unit
- PR:
-
polynomial regression
- FC:
-
fuel consumption
- NOx:
-
NOx emission
- Soot:
-
soot emission
References
Aran, V. and Unel, M. (2018). Gaussian process regression feedforward controller for diesel engine airpath. Int. J. Automotive Technology 19, 4, 635–642.
Bachoc, F., Gamboa, F., Loubes, J. M. and Venet, N. (2018). A Gaussian process regression model for distribution inputs. IEEE Trans. Information Theory 64, 10, 6620–6637.
Belgiorno, G., Dimitrakopoulos, N., Di Blasio, G., Beatrice, C., Tunestål, P. and Tunér, M. (2018). Effect of the engine calibration parameters on gasoline partially premixed combustion performance and emissions compared to conventional diesel combustion in a light-duty Euro 6 engine. Applied Energy, 228, 2221–2234.
Bilionis, I. and Zabaras, N. (2012). Multi-output local Gaussian process regression: Applications to uncertainty quantification. J. Computational Physics 231, 17, 5718–5746.
Bu, Y. and Pan, J. (2015). Stellar atmospheric parameter estimation using Gaussian process regression. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 447, 1, 256–265.
Cai, S., Liu, B., Zhang, F. and Cui, T. (2014). Research on model-based calibration method of electronic control unit pump diesel engine. IEEE Conf. Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific). Beijing, China.
Chai, Z. G., Zhang, F. J., Liu, B. L., Huang, Y. and Fu, G. (2015). Application study of kriging model in common rail diesel engine calibration. Trans. Beijing Institute of Technology 35, 3, 242–245.
Chung, J. W., Kim, N. H., Kim, D. J. and Jang, S. S. (2018). Mean value WGT diesel engine calibration model for effective simulation research. Int. J. Automotive Technology 19, 2, 209–220.
de Santana, L. M. Q., Santos, R. M., Matos, L. N. and Macedo, H. T. (2018). Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in the presence of noise. IEEE Latin America Trans. 16, 3, 918–925.
Fortuna, T., Koegeler, H. M., Kordon, M. and Vitale, G. (2015). DoE and beyond—evolution of the model-based development approach. ATZ Worldwide 117, 2, 30–35.
Grasreiner, S., Neumann, J., Wensing, M. and Hasse, C. (2017). Model-based virtual engine calibration with the help of phenomenological methods for spark-ignited engines. Applied Thermal Engineering, 121, 190–199.
Guo, W., Pan, T., Li, Z. and Chen, S. (2019). Model calibration method for soft sensors using adaptive gaussian process regression. IEEE Access, 7, 168436–168443.
Huang, Y. and Ma, F. (2016). Intelligent regression algorithm study based on performance and NOx emission experimental data of a hydrogen enriched natural gas engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41, 26, 11308–11320.
Isermann, R. and Sequenz, H. (2016). Model-based development of combustion-engine control and optimal calibration for driving cycles: general procedure and application. IFAC-PapersOnLine 49, 11, 633–640.
Jeong, K. and Choi, S. (2019). Model-based sensor fault diagnosis of vehicle suspensions with a support vector machine. Int. J. Automotive Technology 20, 5, 961–970.
Kannan, G. R., Balasubramanian, K. R. and Anand, R. (2013). Artificial neural network approach to study the effect of injection pressure and timing on diesel engine performance fueled with biodiesel. Int. J. Automotive Technology 14, 4, 507–519.
Lee, J. H. and Lee, Y. Z. (2015). Development of a diesel cold performance evaluation method by use of design of experiment. Int. J. Automotive Technology 16, 5, 807–812.
Lee, S. I., Mortazavi, B., Hoffman, H. A., Lu, D. S., Li, C., Paak, B. H., Garst, J. H., Razaghy, M., Espinal, M., Park, E., Lu, D. C. and Sarrafzadeh, M. (2014). A prediction model for functional outcomes in spinal cord disorder patient using gaussian process regression. IEEE J. Biomedical and Health Informatics 20, 1, 91–99.
Liu, D., Pang, J., Zhou, J., Peng, Y. and Pecht, M. (2013). Prognostics for state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on combination Gaussian process functional regression. Microelectronics Reliability 53, 6, 832–839.
Liu, L. and Arcone, S. A. (2013). Forward and inverse problems in GPR research. J. Applied Geophysics, 99, 66–67.
Lu, Z., Sun, J. and Butts, K. (2010). Application of linear programming SVM-ARMA2K for dynamic engine modeling. American Control Conf. Baltimore, MD, USA.
Ma, H., Li, Z., Tayarani, M., Lu, G., Xu, H. and Yao, X. (2019). Model-based computational intelligence multi-objective optimization for gasoline direct injection engine calibration. Proc. Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: J. Automobile Engineering 233, 6, 1391–1402.
Martínez-Morales, J. D., Palacios-Hernández, E. R. and Velázquez-Carrillo, G. A. (2015). Modeling engine fuel consumption and NOx with RBF neural network and MOPSO algorithm. Int. J. Automotive Technology 16, 6, 1041–1049.
Millo, F., Arya, P. and Mallamo, F. (2018). Optimization of automotive diesel engine calibration using genetic algorithm techniques. Energy, 158, 807–819.
Murgovski, N., Grahn, M., Johannesson, L. M. and McKelvey, T. (2014). Automated engine calibration of hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Systems Technology 23, 3, 1063–1074.
Nikzadfar, K. and Shamekhi, A. H. (2019). Investigating a new model-based calibration procedure for optimizing the emissions and performance of a turbocharged diesel engine. Fuel, 242, 455–469.
Nishio, Y., Murata, Y., Yamaya, Y. and Kikuchi, M. (2018). Optimal calibration scheme for map-based control of diesel engines. Science China Information Sciences 61, 7, 1–14.
Park, S., Kim, Y., Woo, S. and Lee, K. (2017). Optimization and calibration strategy using design of experiment for a diesel engine. Applied Thermal Engineering, 123, 917–928.
Ranganathan, A., Yang, M. H. and Ho, J. (2010). Online sparse Gaussian process regression and its applications. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 20, 2, 391–404.
Richardson, R. R., Osborne, M. A. and Howey, D. A. (2017). Gaussian process regression for forecasting battery state of health. J. Power Sources, 357, 209–219.
Sheng, H., Xiao, J., Cheng, Y., Ni, Q. and Wang, S. (2018). Short-term solar power forecasting based on weighted Gaussian process regression. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electronics 65, 1, 300–308.
Toyoda, M. and Shen, T. (2016). D-optimization based mapping calibration of air mass flow in combustion engines. European Control Conf. (ECC). Aalborg, Denmark.
Turkson, R. F., Yan, F., Ali, M. K. A. and Hu, J. (2016). Artificial neural network applications in the calibration of spark-ignition engines: An overview. Engineering Science and Technology, an Int. J. 19, 3, 1346–1359.
van Dooren, S., Balerna, C., Salazar, M., Amstutz, A. and Onder, C. H. (2020). Optimal diesel engine calibration using convex modelling of pareto frontiers. Control Engineering Practice, 96, 104313.
Wong, P. K., Gao, X. H., Wong, K. I. and Vong, C. M. (2018). Online extreme learning machine based modeling and optimization for point-by-point engine calibration. Neurocomputing, 277, 187–197.
Wong, P. K., Vong, C. M. and Ip, W. F. (2010). Modelling of petrol engine power using incremental least-square support vector machines for ECU calibration. Int. Conf. Optoelectronics and Image Processing. Haiko, Hainan, China.
Xiloyannis, M., Gavriel, C., Thomik, A. A. and Faisa, A. A. (2015). Gaussian process regression for accurate prediction of prosthetic limb movements from the natural kinematics of intact limbs. 7th Int. IEEE/EMBS Conf. Neural Engineering (NER). Montpellier, France.
Zhou, G., Liu, R., Ping, Z., Gang, L. and Li, J. A. (2012). The calibration of high-pressure common-rail diesel engine based on polynomial regression model. Automotive Engineering 34, 4, 301–305.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61873113, the Key R&D Program of Jiangsu Province, China under Grant BE2018370, and the Key R&D Program of Zhenjiang under Grant GY2018013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, T., Cai, Y. & Chen, S. Development of an Engine Calibration Model Using Gaussian Process Regression. Int.J Automot. Technol. 22, 327–334 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-021-0031-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-021-0031-5