Abstract
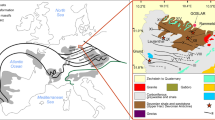
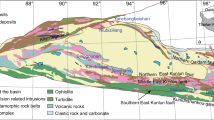
The Aqishan-Yamansu metallogenic belt (AYMB) in East Tianshan hosts abundant submarine volcanic-hosted iron deposits. Although there is agreement with the magmatic source of the ore-forming materials and the role of hydrothermal replacement in iron ore formation, the mineralization processes of these iron deposits remain uncertain. Three ore types are identified on the basis of the geological occurrences of minerals and the sequence of mineral in ores. The type I ores are characterized by magnetite, diopside, amphibole with a few pyrite, and chalcopyrite. The type II ores are mainly composed of magnetite, garnet, chlorite with a few pyrite, while the type III ores are mainly composed of magnetite, quartz, calcite with a few pyrite. In order to constrain the mineralization processes of these ore types, we performed iron isotopes and trace element compositions of magnetite from three typical iron deposits (Yamansu, Duotoushan and Luotuofeng). Trace element and Fe isotope investigations of the three ore types reveal two major groups. The group I consists of analyses of the type I and II ores, with both showing a narrow range of positive δ56Fe values (+0.08‰ to +0.22‰ for type I ores and +0.15‰ to +0.22‰ for type II ores) and plotting in the range of the ortho-magmatic field. In contrast, the group 2 is composed merely of the type III ores, showing a wider range of negative δ56Fe values (-0.49‰ to -0.01‰), which is similar to the features of Fe-skarn magnetite. As shown in the binary diagrams of magnetite trace elements and a fractionation of the Fe isotopes, different ore types were likely produced during gradually changing ore-forming stages from magmatic to hydrothermal. Collectively, the submarine volcanic-hosted iron deposits in the East Tianshan are likely the results of a continuous magmatic-hydrothermal mineralization process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Anbar, A. D., 2004. Iron Stable Isotopes: Beyond Biosignatures. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 217(3/4): 223–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(03)00572-7
BGMRXUAR (Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region), 2010. Geological report of the Yamansu Iron Deposit in Hami, Xinjiang (in Chinese)
Bilenker, L. D., Simon, A. C., Reich, M., et al., 2016. Fe-O Stable Isotope Pairs Elucidate a High-Temperature Origin of Chilean Iron Oxide-Apatite Deposits. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 177: 94–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2016.01.009
Cai, H. M., Yang, H., Gong, X. K., 2019. Geochronology and Petrogenesis of Mafic-Intermediate Intrusions on the Northern Margin of the Central Tianshan (NW China): Implications for Tectonic Evolution. Journal of Earth Science, 30(2): 323–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-1205-6
Charvet, J., Shu, L. S., Laurent-Charvet, S., 2007. Paleozoic Structural and Geodynamic Evolution of Eastern Tianshan (NW China): Welding of the Tarim and Junggar Plates. Episodes, 30(3): 162–186
Chen, B., Jahn, B. M., 2004. Genesis of Post-Collisional Granitoids and Basement Nature of the Junggar Terrane, NW China: Nd-Sr Isotope and Trace Element Evidence. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23(5): 691–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1367-9120(03)00118-4
Chen, F. W., He, G. Q., Li, H. Q., 2003. Tectonic Attribute of Qoltag Orogenic Belt in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains, Northwestern China. Geology in China, 30: 361–366 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Childress, T. M., Simon, A. C., Day, W. C., et al., 2016. Iron and Oxygen Isotope Signatures of the Pea Ridge and Pilot Knob Magnetite-Apatite Deposits, Southeast Missouri, USA. Economic Geology, 111(8): 2033–2044
Cook, N., Ciobanu, C., George, L., et al., 2016. Trace Element Analysis of Minerals in Magmatic-Hydrothermal Ores by Laser Ablation Inductively-Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: Approaches and Opportunities. Minerals, 6(4): 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040111
Dare, S. A. S., Barnes, S. J., Beaudoin, G., 2012. Variation in Trace Element Content of Magnetite Crystallized from a Fractionating Sulfide Liquid, Sudbury, Canada: Implications for Provenance Discrimination. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 88: 27–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2012.04.032
Dare, S. A. S., Barnes, S. J., Beaudoin, G., 2014b. Did the Massive Magnetite “Lava Flows” of El Laco (Chile) Form by Magmatic or Hydrothermal Processes? New Constraints from Magnetite Composition by LA-ICP-MS. Mineralium Deposita, 50(5): 607–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-014-0560-1
Dare, S. A. S., Barnes, S. J., Beaudoin, G., et al., 2014a. Trace Elements in Magnetite as Petrogenetic Indicators. Mineralium Deposita, 49(7): 785–796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-014-0529-0
Du, L., Yuan, C., Li, X. P., et al., 2019. Petrogenesis and Geodynamic Implications of the Carboniferous Granitoids in the Dananhu Belt, Eastern Tianshan Orogenic Belt. Journal of Earth Science, 30(6): 1243–1252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-019-1256-3
Dupuis, C., Beaudoin, G., 2011. Discriminant Diagrams for Iron Oxide Trace Element Fingerprinting of Mineral Deposit Types. Mineralium Deposita, 46(4): 319–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-011-0334-y
Dziony, W., Horn, I., Lattard, D., et al., 2014. In-sittu Fe Isotope Ratio Determination in Fe-Ti Oxides and Sulfides from Drilled Gabbros and Basalt from the IODP Hole 1256D in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific. Chemical Geology, 363(10): 101–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.10.035
Gao, J. F., Zhou, M. F., Lightfoot, P. C., et al., 2013. Sulfide Saturation and Magma Emplacement in the Formation of the Permian Huangshandong Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposit, Xinjiang, Northwestern China. Economic Geology, 108(8): 1833–1848. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.108.8.1833
Gao, J., Long, L. L., Klemd, R., et al., 2009. Tectonic Evolution of the South Tianshan Orogen and Adjacent Regions, NW China: Geochemical and Age Constraints of Granitoid Rocks. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6): 1221–1238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-008-0370-8
Han, B. F., He, G. Q., Wang, X. C., et al., 2011. Late Carboniferous Collision between the Tarim and Kazakhstan-Yili Terranes in the Western Segment of the South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and Implications for the Northern Xinjiang, Western China. Earth-Science Reviews, 109(3/4): 74–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.09.001
Han, J. S., Chen, H. Y., Jiang, H. J., et al., 2019. Genesis of the Paleozoic Aqishan-Yamansu Arc-Basin System and Fe(-Cu) Mineralization in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 105: 55–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.12.012
He X. G., Pan Z. G., Zhou C. P., 2011. Metallogenic Geological Characteristics of Luotuofeng Iron Deposit in Shanshan, Xinjiang. Xinjiang Nonferrous Metals, 4: 1–5 (in Chinese)
Heimann, A., Beard, B. L., Johnson, C. M., 2008. The Role of Volatile Exsolution and Sub-Solidus Fluid/rock Interactions in Producing High 56Fe/54Fe Ratios in Siliceous Igneous Rocks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(17): 4379–4396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2008.06.009
Hou, K. J., Li, Y. H., Tian, Y. Y., 2009. In situ U-Pb Zircon Dating Using Laser Ablation Multiion Counting-ICP-MS. Mineral Deposits, 28: 481–492 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Hou, T., Zhang, Z. C., Pirajno, F., et al., 2014a. Geology, Tectonic Settings and Iron Ore Metallogenesis Associated with Submarine Volcanism in China: An Overview. Ore Geology Reviews, 57: 498–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.08.007
Hou, T., Zhang, Z. C., Santosh, M., et al., 2014b. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Submarine Volcanic Rocks in the Yamansu Iron Deposit, Eastern Tianshan Mountains, NW China: Constraints on the Metallogenesis. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 487–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.03.008
Huang, F., Zhang, Z. F., Lundstrom, C. C., et al., 2011. Iron and Magnesium Isotopic Compositions of Peridotite Xenoliths from Eastern China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(12): 3318–3334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2011.03.036
Huang, X. W., Qi, L., Gao, J. F., et al., 2013b. First Reliable Re-Os Ages of Pyrite and Stable Isotope Compositions of Fe(-Cu) Deposits in the Hami Region, Eastern Tianshan Orogenic Belt, NW China. Resource Geology, 63(2): 166–187. https://doi.org/10.1111/rge.12003
Huang, X. W., Qi, L., Meng, Y. M., 2013a. Trace Element and REE Geochemistry of Minerals from Heifengshan, Shuangfengshan and Shaquanzi (Cu-) Fe Deposits, Eastern Tianshan Mountains. Mineral Deposits, 32: 1188–1210 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Johnson, C. M., Beard, B. L., Roden, E. E., et al., 2004. Isotopic Constraints on Biogeochemical Cycling of Fe. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 55(1): 359–408. https://doi.org/10.2138/gsrmg.55.L359
Knipping, J. L., Bilenker, L. D., Simon, A. C., et al., 2015a. Giant Kiruna-Type Deposits Form by Efficient Flotation of Magmatic Magnetite Suspensions. Geology, 43(7): 591–594. https://doi.org/10.1130/g36650.1
Knipping, J. L., Bilenker, L. D., Simon, A. C., et al., 2015b. Trace Elements in Magnetite from Massive Iron Oxide-Apatite Deposits Indicate a Combined Formation by Igneous and Magmatic-Hydrothermal Processes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 171: 15–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.08.010
Knipping, J. L., Fiege, A., Simon, A. C., et al., 2019. In-situ Iron Isotope Analyses Reveal Igneous and Magmatic-Hydrothermal Growth of Magnetite at the Los Colorados Kiruna-Type Iron Oxide-Apatite Deposit, Chile. American Mineralogist, 104(4): 471–484. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2019-6623
Li, G. R., Wu, C. Z., 2013. Recent Advances in Skarn Forming Models and the Yamansu Skarn Related Deposits. Geological Journal of China Universities, 19(3), 425–436 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, H. M., Ding, J. H., Li, L. X., et al., 2014. The Genesis of the Skarn and the Genetic Type of the Yamansu Iron Deposits, Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang. Acta Geologica Sinica, 12: 2477–2489 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, H. M., Li, L. X., 2013. Metallogenic Map of Iron Deposits in China (1: 5 000 000). Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Li, H. M., Li, L. X., Ding, J. H., et al., 2018. Occurrence of the Iron-Rich Melt in the Heijianshan Iron Deposit, Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Insights into the Origin of Volcanic Rock-Hosted Iron Deposits. Acta Geologica Sinica: English Edition, 92(2): 666–681. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.13548
Li, Q. G., Liu, S. W., Wang, Z. Q., et al., 2008. Electron Microprobe Monazite Geochronological Constraints on the Late Palaeozoic Tectonothermal Evolution in the Chinese Tianshan. Journal of the Geological Society, 165(2): 511–522. https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-76492007-077
Li, W. Q., Ma, H. D., Wang, R., et al., 2008. SHRIMP Dating and Nd-Sr Isotopic Tracing of Kangguertage Ophiolite in East Tianshan, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(4): 773–780 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, F., Chai, F. M., Li, Q., et al., 2019. Constraints on the Timing of Fe-(Cu) Metallogenesis in the Eastern Aqishan-Yamansu-Shaquanzi Metallogenic Belt, Eastern Tianshan, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 113: 103089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103089
Luo, T., Liao, Q. A., Chen, J. P., et al., 2012. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Volcanic Rocks from Yamansu Formation in the Eastern Tianshan, and Its Geological Significance. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 37(6): 1338–1352 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Mandernack, K. W., 1999. Oxygen and Iron Isotope Studies of Magnetite Produced by Magnetotactic Bacteria. Science, 285(5435): 1892–1896. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5435.1892
Mao, J. W., Goldfarb, R. J., Wang, Y. T., et al., 2005. Late Paleozoic Base and Precious Metal Deposits, East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China: Characteristics and Geodynamic Setting. Episodes, 28(1): 23–36. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2005/v28i1/003
Muhetaer, Z., Nijat, A., Wu, Z. N., 2015. Geochemical Characteristics of the Volcanics from the Southern Jueluotage Area and Their Constraints on the Tectonic Evolution of Paleo-Asian Ocean. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1): 238–250 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Nadoll, P., Angerer, T., Mauk, J. L., et al., 2014. The Chemistry of Hydrothermal Magnetite: A Review. Ore Geology Reviews, 61: 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.12.013
Pirajno, F., 2010a. Intracontinental Strike-Slip Faults, Associated Magmatism, Mineral Systems and Mantle Dynamics: Examples from NW China and Altay-Sayan (Siberia). Journal of Geodynamics, 50(3/4): 325–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2010.01.018
Pirajno, F., 2010a. Tianshan, Junggar and Altay Orogens (NW China), the Alpine-Himalayan Fold Belts (Tethyan Orogens), Kunlun and Songpan-Ganzi Terranes. The Geology and Tectonic Settings of China’s Mineral Deposits, 381–545
Qin, K. Z., Peng, X. M., San, J. Z., et al., 2003. Types of Major Ore Deposits, Division of Metallogenic Belts in Eastern Tianshan, and Discrimination of Potential Prospects of Cu, Au, Ni Mineralization. Xinjiang Geology, 21(2): 143–150 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Sang, S. J., Peng, M. X., Guo, Y. H., 2003. Optimized Target Areas and Evaluation Report of Resource in the Caixiashan to Jintan Area. Xingjiang Inst of Geol Investigation, 1: 42–44 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Schüßler, J. A., 2008. Controls on Stable Iron Isotope Variations in Magmatic Systems: Significance of Mineral-Melt Isotopic Fractionation in Experiments and Nature: [Dissertation].
Severmann, S., Anbar, A. D., 2009. Reconstructing Paleoredox Conditions through a Multitracer Approach: The Key to the Past is the Present. Elements, 5(6): 359–364. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.5.6.359
Sun, J., Zhu, X. K., Chen, Y. L., et al., 2012. Fe Isotope Compositions of Related Geological Formation in Bayan Obo Area and Their Constrains on the Genesis of Bayan Obo Ore Deposit. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(5): 819–828 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Teixeira, N. L., Caxito, F. A., Rosière, C. A., et al., 2017. Trace Elements and Isotope Geochemistry (C, O, Fe, Cr) of the Cauê Iron Formation, Quadrilâtero Ferrfero, Brazil: Evidence for Widespread Microbial Dissimilatory Iron Reduction at the Archean/Paleoproterozoic Transition. Precambrian Research, 298: 39–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2017.05.009
Tornos, F., Velasco, F., Hanchar, J. M., 2016. Iron-Rich Melts, Magmatic Magnetite, and Superheated Hydrothermal Systems: The El Laco Deposit, Chile. Geology, 44(6): 427–430. https://doi.org/10.1130/g37705.1
Van Baalen, M. R., 1993. Titanium Mobility in Metamorphic Systems: A Review. Chemical Geology, 110(1/2/3): 233–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(93)90256-i
Wang, Y., Zhu, X. K., Mao, J. W., et al., 2011. Iron Isotope Fractionation during Skarn-Type Metallogeny: A Case Study of Xinqiao Cu-S-Fe-Au Deposit in the Middle-Lower Yangtze Valley. Ore Geology Reviews, 43(1): 194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.12.004
Weis, F., 2013. Oxygen and Iron Isotope Systematics of the Grängesberg Mining District (GMD): [Dissertation]. Uppsala Universitet, Uppsala. 77
Wu, C. Z., Zhang, Z. X., Zaw, K., et al., 2006. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Tectonic Significances of the Hongyuntan Granitoids in the Qoltag Area, Eastern Tianshan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1121–1134 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xiao, W. J., 2004. Paleozoic Accretionary and Collisional Tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China): Implications for the Continental Growth of Central Asia. American Journal of Science, 304(4): 370–395. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.304A370
Xiao, W. J., Han, C. M., Yuan, C., et al., 2008. Middle Cambrian to Permian Subduction-Related Accretionary Orogenesis of Northern Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of Central Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(2/3/4): 102–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.10.008
Xiao, W. J., Windley, B. F., Allen, M. B., et al., 2013. Paleozoic Multiple Accretionary and Collisional Tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan Orogenic Collage. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1316–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2012.01.012
Yang, X. P., Li, A., Hunag, W., 2013. Uplift Differential of Active Fold Zones during the Late Quaternary, Northern Piedmonts of the Tianshan Mountains, China. Science China Earth Sciences, 56(5): 794–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-012-4531-z
Yao, P. H., Wang, K. N., Du, C. L., et al., 1993. Records of China’s Iron Deposits. Metallurgic Industry Press, Beijing. 1–662 (in Chinese)
Zhang, D. Y., Zhou, T. F., Yuan, F., et al., 2014. Genesis of Permian Granites along the Kangguer Shear Zone, Jueluotage Area, Northwest China: Geological and Geochemical Evidence. Lithos, 198/199: 141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.023
Zhang, W. F., Chen, H. Y., Han, J. S., et al., 2016. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Igneous Rocks in the Bailingshan Area: Implications for the Tectonic Setting of Late Paleozoic Magmatism and Iron Skarn Mineralization in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China. Gondwana Research, 38: 40–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.011
Zhang, X. R., Zhao, G. C., Sun, M., et al., 2016. Tectonic Evolution from Subduction to Arc-Continent Collision of the Junggar Ocean: Constraints from U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopes of Detrital Zircons from the North Tianshan Belt, NW China. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 128(3/4): 644–660. https://doi.org/10.1130/b31230.1
Zhang, Z. C., Santosh, M., Li, J. W., 2015. Iron Deposits in Relation to Magmatism in China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 951–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.09.026
Zhao, L. D., Chen, H. Y., Zhang, L., et al., 2017. Geology and Ore Genesis of the Late Paleozoic Heijianshan Fe Oxide-Cu(-Au) Deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 91: 110–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.10.014
Zhu, X. K., Sun, J., Wang, Y., 2016. Fe Isotope Geochemistry of Magmatic System. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 38(1): 1–1 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41672078) and the China Geological Survey (No. DD20190606). We are grateful to Dr. Zhenwu Chen for their assistance with analyses. We appreciate the anonymous reviewers for providing constructive and insightful comments. The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1060-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Li, H., Li, L. et al. Iron Isotopes and Trace Element Compositions of Magnetite from the Submarine Volcanic-Hosted Iron Deposits in East Tianshan, NW China: New Insights into the Mineralization Processes. J. Earth Sci. 32, 219–234 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1060-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1060-0