Abstract—
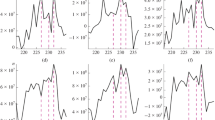
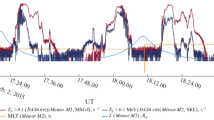
Energetic electron precipitation (EEP) into the atmosphere is one of the mechanisms of depleting the Earth’s outer radiation belt. Precipitating electrons generate bremsstrahlung that penetrates the stratosphere and is recorded by detectors on balloons. However, these observations can be carried out only when the balloon is located at altitudes higher than ~20 km. The near-Earth POES satellites are constantly recording the fluxes of precipitating electrons in the loss cone, but they move too quickly in the space. In this paper, EEPs are compared on the basis of observations in the stratosphere and on satellites during 2003 and estimates of a number of EEP events at Apatity are obtained, assuming that the radiosonde was continuously located at an altitude higher than 26 km.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Stozhkov, Yu.I., Svirzhevsky, N.S., Bazilevskaya, G.A., Kvashnin, A.N., Makhmutov, V.S., and Svirzhevskaya, A.K., Long-term (50 years) measurements of cosmic ray fluxes in the atmosphere, Adv. Space Res., vol. 44, no. 10, pp. 1124–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2008.10.038
Millan, R.M. and Thorne, R.M., Review of radiation belt relativistic electron losses, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2007, vol. 69, no. 3, pp. 362–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2006.06.019
Shprits, Y.Y., Thorne, R.M., Friedel, R., et al., Outward radial diffusion driven by losses at magnetopause, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 2006, vol. 111, no. 11, A11214. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JA011657
Turner, D.L., Shprits, Y., Hartinger, M., and Angelopoulos, V., Explaining sudden losses of outer radiation belt electrons during geomagnetic storms, Nature Phys., 2012, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 208–212. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2185
Green, J.C., Likar, J., and Shprits, Y., Impact of space weather on the satellite industry, Space Weather, 2017, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 804–818. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017SW001646
Inan, U.S., Bell, T.F., Bortnik, J., and Albert, J.M., Controlled precipitation of radiation belt electrons, J. Geophys. Res., 2003, vol. 108, no. A5, p. 1186. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JA009580
Rodger, C.J., Clilverd, M.A., Ulich, Th., et al., The atmospheric implications of radiation belt remediation, Ann. Geophys., 2006, vol. 24, pp. 2025–2041.
https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/d/dsx#launch
Jaynes, A.N., Baker, D.N., and Singer, H.J., et al., Source and seed populations for relativistic electrons: Their roles in radiation belt changes, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 2015, vol. 120, no. 9, pp. 7240–7254. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JA021234
Sinnhuber, M., Nieder, H., and Wieters, N., Energetic particle precipitation and the chemistry of the mesosphere/lower thermosphere, Surv. Geophys., 2012, vol. 33, pp. 1281–1334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-012-9201-3
Andersson, M.E., Verronen, P.T., Rodger, C.J., et al., Missing driver in the Sun–Earth connection from energetic electron precipitation impacts mesospheric ozone, Nature Commun., 2014, vol. 5, no. 10, 5197. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6197
Krivolutsky, A.A. and Repnev, A.I., Vozdeistvie kosmicheskikh faktorov na ozonosferu Zemli (Influence of Cosmic Factors on the Earth’s Ozonosphere), Moscow: GEOS, 2009.
Krivolutsky, A.A. and Repnev, A.I., Impact of space energetic particles on the Earth’s atmosphere (a review), Geomagn Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 2012, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 685–716.
Rozanov, E., Calisto, M., Egorova, T., Peter, T., and Schmutz, W., Influence of the precipitating energetic particles on atmospheric chemistry and climate, Surv. Geophys., 2012, vol. 33, pp. 483–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-012-9192-0
Seppälä, A., Clilverd, M.A., Beharrell, M.J., et al., Substorm-induced energetic electron precipitation: Impact on atmospheric chemistry, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2015, no. 19, p. 8172–8176. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL065523
Andersson, M.E., Verronen, P.T., Marsh, D.R., et al., Polar ozone response to energetic particle precipitation over decadal time scales: The role of medium-energy electrons, J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 2018, vol. 123, no. 1, pp. 607–622. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027605
Matthes, K., Funke, B., Andersson, M.E., et al., Solar forcing for CMIP6 (v3.2), Geosci. Model Dev., 2017, vol. 10, pp. 2247–2302. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-10-2247-2017
Van de Kamp, M., Seppälä, A., Clilverd, M.A., et al., A model providing long-term data sets of energetic electron precipitation during geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 2016, vol. 121, no. 20, pp. 12520–12540. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD024212
Van de Kamp, M., Rodger, C.J., Seppälä, A., et al., An updated model providing long-term datasets of energetic electron precipitation, including zonal dependence, J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 2018, vol. 123, pp. 9891–9915. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JD028253
Mironova, I.A., Artamonov, A.A., Bazilevskaya, G.A., et al., Ionization of the polar atmosphere by energetic electron precipitation retrieved from balloon measurements, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2019, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 990–996. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL079421
Charakhch'yan, A.N., Investigation of stratosphere cosmic ray intensity fluctuations induced by processes on the Sun, Phys.-Usp., 1964, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 358–374.
Makhmutov, V.S., Bazilevskaya, G.A., Stozhkov, Yu.I., et al., Catalogue of electron precipitation events as observed in the long-duration cosmic ray balloon experiment, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2016, vol. 149, pp. 258–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp. 2015.12.006
Bazilevskaya, G.A., Kalinin, M.S., Kvashnin, A.N., et al., Precipitation of energetic magnetospheric electrons and accompanying solar wind characteristics, Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 2017, vol. 57, no. 2, pp. 147–155. https://doi.org/10.7868/S001679401702002X
Bazilevskaya, G.A., Kalinin, M.S., Krainev, M.B., et al., Characteristics of the energetic electron precipitation and magnetospheric conditions in 1994, Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 2018, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 483–492. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016794018040028
Murphy, K.R., Watt, C.E.J., Mann, I.R., et al., The global statistical response of the outer radiation belt during geomagnetic storms, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2017, vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 3783–3792. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL076674
Millan, R.M., McCarthy, M.P., Sample, J.G., et al., The balloon array for RBSP relativistic electron losses (BARREL), Space Sci. Rev., 2013, vol. 179, nos. 1–4, pp. 503–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-013-9971-z
http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/stp/satellite/poes
Yahnin, A.G., Yahnina, T.A., Semenova, N.V., and Gvozdevsky, B.B., Relativistic electron precipitation as seen by NOOAA POES, in Proc. XXXVII Annual Seminar, Apatity, 2014, pp. 46–50.
Yando, K., Millan, R.M., Green, J.C., and Evans, D.S., A Monte Carlo simulation of the NOAA POES medium energy proton and electron detector instrument, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A10231. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JA016671
Millan, R.M., the BARREL team, Understanding relativistic electron losses with BARREL, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2011, vol. 73, pp. 1425–1434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2011.01.006
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank our colleagues from NOAA who provided the POES satellite data via the Internet. G. Bazilevskaya and V. Makhmutov are grateful for stimulating discussions within the framework of the ISSI & ISSI-BJ International Team project “Relativistic Electron Precipitation and Its Atmospheric Effect” under I.A. Mironova’s leadership.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research and the German DFG Foundation, project no. 20-55-120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by Yu. Preobrazhensky
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bazilevskaya, G.A., Dyusembekova, A.S., Kalinin, M.S. et al. Comparison of the Results on Precipitation of High-Energy Electrons in the Stratosphere and on Satellites. Cosmic Res 59, 24–29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952521010020
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952521010020