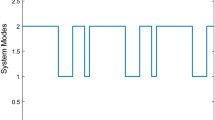
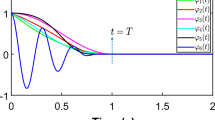
Abstract
When an isolated equilibrium of a nonlinear system is locally attractive, it might be difficult to estimate and then enlarge its Region of Attraction (RA). To solve this problem, this paper, by means of impulsive control, provides an effective method, i.e., state-dependent edge impulse (STDEI) combining with SOS programming and trajectory reversing with convex hull. Based on SOS programming and trajectory reversing, the initial estimation of RA is established. Then, by applying STDEI, we can design and then obtain the enlarged estimation of RA. Three numerical examples are provided to demonstrate the performance of the proposed approaches.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksandr Mikhailovich Lyapunov: The general problem of the stability of motion. Int. J. Control 55(3), 531–534 (1992)
Liu, Xiwei, Chen, Tianping: Synchronization of nonlinear coupled networks via aperiodically intermittent pinning control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 26(1), 113–126 (2014)
Zhou, Yinghua, Li, Chuandong, Wang, Hui: Stability analysis on state-dependent impulsive hopfield neural networks via fixed-time impulsive comparison system method. Neurocomputing 316, 20–29 (2018)
Zhang, Xianxiu, Li, Chuandong, Huang, Tingwen: Hybrid impulsive and switching hopfield neural networks with state-dependent impulses. Neural Netw. 93, 176–184 (2017)
Li, Liangliang, Wang, Xin, Li, Chuandong, Feng, Yuming: Exponential synchronizationlike criterion for state-dependent impulsive dynamical networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(4), 1025–1033 (2018)
Li, C., Wu, S., Feng, G.G., Liao, X.: Stabilizing effects of impulses in discrete-time delayed neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 22(2), 323–329 (2011)
Chu, Chia-Chi., Chiang, Hsiao-Dong.: Boundary properties of the bcu method for power system transient stability assessment. In Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pages 3453–3456. IEEE, 2010
Mazumder, Sudip K., Fuente, Eduardo Pilo de la.: Transient stability analysis of power system using polynomial lyapunov function based approach. In 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting| Conference & Exposition, pages 1–5. IEEE, 2014
Hsiao-Dong, C., Wu, F., Varaiya, P.: Foundations of direct methods for power system transient stability analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst 34(2), 160–173 (1987)
Han, Dongkun., El-Guindy, Ahmed., Althoff, Matthias.: Power systems transient stability analysis via optimal rational lyapunov functions. In 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), pages 1–5. IEEE, 2016
Yang, Xiaofan, Liao, Xiaofeng, Li, Chuandong, Tang, Yuan Yan: Local stability and attractive basin of cohen-grossberg neural networks. Nonlinear Anal.: Real World Appl. 10(5), 2834–2841 (2009)
Jin, Dequan, Huang, Zhili, Peng, Jigen: Approximation on attraction domain of cohen-grossberg neural networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 217(21), 8747–8753 (2011)
Tedrake, Russ, Manchester, Ian R., Tobenkin, Mark, Roberts, John W.: Lqr-trees: feedback motion planning via sums-of-squares verification. Int. J. Robot. Res. 29(8), 1038–1052 (2010)
Tobenkin, Mark M., Manchester, Ian R., Tedrake, Russ: Invariant funnels around trajectories using sum-of-squares programming. IFAC Proc. Vol. 44(1), 9218–9223 (2011)
Chesi, Graziano: Rational lyapunov functions for estimating and controlling the robust domain of attraction. Automatica 49(4), 1051–1057 (2013)
Pitarch, José Luis, Sala, Antonio, Arino, Carlos Vicente: Closed-form estimates of the domain of attraction for nonlinear systems via fuzzy-polynomial models. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44(4), 526–538 (2013)
Saleme, Ahmed, Tibken, Bernd, Warthenpfuhl, Sascha A., Selbach, Christian: Estimation of the domain of attraction for non-polynomial systems: a novel method. IFAC Proc. Vol. 44(1), 10976–10981 (2011)
Chesi, Graziano: Domain of Attraction: Analysis and Control via SOS Programming, vol. 415. Springer Science, Berlin (2011)
Amato, F., Ambrosino, R., De Tommasi, G., Merola, A.: Estimation of the domain of attraction for a class of hybrid systems. Nonlinear Anal.: Hybrid Syst. 5(3), 573–582 (2011)
Chesi, Graziano: Estimating the domain of attraction for non-polynomial systems via lmi optimizations. Automatica 45(6), 1536–1541 (2009)
Li, Chunji., Cao, Lili., Li, Ning., Chen, Xiangyong.: Estimating the domain of attraction of a class of sir epidemic model. In 2008 Chinese Control and Decision Conference, pages 5010–5013. IEEE, 2008
Topcu, Ufuk, Packard, Andrew, Seiler, Peter: Local stability analysis using simulations and sum-of-squares programming. Automatica 44(10), 2669–2675 (2008)
Chowdhury, Dhrubajit., Kant, Nilay., Mukherjee, Ranjan., Khalil, Hassan K.: Enlarging the region of attraction of equilibria of underactuated systems using sum of squares and impulse manifold method. In 2017 American Control Conference (ACC), pages 893–898. IEEE, 2017
Kant, Nilay, Mukherjee, Ranjan, Chowdhury, Dhrubajit, Khalil, Hassan K.: Estimation of the region of attraction of underactuated systems and its enlargement using impulsive inputs. IEEE Trans. Robot. 35(3), 618–632 (2019)
Margolis, S., Vogt, W.: Control engineering applications of vi zubov’s construction procedure for lyapunov functions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 8(2), 104–113 (1963)
Balint, St, Balint, A., Negru, V.: The optimal lyapunov function in diagonalizable case. An. Univ. Timisoara 24(1–2), 1–7 (1986)
Davison, E.J., Kurak, E.M.: A computational method for determining quadratic lyapunov functions for non-linear systems. Automatica 7(5), 627–636 (1971)
Johansson, Mikael: Piecewise quadratic estimates of domains of attraction for linear systems with saturation. IFAC Proc. Vol. 35(1), 187–192 (2002)
Gering, Stefan, Eciolaza, Luka, Adamy, Jürgen, Sugeno, Michio: A piecewise approximation approach to nonlinear systems: stability and region of attraction. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(6), 2231–2244 (2015)
Li, H.., Li, C., Ouyang, D., Nguang, S. K.: Impulsive stabilization of nonlinear time-delay system with input saturation via delay-dependent polytopic approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Syst. 1–12 (2020)
Bakhtiari, R., Yazdanpanah, MJ.: Designing a linear controller for polynomial systems with the largest domain of attraction via lmis. In 2005 International Conference on Control and Automation, volume 1, pages 449–453. IEEE, 2005
Chesi, Graziano: Computing output feedback controllers to enlarge the domain of attraction in polynomial systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 49(10), 1846–1853 (2004)
Li, C., Feng, G., Huang, T.: On hybrid impulsive and switching neural networks. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern. Part B (Cybernetics) 38(6), 1549–1560 (2008)
Parrilo, Pablo A.: Structured semidefinite programs and semialgebraic geometry methods in robustness and optimization. PhD thesis, California Institute of Technology, 2000
Han, Dongkun., Panagou, Dimitra.: Chebyshev approximation and higher order derivatives of lyapunov functions for estimating the domain of attraction. In 2017 IEEE 56th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), pages 1181–1186. IEEE, 2017
Jarvis-Wloszek, Zachary., Feeley, Ryan ., Tan, Weehong., Sun, Kunpeng., Packard, Andrew.: Some controls applications of sum of squares programming. In 42nd IEEE international conference on decision and control (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37475), volume 5, pages 4676–4681. IEEE, 2003
Tan, Weehong, Packard, Andrew: Stability region analysis using polynomial and composite polynomial lyapunov functions and sum-of-squares programming. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 53(2), 565–571 (2008)
Genesio, R., Vicino, A.: New techniques for constructing asymptotic stability regions for nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst 31(6), 574–581 (1984)
Kant, Nilay., Chowdhury, Dhrubajit., Mukherjee, Ranjan ., Khalil, Hassan K.: An algorithm for enlarging the region of attraction using trajectory reversing. In 2017 American Control Conference (ACC), pages 4171–4176. IEEE, 2017
Eddy, William F.: A new convex hull algorithm for planar sets. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 3(4), 398–403 (1977)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Project (2018AAA0100101) , Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant (XDJK 2019B054) , and in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61873213, 61633011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
A Algorithm for STDEI method

B Results of SOS programming
In this paper, we use a linearization system to get candidate Lyapunov function. For system (18), setting \(Q=diag[1\ 1]\), then P can be obtained through solve \(A^{T}P+PA = Q\), where A is the jacobian matrix of system (18).
Then, applying the SOS programing, obtaining \(\gamma =1.0033,\)
Similar, for system (19), set \(Q=diag[1\ 1]\), by simple calculation, we obtain
For point (0, 0), \(\gamma =1.0004,\)
For point (6,-6), \(\gamma =1.0014,\) and
Similar, for system (21), by setting \(Q = diag[1\ 1\ 1]\), P can be obtained as follow
\(V=0.15073x^{2} + 0.037463xy - 0.037463xz + 0.28846y^{2} + 0.28846z^{2}\), and \(\gamma =0.2890.\)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Li, C., He, Z. et al. Estimating and enlarging the region of attraction of multi-equilibrium points system by state-dependent edge impulses. Nonlinear Dyn 103, 2421–2436 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06259-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06259-9