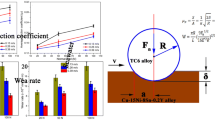
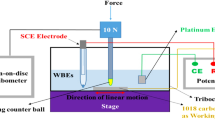
Abstract
Cermets have been widely used in industry to combat wear and erosion because of their elevated strength and hardness and good wear resistance. This study investigated the tribological properties of WC-6Ni (YN6X), WC-6Co (YG6X), and WC-TiC-Co–Ni (TiCN) cermets during sliding over silicon carbide (SiC) in prepared seawater. Tribological experiments of 440C and GCr15 steel coupled with SiC were conducted for comparison. The influence of sliding speed was examined by multiple sequential increases in speed from 0.1 to 0.4 m s−1. The results showed that the tribological properties of the tribopairs were enhanced with growing sliding speed and were influenced by complex factors including material hardness, wear radius, the lubricating medium environment, and the tribochemical reaction. YN6X performed particularly well due to its high hardness and presence of Ni which effectively reduced the corrosion effect of seawater. However, YG6X showed better wear resistance relative to YN6X in tap water due to its higher hardness. In particular, through an investigation of the wear process of the tribopairs in seawater, this study proposed the coefficient of friction model for cermet/SiC. The results indicated that a combination of YN6X/SiC has excellent potential for application to seawater hydraulic components.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, H.Y., Pan, M.: Engineering research in fluid power: a review. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci A 16, 427–442 (2015)
Yin, F.L., Nie, S.L., Ji, H., Huang, Y.Q.: Non-probabilistic reliability analysis and design optimization for valve-port plate pair of seawater hydraulic pump for underwater apparatus. Ocean Eng. 163, 337–347 (2018)
Dong, C.L., Bai, X.Q., Yan, X.P., Yuan, C.Q.: Research status and advances on tribological study of materials under ocean environment. Tribology 33, 311–320 (2013)
Bernat, S., Armada, S., Espallargas, N.: Effect of contamination on the friction and wear of carboxylic acids in aqueous lubricants. Tribol. Lett. 66, 158 (2018)
Meng, Y.G., Xu, J., Jin, Z.L., Prakash, B., Hu, Y.Z.: A review of recent advances in tribology. Friction 8, 221–3500 (2020)
Pang, W., Ni, Z., Wu, J.L., Zhao, Y.W.: Investigation of tribological properties of graphene oxide reinforced ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene under artificial seawater lubricating condition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 434, 273–282 (2018)
Chen, B., Wang, J., Yan, F.: Friction and wear behaviors of several polymers sliding against GCr15 and 316 steel under the lubrication of sea water. Tribol. Lett. 42, 17–25 (2011)
Wang, J., Yan, F., Xue, Q.: Tribological behavior of PTFE sliding against steel in sea water. Wear 267, 1634–1641 (2009)
Chen, W., Wang, Z.X., Liu, X., Jia, J.H., Hua, Y.: Effect of load on the friction and wear characteristics of Si3N4-hBN ceramic composites sliding against PEEK in artificial seawater. Tribol. Int. 141, 105902 (2020)
Yin, X., Wu, J., Li, C., Lu, X., Feng, X., Shi, Y.: Right way of using graphene oxide additives for water-lubricated PEEK: adding in polymer or water? Tribol. Lett. 66, 103 (2018)
Chen, J., Zhang, Q., Li, Q.N., Fu, S.L., Wang, J.Z.: Corrosion and tribocorrosion behaviors of AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys in artificial seawater. Trans. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 24, 1022–1031 (2014)
Ding, H.Y., Zhou, G.H., Dai, Z.D., Bu, Y.F., Jiang, T.Y.: Corrosion wear behaviors of 2024Al in artificial rainwater and seawater at fretting contact. Wear 267, 292–298 (2009)
Cheng, J.J., Gan, X.P., Lei, Q., Mao, M.C., Li, Z., Zhou, K.: Tribological behaviors of an ultrahigh strength Cu-15Ni-8Sn-0.2Y alloy sliding against TC6 Titanium alloy in deionized water and seawater. Tribol. Lett. 68, 21 (2020)
Yan, Z., Jiang, D., Gao, X.M., Hu, M., Wang, D.S., Fu, Y.L., Sun, J.Y., Feng, D.P., Weng, L.J.: Friction and wear behavior of TiN films against ceramic and steel balls. Tribol. Int. 124, 61–69 (2018)
Chen, W., Wang, K., Liu, X., He, N.R., Xin, H., Hao, W.H.: Investigation of the friction and wear characteristics of Si3N4-hBN ceramic composites under marine atmospheric environment. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 81, 345–357 (2019)
Lin, B., Wang, A.Y., Sui, T.Y., Wei, C.B., Wei, J.H., Yan, S.: Friction and wear resistance of polytetrafluoroethylene-based composites reinforced with ceramic particles under aqueous environment. Surf. Topogr.-Metrol. 8, 015006 (2020)
Wu, D.F., Liu, Y.S., Li, D.L., Zhao, X.F., Liu, Y.: Tribo-corrosion properties of WC-10Co-4Cr coating in natural silt-laden waters when sliding against Si3N4. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 58, 143–151 (2016)
Sun, S.Q., Wang, Y.X., Lu, X.J., Lu, X., Mao, C.L., Zeng, Z.X., Xue, Q.J.: Achieving excellent tribological performance of a-C: WC film by controlling sub-nano-structure. Tribol. Int. 128, 65–74 (2018)
Wang, C.T., Ye, Y.W., Guan, X.Y., Hu, J.M., Wang, Y.X., Li, J.L.: An analysis of tribological performance on Cr/GLC film coupling with Si3N4, SiC, WC, Al2O3 and ZrO2 in seawater. Tribol. Int. 96, 77–86 (2016)
Zhu, S.Y., Ma, J.Q., Tan, H., Cheng, J., Yu, Y., Qiao, Z.H., Yang, J.: Tribological behavior of nickel aluminum-silver solid-lubricating alloy coupled with different tribo-pairs lubricated by seawater. Tribol. Int. 131, 158–166 (2019)
Liu, N., Wang, J.Z., Chen, B.B., Yan, F.Y.: Tribochemical aspects of silicon nitride ceramic sliding against stainless steel under the lubrication of seawater. Tribol. Int. 61, 205–213 (2013)
Su, Y.L., Yao, S.H., Leu, Z.L., Wei, C.S., Wu, C.T.: Comparison of tribological behavior of three films-TiN, TiCN and CrN-grown by physical vapor deposition. Wear 213, 165–174 (1997)
Ouyang, J.H., Yang, Z.L., Liu, Z.G., Liang, X.S.: Friction and wear properties of reactive hot-pressed TiB2-TiN composites in sliding against Al2O3 ball at elevated temperatures. Wear 271, 1966–1973 (2011)
Zhou, F., Suh, C.M., Kim, S.S., Murakami, R.: Sliding-wear behavior of TiN-and CrN-coated 2024 aluminum alloy against an Al2O3 ball. Tribol. Lett. 13, 173–178 (2002)
Fateh, N., Fontalvo, G.A., Gassner, G., Mitterer, C.: Influence of high-temperature oxide formation on the tribological behaviour of TiN and VN coatings. Wear 262, 1152–1158 (2007)
Wilson, S., Alpas, A.T.: Dry sliding wear of a PVD TiN coating against Si3N4 at elevated temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 86, 75–81 (1996)
Vashishtha, N., Sapate, S.G., Gahlot, J.S., Bagde, P.: Effect of tribo-oxidation on friction and wear behaviour of HVOF sprayed WC-10Co-4Cr coating. Tribol. Lett. 66, 56 (2018)
Sharma, S.K., Kumar, B.V.M., Kim, Y.W.: Tribology of WC reinforced SiC ceramics: Influence of counterbody. Friction 7, 129–142 (2019)
Federici, M., Perricone, G., Gialanella, S., Straffelini, G.: Sliding behaviour of friction material against cermet coatings: pin-on-disc study of the running-in stage. Tribol. Lett. 66, 53 (2018)
Ji, W.B., Yuan, Y.K., Zou, B., Dai, S.J., Zhang, H.B.: Friction and wear behaviour of cemented carbide tool materials sliding against Al2O3 and Si3N4 ceramics under dry condition. Ceram. Int. 44, 17486–17491 (2018)
Nie, S.L., Xu, W.H., Yin, F.L., Ji, H., Xu, Y.J., Hu, Z., Guo, M., Zhou, X.: Investigation of the tribological behaviour of cermets sliding against Si3N4 for seawater hydraulic components applications. Surf. Topogr.-Metrol. 7, 045025 (2019)
Zhang, J.J., Liu, J.C., Wang, Z.X., Chen, W., Hu, B., Zhang, Y., Liao, H.M., Ma, S.D.: Tribological behavior and lubricating mechanism of Si3N4 in artificial seawater. Ceram. Int. 46, 14361–14368 (2020)
Wang, S., Cheng, J., Zhu, S.Y., Qiao, Z.H., Yang, J., Liu, W.M.: Frictional properties of Ti3AlC2 ceramic against different counterparts in deionized water and artificial seawater. Ceram. Int. 42, 4578–4585 (2016)
Wang, Y.X., Wang, L.P., Xue, Q.J.: Improvement in the tribological performances of Si3N4, SiC and WC by graphite-like carbon films under dry and water-lubricated sliding conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205, 2770–2777 (2011)
Wang, Q.Z., Zhou, F., Chen, K.M., Wang, M.L., Qian, T.: Friction and wear properties of TiCN coatings sliding against SiC and steel balls in air and water. Thin Solid Films 519, 4830–4841 (2011)
Wang, Q.Z., Zhou, F., Zhu, L., Zhang, M.D.: Tribological dependence of CrSiBCN composite coatings on different counterparts in water lubrication. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 42, 17–25 (2020)
Verma, V., Kumar, B.V.M.: Tribological characteristics of conventionally sintered TiCN-WC-Ni/Co cermets against cemented carbide. Ceram. Int. 43, 368–375 (2017)
Tang, Q.G., Chen, J.T., Liu, L.P.: Tribological behaviours of carbon fibre reinforced PEEK sliding on silicon nitride lubricated with water. Wear 269, 541–546 (2010)
Bhushan, B.: Introduction to tribology. Wiley, Hoboken (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52075007, 51905011, 51975010 and 52005013), Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Project (Grant Nos. KM201810005014, KM201910005033 and KM202110005031), and Beijing Postdoctoral Research Foundation (Grant No. 2020-ZZ-033). Thanks are also given to Miss Wenhui Xu and Mr Fangli Lou for their help in preparing specimens, experiment, and polishing of the manuscript. The authors are very grateful to the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, F., Wang, Y., Ji, H. et al. Impact of Sliding Speed on the Tribological Behaviors of Cermet and Steel Balls Sliding Against SiC Lubricated with Seawater. Tribol Lett 69, 39 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01413-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01413-1