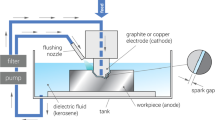
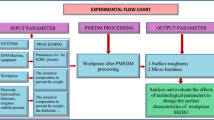
Abstract
Powder mixed electric discharge machining is one of the important recent trends in electric discharge machining process which successfully addresses some of the issues associated with the normal die-sinking EDM process. Since the performance of powder mixed EDM is based on work and tool material combination besides other process parameters, various research works have been reported by experimenting with different materials. This work aims to study the influence of different tool materials on powder mixed EDM of a nickel-based superalloy, Nimonic 75, along with using three different powders (zinc, Co and Mo). Nimonic 75 material is being widely used in aerospace and high-temperature applications. Besides the powders type and tool material (Cu, brass and W), the other process parameters are concentration of powder (Cp), peak current (Ip) and pulse on time (Ton). The performance measures considered in this study are material removal rate (MRR), tool wear rate (TWR) and surface roughness (SR). The experiments were conducted based on Taguchi’s orthogonal array (L27 313). Using ANOVA, it was identified that peak current and tool material had much greater influence over MRR, TWR and SR. Zinc powder yielded highest MRR, and molybdenum powder produced good finish of the components. It was also observed that copper yielded highest MRR, tungsten experienced low TWR, and brass tool electrode produced very smooth surface finish.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeswani L M, Wear 70 (1981) 133.
Ming Q Y, and He L Y, J Mater Process Technol 52 (1995) 44.
Wong Y S, Lim L C, Rahuman I, and Tee W M, J Mater Process Technol 79 (1998) 30.
Chow H M, Yan B H, Huang F Y, and Hung J C, J Mater Process Technol 101 (2000) 95.
Tzeng Y F, and Lee C Y, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 17 (2001) 586.
Zhao W S, Meng Q G, and Wang Z L, J Mater Process Technol 129 (2002) 30.
Pecas P, and Henriques E A, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43 (2003) 1465.
Pecas P, and Henriques E, J Mater Process Technol 200 (2008) 250.
Wu K L, Yan B H, Huang F Y, and Chen S C, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45 (2005) 1195.
Fong T Y, and Chen C F, J Mater Process Technol 170 (2005) 385.
Kansal H K, Singh S, and Kumar P, J Manuf Process 9 (2007) 13.
Chow H M, Yang L D, Lin C T, and Chen Y F, J Mater Process Technol 195 (2008) 160.
Kung K Y, Horng J T, and Chiang K T, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 4 (2009) 95.
Ojha K, Garg R K, and Sing K K, Int J Appl Sci Eng 2 (2011) 65.
Bhattacharya A, Batish A, Singh G, and Singla V K, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61 (2012) 537.
Bai X, Zhang Q-H, Yang T-Y, and Zhang J-H, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68 (2013) 1757.
Jabbaripour B, Sadeghi M H, Shabgard M R, and Faraji H, J Manuf Process 15 (2013) 56.
Kumar H, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 76 (2015) 105.
Singh A K, Kumar S, and Singh V P, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77 (2015) 99.
Unses E, and Cogun C, Strojniški vestnik - J Mech Eng 61 (2015) 409.
Talla G, Gangopadhyay S, and Biswas C K, J Mater Eng Perform 25 (2016) 704.
Long B T, Phan N H, Cuong N, and Jatti V S, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87 (2016) 1929.
Shabgard M, and Khosrozadeh B, J Manuf Process 25 (2017) 212.
Ou S F, and Wang C Y, J Mater Process Technol 245 (2017) 70.
Singh S, Maheshwari S, and Pandey P C, J Mater Process Technol 149 (2004) 272.
Baseri H, and Sadeghian S, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83 (2016) 519.
Rathi M G, and Mane D V, Int J Sci Res Publ 4 (2014) 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, S., Jenarthanan, M.P. Investigation of Powder Mixed EDM of Nickel-Based Superalloy Using Cobalt, Zinc and Molybdenum Powders. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 923–936 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02170-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02170-w