Abstract
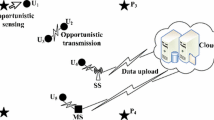
Wireless sensor networks are widely used today in environmental and home applications. Among these applications are some that require a bounded end-to-end delay since a delay may render some detected information useless or even causes damages in some critical applications. In this context we study the effect of anycast in the minimization of the end-to-end delay and we validate the study by simulations. We also propose a mobile base station technique with limited residence time to avoid the loss of time in data collection. We validate the work with a formulation in linear programming and numerical experiences.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ametller, J., Robles, S., & Borrell, J. (2003). Agent migration over FIPA ACL messages. In MATA: International workshop on mobile agents for telecommunication applications.
Cheick Tidjane, K. O. N. E. (2011). Design of a large dimension sensor network architectue, thesis report. France: Henry Poincaré University.
Akyildiz, I. F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., & Cayirci, E. (2002). Wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 393–422.
Mouradian, A. (2013). Proposal and formal verification of real-time communication protocols for wireless sensor networks. Thesis report, Lyon.
Sugihara, R., & Gupta, R. K. (2008). Improving the data delivery latency in sensor networks with controlled mobility. In International conference on distributed computing in sensor systems, DCOSS 2008.
Yan, Y. S., & Xia, Y. (2010). Maximising the lifetime of wireless sensor networks with mobile sink in delay-tolerant applications. University of Florida, Computer and Information Science and Engineering Department.
Aloui, I. Mobile agent approach for sensor networks. Thesis Report, Mohamed Khedher University, Algeria.
Kim, J., Lin, X., Shroff, N. B., & Sinha, P. (2010). Minimizing delay and maximizing lifetime for wireless sensor networks with anycast. In IEEE/ACM transactions on networking (vol. 18, issue 2).
Lpsolve Reference Guide. [Online]: http://lpsolve.sourceforge.net/5.5/.
ANR Project Persetpeur. (2015). Cupcarbon simulator, [Online] http://www.cupcarbon.com.
Gray, R. S., Cybenko, G., Kotz, D., Peterson, R. A., & Rus, D. (2001). D’Agents: Applications and performance of a mobile-agent system.
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my special thanks of gratitude to Dr. Zoubeir Mlika, a telecommunications researcher in department of computer sciences, university of Quebec at Montreal for his contribution and the revision of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Achour, M. Minimizing End-To-End Delay with Anycast and Controlled Mobility in Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 118, 2621–2630 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08146-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08146-3