Abstract
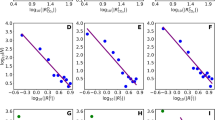
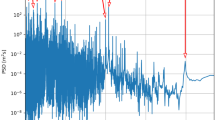
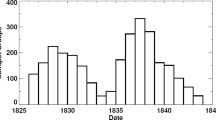
The solar cycle represents the Sun’s periodically changing magnetic state, which is potentially subject to global magnetic anomalies emerging on it. What the characteristics are of the Sun’s large-scale magnetic field playing roles in these anomalies is a key to clarifying how the Sun deviates from its normal magnetic state. This article reports aggregation characteristics of the large-scale magnetic field associated with a global magnetic anomaly that emerged when the Sun went through one of the longest solar cycles in two hundred years. The characteristics were identified by extracting cluster feature values of solar surface magnetic fields via a population ecological method from synoptic maps, obtained by the longest homogeneous series of magnetic field observations for the past several decades. We found that the anomaly was due to the uneven clustering of positive and negative surface magnetic fields that occurred during the solar minimum leading to the last extended solar cycle. Our findings may provide new insight into magnetic field characteristics peculiar to a solar minimum with an extended cycle length.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler, M.D., Newkirk, G.: 1969, Magnetic fields and the structure of the solar corona. I: methods of calculating coronal fields. Solar Phys. 9, 131.
Bakus, G.: 2007, Quantitative Analysis of Marine Biological Communities: Field Biology and Environment, Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken. Wiley.
Borrero, J.M., Ichimoto, K.: 2011, Magnetic structure of sunspots. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 8, 4.
Clette, F., Svalgaard, L., Vaquero, J.M., Cliver, E.W.: 2014, Revisiting the sunspot number. A 400-year perspective on the solar cycle. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 35.
Clyne, J., Mininni, P., Norton, A., Rast, M.: 2007, Interactive desktop analysis of high resolution simulations: application to turbulent plume dynamics and current sheet formation. New J. Phys. 9, 301.
Delaboudinire, J., Artzner, G.E., Brunaud, J., Gabriel, A.H., Hochedez, J.F., Millier, F., Song, X.Y., Au, B., Dere, K.P., Howard, R., Kreplin, R., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., Defise, J.M., Jamar, C., Rochus, P., Chauvineau, J.P., Marioge, J.P., Catura, R.C., Lemen, J.R., Shing, L., Stern, R.A., Gurman, J.B., Neupert, W.M., Maucherat, A., Clette, F., Cugnon, P., Van Dessel, E.L.: 1995, EIT: Extreme-ultraviolet Imaging Telescope for the SOHO mission. Solar Phys. 162, 291.
Duvall, T.L. Jr., Wilcox, J.M., Svalgaard, L., Scherrer, P.H., McIntosh, P.S.: 1977, Comparison of \(\text{H}\alpha \) synoptic charts with the large-scale solar magnetic field as observed at Stanford. Solar Phys. 55, 63.
Fan, Y.: 2001, The emergence of a twisted \(\Omega \)-tube into the solar atmosphere. Astrophys. J. Lett. 554, 111.
Hale, G.E.: 1924, Sun-spots as magnets and the periodic reversal of their polarity. Nature 113, 105.
Hathaway, D.H.: 2015, The solar cycle. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 12, 1.
Hoeksema, T., Scherrer, P.: 1986, An atlas of photospheric magnetic field observations and computed coronal magnetic fields: 1976–1985. Solar Phys. 105, 205.
Imada, S., Fujiyama, M.: 2018, Effect of magnetic field strength on solar differential rotation and meridional circulation. Astrophys. J. 864, L5.
Jeong, H., Chae, J.: 2007, Magnetic helicity injection in active regions. Astrophys. J. 671, 1022.
Knaack, R., Stenflo, J.O., Berdyugina, S.V.: 2005, Evolution and rotation of large-scale photospheric magnetic fields of the Sun during cycles 21–23. Periodicities, North–South asymmetries and r-mode signatures. Astron. Astrophys. 438, 1067.
Lites, B.W., Low, B.C., Martines Pillet, V., Seagraves, P., Skumanich, A., Frank, Z.A., Shine, R.A., Tsuneta, S.: 1995, The possible ascent of a closed magnetic system through the photosphere. Astrophys. J. 446, 877L.
Low, B.C.: 1996, Solar activity and the corona. Solar Phys. 167, 217.
Magara, T.: 2009, Characteristic development of magnetic shear in a flare-producing sunspot obtained from vector magnetic field measurements by Hinode. Astrophys. J. 702, 386.
Magara, T.: 2017, An inversion method for deriving physical properties of a subsurface magnetic field from surface magnetic field evolution I. Application to simulated data. J. Korean Astron. Soc. 50, 179.
Maunder, E.W.: 1922, The Sun and Sun-spots, 1820–1920. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 82, 534.
Morisita, M.: 1959, Measuring of the dispersion and analysis of distribution patterns. Mem. Fac. Sci. Kyushu Univ., Ser. E 2, 215.
Muoz-Jaramillo, A., Vaquero, J.M.: 2019, Visualization of the challenges and limitations of the long-term sunspot number record. Nat. Astron. 3, 205.
Nakamizo, A., Tanaka, T., Kubo, Y., Kamei, S., Shimazu, H., Shinagawa, H.: 2009, Development of the 3-D MHD model of the solar corona-solar wind combining system. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A07109.
Reeves, E.M., Huber, M.C.E., Timothy, J.G.: 1977, Extreme UV spectroheliometer on the Apollo Telescope Mount. Appl. Opt. 16, 837.
Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1969, A model of interplanetary and coronal magnetic fields. Solar Phys. 6, 442.
Scherrer, P.H., Wilcox, J.M., Svalgaard, L., Duvall, T.L., Dittmer, P.H., Gustafson, E.K.: 1977, The mean magnetic field of the Sun: observations at Stanford. Solar Phys. 54, 353.
Scherrer, P.H., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Hoeksema, J.T., Kosovichev, A.G., Schou, J., Rosenberg, W., Springer, L., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A., Wolfson, C.J., Zayer, I. (MDI Engineering Team): 1995, The solar oscillations investigation – Michelson Doppler Imager. Solar Phys. 162, 129.
Schwabe, M.: 1844, Sonnenbeobachtungen im Jahre 1843. Von Herrn Hofrath Schwabe in Dessau. Astron. Nachr. 21, 233.
Siu-Tapia, A., Lagg, A., van Noort, M., Rempel, M., Solanki, S.: 2019, Superstrong photospheric magnetic fields in sunspot penumbrae. Astron. Astrophys. 631, 99.
Snyder, J.P.: 1987, Map projections – a working manual. US Government Printing Office, 1395.
Sokoloff, D., Nesme-Ribes, E.: 1994, The Maunder minimum: a mixed-parity dynamo mode? Astron. Astrophys. 288, 293.
Solanki, S.K., Schüssler, M., Fligge, M.: 2000, Evolution of the Sun’s large-scale magnetic field since the Maunder minimum. Nature 408, 445.
Stix, M.: 1991, The Sun: An Introduction, Astronomy and Astrophysics Library, Springer, Berlin, 301.
Tanaka, K.: 1991, Studies on a very flare-active \(\delta \) group: peculiar \(\delta\) spot evolution and inferred subsurface magnetic rope structure. Solar Phys. 136, 13.
Virtanen, I., Mursula, K.: 2017, Photospheric and coronal magnetic fields in six magnetographs. II. Harmonic scaling of field intensities. Astron. Astrophys. 604, 7.
Zwaan, C.: 1985, The emergence of magnetic flux. Solar Phys. 100, 397.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge detailed comments and suggestions by G. Choe and S. Solanki which were very helpful for improving the manuscript. We also appreciate the reviewer’s useful comments. We used the synoptic charts of the Sun’s large-scale magnetic field provided by Wilcox Solar Observatory, Stanford University (http://wso.stanford.edu). The EUV and MDI data used here are produced by the SOHO/EIT and SOHO/MDI Consortiums; SOHO is a joint ESA-NASA program. Figure 4a was made using VAPOR (Clyne et al., 2007). This work was financially supported by the Core Research Program (NRF-2017R1A2B4002383) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MIST), as well as by the BK21 plus program through the NRF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magara, T., An, J., Lee, H. et al. Aggregation Characteristics of the Sun’s Large-Scale Magnetic Field Associated with a Global Magnetic Anomaly in the Last Extended Solar Cycle. Sol Phys 296, 41 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01782-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01782-9