Abstract
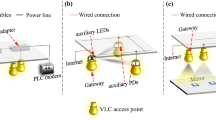
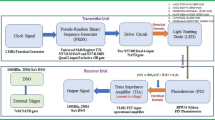
Visible light communication (VLC) is a promising technology that addresses the bandwidth bottleneck of radio-frequency based indoor wireless networks. Optical attocell networks using VLC backhaul links have been proposed. Line-of-sight (LOS) and mirror-aided non-LOS links can be used for backhaul transmission. As the visible light spectrum is used for both access downlink and bidirectional backhaul transmission, co-channel interference is a major issue. In this paper, we analyze the performance of optical attocell networks using VLC backhaul links taking into account illumination and eye safety requirements. Based on the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio of different backhaul links, the bandwidth allocation ratio when using an in-band frequency reused scheme is discussed. Finally, aggregate data rates of networks using different VLC backhaul configurations are compared. Results show that LOS backhaul configuration can achieve nearly optimal network performance while mirror-aided non-LOS backhaul configuration is more robust against misalignment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burchardt, H., Serafimovski, N., Tsonev, D., Videv, S., Haas, H.: VLC : Beyond Point-to-Point Communication. IEEE Commun. Mag. 52(7), 98 (2014)
Sevincer, A., Member, A.B., Member, M.B.: LIGHTNETs: smart LIGHTing and mobile optical wireless NETworks—a survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 15(4), 1620 (2013)
Borah, D.K., Boucouvalas, A.C., Davis, C.C., Hranilovic, S., Yiannopoulos, K.: A review of communication-oriented optical wireless systems. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2012(1), 1–28 (2012)
Jungnickel, V., Uysal, M., Serafimovski, N., Baykas, T., Ciaramella, E., Ghassemlooy, Z., Green, R., Haas, H., Haigh, P.A., Jimenez, V.P.G., Miramirkhani, F., Wolf, M.: A European View on the Next Generation Optical Wireless Communication Standard. In: IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN) (2015), pp. 106–111
Elgala, H., Mesleh, R., Haas, H.: Indoor optical wireless communication: potential and state-of-the-art. IEEE Commun. Mag. 49(9), 56 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2011.6011734
Kazemi, H., Haas, H.: Downlink cooperation with fractional frequency reuse in DCO-OFDMA optical attocell networks. IEEE Int. Conf. Commun. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICC.2016.7511475
Chen, C., Basnayaka, D.A., Haas, H.: Downlink performance of optical attocell networks. J. Lightwave Technol. 34(1), 137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2015.2511015
Stefan, I., Burchardt, H., Haas, H.: Area spectral efficiency performance comparison between VLC and RF femtocell networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Communications pp. 3825–3829 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICC.2013.6655152
Komine, T., Nakagawa, M.: Integrated system of white LED visible light communication and power line communication. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(1), 71 (2003)
Wang, Y., Chi, N., Wang, Y., Tao, L., Shi, J.: Network architecture of a high-speed visible light communication local area network. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 27(2), 197 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2014.2364955
Karunatilaka, D., Zafar, F., Kalavally, V., Parthiban, R.: LED based indoor visible light communications: state of the art. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 17(3), 1649 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2015.2417576
Liu, J., Zhao, B., Geng, L., Yuan, Z., Wang, Y.: Communication performance of broadband PLC technologies for smart grid. IEEE Int. Symp. Power Line Commun. Appl. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISPLC.2011.5764448
Feng, L., Hu, R.Q., Wang, J., Xu, P., Qian, Y.: Applying VLC in 5G networks: architectures and key technologies. IEEE Netw. 30(6), 77 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2016.1500236RP
Wu, T., Rappaport, T.S., Collins, C.M.: Safe for generations to come: considerations of safety for millimeter waves in wireless communications. IEEE Microwave Mag. 16(2), 65 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/MMM.2014.2377587
Kazemi, H., Safari, M., Haas, H.: A wireless backhaul solution using visible light communication for indoor Li-fi attocell networks. In IEEE ICC 2017 Optical Networks and Systems Symposium (2017)
Kazemi, H., Safari, M., Haas, H.: A Wireless Optical Backhaul Solution for Optical Attocell Networks. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 18(2), 807 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2018.2883465
Wu, Y., Audenaert, P., Pickavet, M., Colle, D.: Mirror-aided non-LOS VLC channel characterizations with a time-efficient simulation model. Photon Netw. Commun. 38(38), 151 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-019-00841-3
Chen, C., Videv, S., Tsonev, D., Haas, H.: Fractional frequency rreuse in DCO-OFDM-based optical attocell networks. J. Lightwave Technol. 33(19), 3986 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2015.2458325
Gfeller, F.R., Bapst, U.: Wireless in-house data communication via diffuse infrared radiation. Proc. IEEE 67(11), 1474 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1109/proc.1979.11508
Kahn, J., Barry, J.: Wireless infrared communications. Proc. IEEE 85(2), 265 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-2700-8
Armstrong, J., Schmidt, B.J.C.: Comparison of asymmetrically clipped optical OFDM and DC-biased optical OFDM in AWGN. IEEE Commun. Lett. 12(5), 343 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2008.080193
Yang, H., Pandharipande, A.: Full-duplex relay VLC in LED lighting linear system topology. In: Industrial Electronics Conference (IEEE), pp. 6075–6080 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2013.6700133
Narmanlioglu, O., Kizilirmak, R.C., Miramirkhani, F., Uysal, M.: Cooperative visible light communications with full-duplex relaying. IEEE Photonics J. 9(3), 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2017.2708746
Radiation Safety Office, Laser Safety Mannual (2007)
European Committee for Standardization, Light and lighting - Lighting of work places - Part 1 : Indoor work (2002)
Suk, J.Y.: Luminance and vertical eye illuminance thresholds for occupants’ visual comfort in daylit office environments. Build. Environ. 148, 107 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.10.058
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Pickavet, M. & Colle, D. Analysis of interference on mirror-aided non-LOS backhaul data transmission in VLC attocell networks. Photon Netw Commun 41, 189–201 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-021-00928-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-021-00928-w