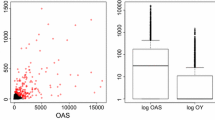
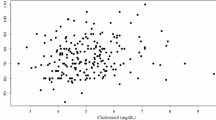
Abstract
Several methods have been devised to mitigate the effects of outlier values on survey estimates. If outliers are a concern for estimation of population quantities, it is even more necessary to pay attention to them in a small area estimation (SAE) context, where sample size is usually very small and the estimation in often model based. In this paper we set two goals: The first is to review recent developments in outlier robust SAE. In particular, we focus on the use of partial bias corrections when outlier robust fitted values under a working model generate biased predictions from sample data containing representative outliers. Then we propose an outlier robust bootstrap MSE estimator for M-quantile based small area predictors which considers a bounded-block-bootstrap approach. We illustrate these methods through model based and design based simulations and in the context of a particular survey data set that has many of the outlier characteristics that are observed in business surveys.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battese GE, Harter RM, Fuller WA (1988) An error-components model for prediction of county crop areas using survey and satellite data. J Am Stat Assoc 83(401):28–36
Booth JG, Hobert JP (1998) Standard errors of prediction in generalized linear mixed models. J Am Stat Assoc 93(441):262–272
Breckling J, Chambers R (1988) M-quantiles. Biometrika 75(4):761–771
Chambers RL (1986) Outlier robust finite population estimation. J Am Stat Assoc 81(396):1063–1069
Chambers R, Chandra H (2013) A random effect block bootstrap for clustered data. J Comput Graph Stat 22(2):452–470
Chambers R, Tzavidis N (2006) M-quantile models for small area estimation. Biometrika 93(2):255–268
Chambers R, Chandra H, Tzavidis N (2011) On bias-robust mean squared error estimation for pseudo-linear small area estimators. Surv Methodol 37:153–170
Chambers R, Chandra H, Salvati N, Tzavidis N (2014) Outlier robust small area estimation. J R Stat Soc: Ser B (Stat Methodol) 76(1):47–69
Davison AC, Hinkley DV et al (1997) Bootstrap methods and their application, vol 1. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Efron B (1992) Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife. In: Kotz S, Johnson NL (eds) Breakthroughs in statistics. Springer, New York, pp 569–593
Emerson J, Stoto M (1983) Understanding robust and exploratory data analysis. Wiley, New York
Fama EF, French KR (1988) Dividend yields and expected stock returns. J Financ Econ 22(1):3–25
Fellner WH (1986) Robust estimation of variance components. Technometrics 28(1):51–60
Giusti C, Pratesi M, Stefano M, Salvati N (2012) Robust small area estimation and oversampling in the estimation of poverty indicators. Surv Res Methods 6(3):155–163
Gonzalez ME, Ogus JL, Shapiro G, Tepping BJ (1975) Standards for discussion and presentation of errors in survey and census data. J Am Stat Assoc 70(351b):5–23
González-Manteiga W, Lombardía MJ, Molina I, Morales D, Santamaría L (2007) Estimation of the mean squared error of predictors of small area linear parameters under a logistic mixed model. Comput Stat Data Anal 51(5):2720–2733
Hall P, Maiti T (2006) On parametric bootstrap methods for small area prediction. J R Stat Soc: Ser B (Stat Methodol) 68(2):221–238
He X (1997) Quantile curves without crossing. Am Stat 51(2):186–192
Jiongo VD, Haziza D, Duchesne P (2013) Controlling the bias of robust small-area estimators. Biometrika 100(4):843–858
Koenker R, Bassett G Jr (1978) Regression quantiles. Econom: J Econom Soc 46:33–50
Newey WK, Powell JL (1987) Asymmetric least squares estimation and testing. Econom: J Econom Soc 55:819–847
Oltean E (2016) Modelling income, wealth, and expenditure data by use of econophysics. Ph.D. thesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:160308383
Prasad NN, Rao JN (1990) The estimation of the mean squared error of small-area estimators. J Am Stat Assoc 85(409):163–171
Pratesi M, Ranalli MG, Salvati N (2009) Nonparametric M-quantile regression using penalised splines. J Nonparametr Stat 21(3):287–304
Rao J, Molina I (2015) Small area estimation. Wiley, New York
Salvati N, Tzavidis N, Pratesi M, Chambers R (2012) Small area estimation via M-quantile geographically weighted regression. Test 21(1):1–28
Schoch T (2014) rsae: robust small area estimation. R package version 0.1-5
Schoch T (2012) Robust unit-level small area estimation: a fast algorithm for large data sets. Austrian J Stat 41(4):243–265
Sinha SK, Rao J (2009) Robust small area estimation. Can J Stat 37(3):381–399
Street JO, Carroll RJ, Ruppert D (1988) A note on computing robust regression estimates via iteratively reweighted least squares. Am Stat 42(2):152–154
Tibshirani RJ, Efron B (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. Monogr Stat Appl Probab 57:1–436
Tzavidis N, Marchetti S, Chambers R (2010) Robust estimation of small area means and quantiles. Aust N Z J Stat 52:167–186
Welsh AH, Ronchetti E (1998) Bias-calibrated estimation from sample surveys containing outliers. J R Stat Soc: Ser B (Stat Methodol) 60(2):413–428
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by European H2020 InGRID- 2 European Project (Grant No. 730998) and Università degli Studi di Pisa (IT) (Grant No. PRA 2018-2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertarelli, G., Chambers, R. & Salvati, N. Outlier robust small domain estimation via bias correction and robust bootstrapping. Stat Methods Appl 30, 331–357 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-020-00514-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260-020-00514-w