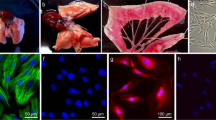
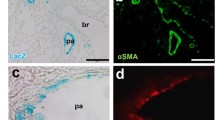
Abstract
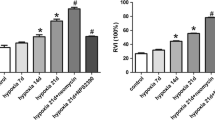
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is characterized by pulmonary vascular remodeling, which exists in both pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins. Pulmonary vascular remodeling stems from excessive proliferation of pulmonary vascular myocytes. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is a vital vascular regulator whose level increases in PH human lungs. Although the mechanisms by which pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells respond to PDGF-BB have been studied extensively, the effects of PDGF-BB on pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells (PVSMCs) remain unknown. We herein examined the involvement of calcium sensing receptor (CaSR) in PDGF-BB-induced PVSMCs proliferation under hypoxic conditions. In PVSMCs isolated from rat intrapulmonary veins, PDGF-BB increased the cell number and DNA synthesis under normoxic and hypoxic conditions, which was accompanied by upregulated CaSR expression. The influences of PDGF-BB on proliferation and CaSR expression in hypoxic PVSMCs were greater than that in normoxic PVSMCs. In hypoxic PVSMCs superfused with Ca2+-free solution, restoration of extracellular Ca2+ induced an increase of [Ca2+]i, which was significantly smaller than that in PDGF-BB-treated hypoxic PVSMCs. The positive CaSR modulator spermine enhanced, whereas the negative CaSR modulator NPS2143 attenuated, the extracellular Ca2+-induced [Ca2+]i increase in PDGF-BB-treated hypoxic PVSMCs. Furthermore, the spermine enhanced, whereas the NPS2143 inhibited, PDGF-BB-induced proliferation in hypoxic PVSMCs. Silencing CaSR with siRNA attenuated the extracellular Ca2+-induced [Ca2+]i increase in PDGF-BB-treated hypoxic PVSMCs and inhibited PDGF-BB-induced proliferation in hypoxic PVSMCs. In conclusion, these results demonstrated that CaSR mediating PDGF-BB-induced excessive PVSMCs proliferation is an important mechanism involved in the initiation and progression of PVSMCs proliferation under hypoxic conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 September 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-021-00488-x
References
Andersen KH, Andersen CB, Gustafsson F, Carlsen J (2017) Pulmonary venous remodeling in COPD-pulmonary hypertension and idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Circ 7:514–521. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045893217709762
Berg JT, Breen EC, Fu Z, Mathieu-Costello O, West JB (1998) Alveolar hypoxia increases gene expression of extracellular matrix proteins and platelet-derived growth factor-B in lung parenchyma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158:1920–1928. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.158.6.9804076
Brown EM, MacLeod RJ (2001) Extracellular calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiol Rev 81:239–297. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.2001.81.1.239
Chakravarti B, Chattopadhyay N, Brown EM (2012) Signaling through the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Adv Exp Med Biol 740:103–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2888-2_5
Chen B, Nelin VE, Locy ML, Jin Y, Tipple TE (2013) Thioredoxin-1 mediates hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 305:L389–L395. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00432.2012
Diez-Fraile A, Lammens T, Benoit Y, D’Herde KG (2013) The calcium-sensing receptor as a regulator of cellular fate in normal and pathological conditions. Curr Mol Med 13:282–295
Dorfmuller P et al (2014) Microvascular disease in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a role for pulmonary veins and systemic vasculature. Eur Respir J 44:1275–1288. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00169113
Fayyaz AU et al (2018) Global pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension associated with heart failure and preserved or reduced ejection fraction. Circulation 137:1796–1810. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031608
Hofer AM, Brown EM (2003) Extracellular calcium sensing and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:530–538. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1154
Hong W et al (2017) Nicotine-induced airway smooth muscle cell proliferation involves TRPC6-dependent calcium influx via alpha7 nAChR. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 43:986–1002. https://doi.org/10.1159/000481651
Humbert M et al (1998) Platelet-derived growth factor expression in primary pulmonary hypertension: comparison of HIV seropositive and HIV seronegative patients. Eur Respir J 11:554–559
Humbert M et al (2019) Pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension: state of the art and research perspectives. Eur Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01887-2018
Jiang Y et al (2018) Topotecan prevents hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension and inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and TRPC channels. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 104:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2018.09.010
Johar D, Magdeldin S (2018) Application of laser scanning cytometry in vascular smooth muscle remodeling. Hypertens Res Off J Jpn Soc Hypertens 41:869–885. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-018-0077-6
Kunichika N, Landsberg JW, Yu Y, Kunichika H, Thistlethwaite PA, Rubin LJ, Yuan JX (2004) Bosentan inhibits transient receptor potential channel expression in pulmonary vascular myocytes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:1101–1107. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200312-1668OC
Latson LA, Prieto LR (2007) Congenital and acquired pulmonary vein stenosis. Circulation 115:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.646166
Leopold JA (2018) Pulmonary venous remodeling in pulmonary hypertension: the veins take center stage. Circulation 137:1811–1813. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033013
Li GW et al (2011) The functional expression of extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci 18:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-18-16
Li YX, Run L, Shi T, Zhang YJ (2017) CTRP9 regulates hypoxia-mediated human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration via TGF-beta1/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:1319–1325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.020
Li S et al (2020) A novel function of calcium sensing receptor in chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells proliferation. Hypertens Res Off J Jpn Soc Hypertens 43:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-019-0373-9
Liu G et al (2018) Upregulation of microRNA-17-5p contributes to hypoxia-induced proliferation in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells through modulation of p21 and PTEN. Respir Res 19:200. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0902-0
Luo Y et al (2019) CD146-HIF-1alpha hypoxic reprogramming drives vascular remodeling and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Commun 10:3551. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11500-6
Omura J et al (2019) ADAMTS8 promotes the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension and right ventricular failure: a possible novel therapeutic target. Circ Res 125:884–906. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315398
Peng G, Lu W, Li X, Chen Y, Zhong N, Ran P, Wang J (2010a) Expression of store-operated Ca2+ entry and transient receptor potential canonical and vanilloid-related proteins in rat distal pulmonary venous smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 299:L621–L630. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00176.2009
Peng G, Wang J, Lu W, Ran P (2010b) Isolation and primary culture of rat distal pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells. Hypertens Res Off J Jpn Soc Hypertens 33:308–313. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2009.234
Peng G et al (2015) Chronic hypoxia increases intracellular Ca(2+) concentration via enhanced Ca(2+) entry through receptor-operated Ca(2+) channels in pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells. Circ J 79:2058–2068. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-15-0067
Peng G et al (2017) Isolation, culture and identification of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells from rat distal pulmonary arteries. Cytotechnology 69:831–840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-017-0081-8
Salic A, Mitchison TJ (2008) A chemical method for fast and sensitive detection of DNA synthesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2415–2420. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0712168105
Smith KA, Ayon RJ, Tang H, Makino A, Yuan JX (2016) Calcium-sensing receptor regulates cytosolic [Ca (2+)] and plays a major role in the development of pulmonary hypertension. Front Physiol 7:517. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2016.00517
Song S et al (2016) The role of PDGF-B/TGF-beta1/neprilysin network in regulating endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary artery remodeling. Cell Signal 28:1489–1501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.06.022
Suntharos P, Setser RM, Bradley-Skelton S, Prieto LR (2017) Real-time three dimensional CT and MRI to guide interventions for congenital heart disease and acquired pulmonary vein stenosis. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 33:1619–1626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-017-1151-x
Takahashi H, Soma S, Muramatsu M, Oka M, Fukuchi Y (2001) Upregulation of ET-1 and its receptors and remodeling in small pulmonary veins under hypoxic conditions. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280:L1104–L1114. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.6.L1104
van Son JA, Danielson GK, Puga FJ, Edwards WD, Driscoll DJ (1995) Repair of congenital and acquired pulmonary vein stenosis. Ann Thorac Surg 60:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-4975(95)00325-f
Wang Q, Wang D, Yan G, Sun L, Tang C (2016) TRPC6 is required for hypoxia-induced basal intracellular calcium concentration elevation, and for the proliferation and migration of rat distal pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells. Mol Med Rep 13:1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4750
Yamamura A et al (2012) Enhanced Ca(2+)-sensing receptor function in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ Res 111:469–481. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.266361
Yu Y, Sweeney M, Zhang S, Platoshyn O, Landsberg J, Rothman A, Yuan JX (2003) PDGF stimulates pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by upregulating TRPC6 expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284:C316–C330. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00125.2002
Zhang L et al (2012) Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) induces pulmonary vascular remodeling through 15-LO/15-HETE pathway under hypoxic condition. Cell Signal 24:1931–1939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.06.007
Zhang WF, Xiong YW, Zhu TT, Xiong AZ, Bao HH, Cheng XS (2017) MicroRNA let-7g inhibited hypoxia-induced proliferation of PASMCs via G0/G1 cell cycle arrest by targeting c-myc. Life Sci 170:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.11.020
Zhao Y et al (2019) ALDH2 (aldehyde dehydrogenase 2) protects against hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 39:2303–2319. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312946
Ziegelstein RC, Xiong Y, He C, Hu Q (2006) Expression of a functional extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in human aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.135
Zurlo G et al (2018) Sirtuin 1 regulates pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation: role in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 36:1164–1177. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000001676
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program (2017BT01S155), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2114050001676, 2017A030313683, 2017A030310419), the National key Research and Development program of China (2016YFC1304100, 2016YFC1304104, 2018YFC1311600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81570045), the Science and technology program of Guangzhou (201504010018), a Training Program for Academic Backbone of High Level Universities of Guangzhou Medical University (2017210) and a Grant of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University (201619). Dr. Peng was supported by the Scholarship of Guangzhou Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Xu, J., Jiang, Y. et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells proliferation by upregulating calcium sensing receptor under hypoxic conditions. Cytotechnology 73, 189–201 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-021-00456-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-021-00456-5