Abstract
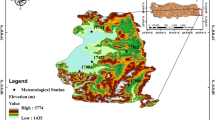
It is a known fact that the size, frequency, and spatial variability of hydrometeorological variables will irregularly increase under the impact of climate change. Among the hydrometeorological variables, rainfall is one of the most important. Trend analysis is one of the most effective methods of observing the effects of climate change on rainfall. Recently, new graphical methods have been proposed as an alternative to classical trend analysis methods. Innovative Polygon Trend Analysis (IPTA), which evolved from Innovative Trend Analysis (ITA), is currently one of the proposed methods and it does not contain any assumptions. The aim of this study is to compare IPTA, ITA with the Significance Test and Mann-Kendall (MK) methods. To achieve this, the monthly total rainfall trends of 15 stations in the Vu Gia-Thu Bon River Basin (VGTBRB) of Vietnam have been examined for the period 1979–2016. The analyses show that rainfall tends to increase (decrease) in March (June) at nearly all stations. IPTA and ITA with the Significance Test are more sensitive than MK in determining the trends. While trends were detected in approximately 90% of all months in IPTA and ITA with the Significance Test, this rate was only 23% in the MK test. Although the arithmetic mean graphs in the 1-year hydrometeorological cycle are considerably regular at almost all stations, their standard deviations are relatively irregular. The most critical month for trend transitions between consecutive months for all the stations is October, which has an average trend slope of −1.35 and a trend slope ranging from −3.98 to −0.21, which shows a decreasing trend.






Similar content being viewed by others

Data Availability
The codes and visualizations required for the study were made in MATLAB 2014a software. The data and code are available from the author (Quoc Bao Pham; phambaoquoc@tdtu.edu.vn) upon reasonable request.
References
Abdi A, Hassanzadeh Y, Talatahari S, Fakheri-Fard A, Mirabbasi R (2017) Regional drought frequency analysis using L-moments and adjusted charged system search. J Hydroinf 19:426–442. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2016.228
Ahmad I, Zhang F, Tayyab M, Anjum MN, Zaman M, Liu J, Farid HU, Saddique Q (2018) Spatiotemporal analysis of precipitation variability in annual, seasonal and extreme values over upper Indus River basin. Atmos Res 213:346–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.06.019
Ahmadi F, Nazeri Tahroudi M, Mirabbasi R, Khalili K, Jhajharia D (2018) Spatiotemporal trend and abrupt change analysis of temperature in Iran. Meteorol Appl 25:314–321. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1694
Alashan S (2018a) An improved version of innovative trend analyses. Arab J Geosci 11:50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3393-x
Alashan S (2018b) Data analysis in nonstationary state. Water Resour Manag 32:2277–2286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-1928-2
Alexandersson H (1986) A homogeneity test applied to precipitation data. J Climatol 6:661–675. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3370060607
Ali R, Kuriqi A, Abubaker S, Kisi O (2019) Long-term trends and seasonality detection of the observed flow in Yangtze River using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s innovative trend method. Water (Switzerland) 11:1855
Almazroui M, Şen Z, Mohorji AM, Islam MN (2019) Impacts of climate change on water engineering structures in arid regions: case studies in Turkey and Saudi Arabia. Earth Syst Environ 3:43–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-018-0082-6
Ay M (2020) Trend and homogeneity analysis in temperature and rainfall series in western Black Sea region, Turkey. Theor Appl Climatol 139:837–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-03066-6
Ay M, Kisi O (2015) Investigation of trend analysis of monthly total precipitation by an innovative method. Theor Appl Climatol 120:617–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-014-1198-8
Buishand TA (1982) Some methods for testing the homogeneity of rainfall records. J Hydrol 58:11–27
Caloiero T, Coscarelli R, Ferrari E (2018) Application of the innovative trend analysis method for the trend analysis of rainfall anomalies in Southern Italy. Water Resour Manag 32:4971–4983
Ceribasi G, Ceyhunlu AI (2020) Analysis of total monthly precipitation of Susurluk Basin in Turkey using innovative polygon trend analysis method. J Water Clim Chang. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2020.253
Dabanli I, Şen Z (2018) Classical and innovative-Şen trend assessment under climate change perspective. Int J Glob Warm 15:19–37. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGW.2018.091951
Dabanlı İ, Şen Z, Yeleğen MÖ, Şişman E, Selek B, Güçlü YS (2016) Trend assessment by the innovative-Şen method. Water Resour Manag 30:5193–5203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1478-4
Dinpashoh Y, Mirabbasi R, Jhajharia D, Abianeh HZ, Mostafaeipour A (2014) Effect of short-term and long-term persistence on identification of temporal trends. J Hydrol Eng 19:617–625. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000819
Diop L, Yaseen ZM, Bodian A, Djaman K (2018) Trend analysis of streamflow with different time scales : a case study of the upper Senegal River. ISH J Hydraul Eng 24:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2017.1333045
Douglas EM, Vogel RM, Kroll CN (2000) Trends in floods and low flows in the United States: impact of spatial correlation. J Hydrol 240:90–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00336-X
Elouissi A, Şen Z, Habi M (2016) Algerian rainfall innovative trend analysis and its implications to Macta watershed. Arab J Geosci 9:303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2325-x
Gajbhiye S, Meshram C, Mirabbasi R, Sharma SK (2016) Trend analysis of rainfall time series for Sindh river basin in India. Theor Appl Climatol 125:593–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1529-4
Güçlü YS (2018) Alternative trend analysis: half time series methodology. Water Resour Manag 32:2489–2504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-1942-4
Güçlü YS (2020) Improved visualization for trend analysis by comparing with classical Mann-Kendall test and ITA. J Hydrol 584:124674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124674
Güçlü YS, Şişman E, Dabanlı İ (2020) Innovative triangular trend analysis. Arab J Geosci 13:27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-5048-y
Güçlü YS, Şişman E, Yeleğen M (2018) Climate change and frequency–intensity–duration (FID) curves for Florya station, Istanbul. J Flood Risk Manag 11:S403–S418. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12229
Haktanir T, Citakoglu H (2014) Trend, independence, stationarity, and homogeneity tests on maximum rainfall series of standard durations recorded in Turkey. J Hydrol Eng 19:05014009. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000973
Haktanir T, Citakoglu H (2015) Closure to “Trend, independence, stationarity, and homogeneity tests on maximum rainfall series of standard durations recorded in Turkey” by Tefaruk Haktanir and Hatice Citakoglu. J Hydrol Eng 20:07015017. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001246
IPCC (2013) Climate Change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Stocker TFD, Qin GK, Plattner M, Tignor SK, Allen J, Boschung A, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Cambridge University press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1535 pp, 2013
IPCC (2007) IPCC fourth assessment report working group I report “the physical science basis.” New York
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation methods. Griffin, London
Kumar S, Merwade V, Kam J, Thurner K (2009) Streamflow trends in Indiana: effects of long term persistence, precipitation and subsurface drains. J Hydrol 374:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.06.012
Malik A, Kumar A, Guhathakurta P, Kisi O (2019) Spatial-temporal trend analysis of seasonal and annual rainfall (1966–2015) using innovative trend analysis method with significance test. Arab J Geosci 12:328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4454-5
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13:245–259
Meshram SG, Kahya E, Meshram C, Ghorbani MA, Ambade B, Mirabbasi R (2020) Long-term temperature trend analysis associated with agriculture crops. Theor Appl Climatol 140:1139–1159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03137-z
Mohorji AM, Şen Z, Almazroui M (2017) Trend analyses revision and global monthly temperature innovative multi-duration analysis. Earth Syst Environ 1:9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-017-0014-x
Onyutha C (2016) Identification of sub-trends from hydro-meteorological series. Stoch Environ Res Risk A 30:189–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1070-0
Peterson TC, Easterling DR, Karl TR, Groisman P, Nicholls N, Plummer N, Torok S, Auer I, Boehm R, Gullett D, Vincent L, Heino R, Tuomenvirta H, Mestre O, Szentimrey T, Salinger J, Førland EJ, Hanssen-Bauer I, Alexandersson H, Jones P, Parker D (1998) Homogeneity adjustments of in situ atmospheric climate data: a review. Int J Climatol 18:1493–1517. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(19981115)18:13<1493::AID-JOC329>3.0.CO;2-T
Pettitt AN (1979) A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. Jstor 28:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2008.06.016
Pham QB, Abba SI, Usman AG, Linh NTT, Gupta V, Malik A, ... Tri DQ (2019) Potential of hybrid data-intelligence algorithms for multi-station modelling of rainfall. Water Resour Manag 33(15):5067–5087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02408-3
Pham QB, Afan HA, Mohammadi B, Ahmed AN, Linh NTT, Vo ND, ... El-Shafie A (2020) Hybrid model to improve the river streamflow forecasting utilizing multi-layer perceptron-based intelligent water drop optimization algorithm. Soft Comput 24:18039–18056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05058-5
Phuong DND, Tram VNQ, Nhat TT, Ly TD, Loi NK (2020) Hydro-meteorological trend analysis using the Mann-Kendall and innovative-Şen methodologies: a case study. Int J Glob Warm 20:145–164. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGW.2020.105385
Sagarika S, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2014) Evaluating the effect of persistence on long-term trends and analyzing step changes in streamflows of the continental United States. J Hydrol 517:36–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.05.002
Sanikhani H, Kisi O, Mirabbasi R, Meshram SG (2018) Trend analysis of rainfall pattern over the Central India during 1901–2010. Arab J Geosci 11:437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3800-3
Saplioǧlu K (2015) A new methodology for trend analysis: a case study in Burdur and Isparta, Turkey. Fresenius Environ Bull 24:3344–3351
Saplıoğlu K, Kilit M, Yavuz BK (2014) Trend analysis of streams in the Western Mediterranean Basin of Turkey. Fresenius Environ Bull 23:313–324
Şen Z (2017) Innovative trend significance test and applications. Theor Appl Climatol 127:939–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1681-x
Şen Z (2020a) Water structures and climate change impact: a review. Water Resour Manag 34:4197–4216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02665-7
Şen Z (2012) Innovative trend analysis methodology. J Hydrol Eng 17:1042–1046. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000556
Şen Z (2014) Trend identification simulation and application. J Hydrol Eng 19:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000811
Şen Z (2019) Partial trend identification by change-point successive average methodology (SAM). J Hydrol 571:288–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.02.007
Şen Z (2018) Crossing trend analysis methodology and application for Turkish rainfall records. Theor Appl Climatol 131:285–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1980-x
Şen Z (2020b) Probabilistic innovative trend analysis. Int J Glob Warm 20:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGW.2020.105387
Şen Z, Şişman E, Dabanli I (2019) Innovative polygon trend analysis (IPTA) and applications. J Hydrol 575:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.05.028
Souvignet M, Laux P, Freer J, Cloke H, Thinh DQ, Thuc T, Cullmann J, Nauditt A, Flügel WA, Kunstmann H, Ribbe L (2014) Recent climatic trends and linkages to river discharge in Central Vietnam. Hydrol Process 28:1587–1601. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9693
Tabari H, Taye MT, Onyutha C, Willems P (2017) Decadal analysis of river flow extremes using quantile-based approaches. Water Resour Manag 31:3371–3387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1673-y
To TN (2005) Strategic plan for integrated water resources management of the Vu Gia Thu Bon Basin Organization
Vo ND, Gourbesville P, Vu MT, Raghavan SV, Liong SY (2016) A deterministic hydrological approach to estimate climate change impact on river flow: Vu Gia–Thu Bon catchment, Vietnam. J Hydro-Environ Res 11:59–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2015.11.001
Von Neumann J (1941) Distribution of the ratio of the mean square successive difference to the variance. Ann Math Stat 12:367–395
Wijngaard JB, Klein Tank AMG, Können GP (2003) Homogeneity of 20th century European daily temperature and precipitation series. Int J Climatol 23:679–692. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.906
Wu H, Qian H (2017) Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall and extreme values in Shaanxi, China, since the 1950s. Int J Climatol 37:2582–2592. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4866
Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney B, Cavadias G (2002) The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol Process 16:1807–1829. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1095
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Murat Şan: writing—original draft and software. Fatma Akçay: formal analysis, visualization, and data curation. Nguyen Thi Thuy Linh: writing—original draft, review, and editing. Murat Kankal: project administration, supervision, review, and editing. Quoc Bao Pham: supervision, review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Competing interests
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
This manuscript has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or in entirety and is not under consideration by another journal.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şan, M., Akçay, F., Linh, N.T.T. et al. Innovative and polygonal trend analyses applications for rainfall data in Vietnam. Theor Appl Climatol 144, 809–822 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03574-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03574-4