Abstract—
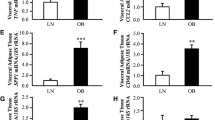
The study aimed to investigate tissue-specific gene expression of ABCA1 and ABCG1, encoding cholesterol transporters, as well as PPARG, LXRβ (NR1H2), and RORA, encoding the most important transcriptional regulators of lipid metabolism, in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue (SAT and VAT) in women with metabolic syndrome. It was shown that the ABCG1 mRNA SAT/VAT ratio decreases with age and correlates with the development of metabolic syndrome. After age adjustment, women have reduced chances of metabolic syndrome development when ABCG1 gene expression in SAT is higher relative to VAT than women with VAT ABCG1 gene expression higher or comparable to SAT: OR = 0.15 (95% CI 0.03–0.76), p = 0.023. The ABCA1 mRNA SAT/VAT ratio positively correlated with HDL cholesterol levels (after age adjustment β = 0.350, p = 0.046), therefore individuals with higher ABCA1 mRNA level in SAT relative to VAT had elevated HDL levels. The ABCA1 mRNA level in SAT was decreased in smokers (p = 0.001). There was a negative correlation between the PPARG mRNA level in SAT with body mass index and waist circumference in the general sample (β = –0.602, p = 0.003 and β = –0.642, p = 0.001, respectively, after age adjustment). A decrease of the PPARG mRNA SAT/VAT ratio was associated with elevated plasma insulin level and the insulin resistance index HOMA-IR (β = –0.819, p = 0.004 and β = –1.053, p = 0.008, respectively, after age adjustment). Thus, the study has shown that the ratio of ABCA1, ABCG1, and PPARG genes expression in different types of adipose tissue (SAT/VAT) could be a significant factor that predicts the development of atherogenic dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, and insulin resistance in obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tchernof A., Despres J.P. 2013. Pathophysiology of human visceral obesity: An update. Physiol. Rev. 93 (1), 359–404.
Despres J.P., Lemieux I. 2006. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature. 444 (7121), 881–887.
Engin A. 2017. The pathogenesis of obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 960, 221–245.
Yu B.L., Zhao S.P., Hu J.R. 2010. Cholesterol imbalance in adipocytes: A possible mechanism of adipocytes dysfunction in obesity. Obes. Rev. 11, 560–567.
Le Lay S., Ferre P., Dugail I. 2004. Adipocyte cholesterol balance in obesity. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 32, 103–106.
Aguilar D., Luz Fernandez M. 2014. Hypercholesterolemia induces adipose dysfunction in conditions of obesity and nonobesity. Adv. Nutr. 5 (5), 497–502.
la Rose A.M, Bazioti V., Westerterp M. 2018. Adipocyte membrane cholesterol regulates obesity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 38, 687–689.
Chung S., Sawyer J.K., Gebre A.K., Maeda N., Parks J.S. 2011. Adipose tissue ATP binding cassette transporter A1 contributes to high-density lipoprotein biogenesis in vivo. Circulation. 124, 1663–1672.
Frisdal E., Le Lay S., Hooton H., Poupel L., Olivier M., Alili R., Plengpanich W., Villard E.F., Gilibert S., Lhomme M., Superville A., Miftah-Alkhair L., Chapman M.J., Dallinga-Thie, Venteclef N., et al. 2015. Adipocyte ATP-binding cassette G1 promotes triglyceride storage, fat mass growth, and human obesity. Diabetes. 64 (3), 840–855.
Demina E.P., Miroshnikova V.V., Shvartsman A.L. 2016. Role of the ABC transporters A1 and G1, key reverse cholesterol transport proteins, in atherosclerosis. Mol. Biol. (Moscow). 50 (2), 193–199.
Cuffe H., Liu M., Key C.C., Boudyguina E., Sawyer J.K., Weckerle A., Bashore A., Fried S.K., Chung S., Parks J.S. 2018. Targeted deletion of adipocyte ABCA1 (ATP-binding cassette transporter A1) impairs diet-induced obesity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 38 (4), 733–743.
de Haan W., Bhattacharjee A., Ruddle P., Kang M.H., Hayden M.R. 2014. ABCA1 in adipocytes regulates adipose tissue lipid content, glucose tolerance, and insulin sensitivity. J. Lipid Res. 55 (3), 516–523.
Murphy A.J., Yvan-Charvet L. 2015. Adipose modulation of ABCG1 uncovers an intimate link between sphingomyelin and triglyceride storage. Diabetes. 64, 689–692.
Hardy L.M., Frisdal E., Le Goff W. 2017. Critical role of the human ATP-binding cassette G1 transporter in cardiometabolic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18 (9), 1892.
Kim K., Boo K., Yu Y.S., Oh S.K., Kim H., Jeon Y., Bhin J., Hwang D., Kim K.I., Lee J.S., Im S.S., Yoon S.G., Kim I.Y., Seong J.K., et al. 2017. RORα controls hepatic lipid homeostasis via negative regulation of PPARγ transcriptional network. Nat. Commun. 8, 162.
Laurencikiene J., Rydén M. 2012. Liver X receptors and fat cell metabolism. Int. J. Obesity. 36, 1494–1502.
Grygiel-Górniak B. 2014. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: Nutritional and clinical implications. Nutr. J. 14, 13–17.
Xu P., Zhai Y., Wang J. 2018. The role of PPAR and its cross-talk with CAR and LXR in obesity and atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (4), 1260.
Kidani Y., Bensinger S.J. 2012. LXR and PPAR as integrators of lipid homeostasis and immunity. Immunol. Rev. 249 (1), 72–83.
Jetten A.M., Kang H.S, Takeda Y. 2013. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptors α and γ: key regulators of lipid/glucose metabolism, inflammation, and insulin sensitivity. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 4, 1.
Matsuoka H., Tokunaga R., Katayama M., Hosoda Y., Miya K., Sumi K., Ohishi A., Kamishikiryo J., Shima A., Michihara A. 2020. Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor α reduces lipid droplets by upregulating neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 in macrophages. BMC Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 32.
Miroshnikova V.V., Panteleeva A.A., Bazhenova E.A., Demina E.P., Usenko T.S., Nikolaev M.A., Seme-nova I.A., Neimark A.E., Khe Chzh., Belyaeva O.D., Berkovich O.A., Baranova E.I., Pchelina S.N. 2016. Regulation of ABCA1 and ABCG1 transporter gene expression in the intraabdominal adipose tissue. Biomed. Khim. 62 (3), 283–289.
Porter S.A., Massaro J.M., Hoffmann U., Vasan R.S., O’Donnel C.J. 2009. Abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue: A protective fat depot. Diabetes Care. 32 (6), 1068–1075.
Narumia H., Yoshidab K., Hashimotoc N., Umeharab I., Funabashia N., Yoshidab S., Komuroa I. 2009. Increased subcutaneous fat accumulation has a protective role against subclinical atherosclerosis in asymptomatic subjects undergoing general health screening. Internat. J. Cardiol. 135 (2), 150–155.
Ladeiras-Lopes R., Sampaio F., Bettencourt N., Fontes-Carvalho R., Ferreira N., Leite-Moreira A., Gama V. 2017. The ratio between visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat assessed by computed tomography is an independent predictor of mortality and cardiac events. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 70 (5), 331–337.
Oh Y.H., Moon J.H., Kim H.J., Kong M.H. 2017. Visceral-to-subcutaneous fat ratio as a predictor of the multiple metabolic risk factors for subjects with normal waist circumference in Korea. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 10, 505–511.
Alberti K.G., Eckel R.H., Grundy S.M., Zimmet P.Z., Cleeman J.I., Donato K.A., Fruchart J.C., James W.P., Loria C.M., Smith S.C. International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; Hational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; International Association for the Study of Obesity. 2009. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 120 (16), 1640–1645.
Rotar’ O.P., Libis R.A., Isaeva E.N., Erina A.M., Shavshin D.A., Moguchaya E.V., Kolesova E.P., Boyarinova M.A., Moroshkina N.V., Yakovleva O.I., Solntsev V.N., Konradi A.O., Shlyakhto E.V. 2012. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in different cities of the Russian Federation. Kardiol. Zh. 2, 55–62.
Mogilenko D.A., Shavva V.S., Dizhe E.B., Orlov S.V., Perevozchikov A.P. 2010. PPARγ activates ABCA1 gene transcription but reduces the level of ABCA1 protein in HepG2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 402, 477–482.
Brovin D.L., Dracheva K.V., Panteleeva A.A., Belyaeva O.D., Bazhenova E.A., Karonova T.L., Kolodina D.A., Polyakova E.A., Volkova A.R., Kozlova S.N., Berkovich O.A., Pchelina S.N., Baranova E.I. 2019. Adiponectin gene (ADIPOQ) variants rs2241766 and rs266729: Association with total and high-molecular serum adiponectin in women with abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Med. Genet. 18 (1), 25–34.
Mancuso P., Bouchard B. 2019. The impact of aging on adipose function and adipokine synthesis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 11 (10), 137.
Choromanska B., Mysliwiec P., Hady H.R., Dadan J., Mysliwiec H., Bonda T., Chabowski A., Miklosz A. 2019. The implication of adipocyte ATP-binding cassette A1 and G1 transporters in metabolic complications of obesity. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 70 (1), 143–152.
Vincent V., Thakkar H., Aggarwal S., Mridha AS., Ramakrishnan L., Singh A. 2019. ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) expression in adipose tissue and its modulation with insulin resistance in obesity diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity. Targets Therapy. 12, 275–284.
Song W., Wang W., Dou L.Y., Wang Y., Xu Y., Chen L.F., Yan X.W. 2015. The implication of cigarette smoking and cessation on macrophage cholesterol efflux in coronary artery disease patients. J. Lipid Res. 56 (3), 682–691.
Tavoosi Z., Moradi-Sardareh H., Saidijam M., Yadegarazari R., Borzuei S., Soltanian A., Goodarzi M.T. 2015. Cholesterol transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1 gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with metabolic syndrome. Cholesterol. 2015, 682904.
Akinyemiju T., Do A.N., Patki A., Aslibekyan S., Zhi D., Hidalgo B., Tiwari H.K., Absher D., Geng X., Arnett D.K., Irvin M.R. 2018. Epigenome-wide association study of metabolic syndrome in African–American adults. Clin. Epigenet. 10, 49.
Miroshnikova V.V., Demina E.P., Maiorov N.V., Davydenko V.V., Kur’yanov P.S., Vavilov V.N., Vinogradov V.G., Denisenko A.D., Shvartsman A.L. 2014. The expression of ABCG1 transporter gene in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with atherosclerosis. Cell Tissue Biol. 8 (4), 337–343.
Borja M.S., Hammerson B., Tang C., Savinova O.V., Shearer G.C., Oda M.N. 2017. Apolipoprotein A-I exchange is impaired in metabolic syndrome patients asymptomatic for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. PLoS One. 12 (8), e0182217. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182217
Ma X., Wang D., Zhao W., Xu L. 2018. Deciphering the roles of PPAR γ in adipocytes via dynamic change of transcription complex. Front. Endocrinol. 9, 473.
Leyvraz C., Verdumo C., Suter M., Paroz A., Calmes J.-M., Marques-Vidal P.M., Giusti V. 2012. Changes in gene expression profile in human subcutaneous adipose tissue during significant weight loss. Obes. Facts. 5, 440–445.
Dubois S.G., Heilbronn L.K., Smith S.R., Albu J.B., Kelley D.E., Ravussin E. 2006. Decreased expression of adipogenic genes in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes. Obesity. 14, 1543–1552.
Giusti V., Verdumo C., Suter M., Gaillard R.C., Burckhardt P., Pralong F. 2003. Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma2 in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese women. Diabetes. 52, 1673–1676.
Hammes T.O., Costa Cdos S., Rohden F., Margis R., de Almeida J.C., Padoin A.V., Mottin C.C., Gua-ragna R.M. 2012. Parallel down-regulation of FOXO1, PPARγ and adiponectin mRNA expression in visceral adipose tissue of class III obese individuals. Obes. Facts. 5 (3), 452–459.
Laplante M., Festuccia W.T., Soucy G., Gelinas Y., Lalonde J., Berger J.P., Deshaies Y. 2006. Mechanisms of the depot specificity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor action on adipose tissue metabolism. Diabetes. 55 (10), 2771–2778.
Sugden M.C., Holness M.J. 2008. Role of nuclear receptors in the modulation of insulin secretion in lipid-induced insulin resistance. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36(5), 891–900.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the team from the Department of General Surgery with the Clinic and the Clinic of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Pavlov First St. Petersburg State Medical University for their assistance in preparation of biomaterial.
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project No. а 20-015-00502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the ethics committee of the Pavlov First St. Petersburg State Medical University. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Additional information
Translated by M. Novikova
Abbreviations: VAT, visceral adipose tissue; HDL, high density lipoproteins; LDL, low density lipoproteins; MS, metabolic syndrome; RCT, reverse cholesterol transport; SAT, subcutaneous adipose tissue; CL, cholesterol; HOMA-IR, insulin resistance index.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panteleeva, A.A., Razgildina, N.D., Brovin, D.L. et al. The Expression of Genes Encoding ABCA1 and ABCG1 Transporters and PPARγ, LXRβ, and RORα Transcriptional Factors in Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Women with Metabolic Syndrome. Mol Biol 55, 56–65 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321010131
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321010131