Abstract
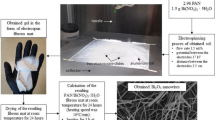
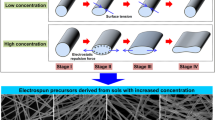
The nanostructured powder of multicomponent oxides, borides, and borates is widely used due to its high hardness, corrosion resistance, high melting point, insulating, and abrasive. In the present work, the effect of boron content on the morphology of electrospun multicomponent oxide, boride, and borate nanostructures in a quaternary Ti–Al–O–B system was investigated. Different molar ratios of B/(Ti + Al) (0.8, 1.6, and 2.4) were employed and evaluated. Imaging with the field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) and the transmission electron microscope (TEM) revealed that after one hour of thermal treatment at 1100 °C, the hybrid electrospun nanofibers (NFs) in the fibrous platform transformed into nanoparticles (NPs), nano-needles, and nano-whiskers at B/(Ti + Al) molar ratios of 0.8, 1.6, and 2.4, respectively. The binding energies were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), whereas the phase study was conducted via the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique. The results confirmed the formation of nanostructured ceramic powder platforms composed of multiple components, namely oxides (e.g., B-doped TiO2; Al2O3), borides (TiB, TiB2, Ti2B5, TiB12, and AlB2), and borates (TiBO3; Al18B4O33). Simultaneous thermal analysis (STA) of the Ti–Al–O–B mats indicated that the borides and borates formed consecutively at temperatures above 800 °C through reactions involving molten B2O3. We found that the obtained NPs were well arranged and sintered together throughout the fibers.

Highlights
-
Electrospinning method for fabrication of nanoparticles, nano-needles, and nano-whiskers
-
Oxides, borides, and borates in the quad system of Ti–Al–O–B were formed.
-
This study investigates comprehensively by XPS, TEM, EDS, XRD, STA, and FESEM techniques.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xin Y, Takeuchi Y, Hattori M, Shirai T (2019) Enhanced electrical conductivity of alumina/nano-carbon ceramic composite via iodine impregnation of gel-casted alumina body and reductive sintering. J Eur Ceram Soc 39(14):4440–4444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.06.002
Mazaheri Y, Meratian M, Emadi R, Najarian AR (2013) Comparison of microstructural and mechanical properties of Al–TiC, Al–B4C and Al–TiC–B4C composites prepared by casting techniques. Mat Sci Eng A Struct 560:278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.09.068
Wu C, Li Y (2020) AlN-induced reinforcement of nano-amorphous B–C–N compound for TiB2–B4C ceramic composite. J Alloy Compd 831(5):154074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154074
Yin T, Jiang B, Su Z, Huang Q (2018) Effects of mannitol on the synthesis of ultra-fine ZrB2 powders. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 85:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4514-9
Du J, Sanders AP, Jindal V, Chandran KSR (2016) Rapid in situ formation and densification of titanium boride (TiB) nano-ceramic via transient liquid phase in electric field activated sintering. Scr Mater 123:95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.06.010
Salahi E, Esfahani H, Mobasherpour I, Bijarchi MA, Taheri M (2014) Sintering behavior and mechanical properties of alumina/zirconia multilayers composite via nano-powder processing. Ceram Int 40:2717–2722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.10.051
Song HS, Zhang J, Lin J, Liu SJ, Luo JJ, Huang Y, Elssfah EM, Elsanousi A, Ding XX, Gao JM, Tang Chengcun (2007) Coating aluminum borate (Al18B4O33) nanowire webs with BN. J Phys Chem C 111:1136–1139. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp067393u
Lepakova OK, Raskolenko LG, Maksimov YUM (2000) Titanium borides prepared by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. J Inorg Mater 36(6):568–575. 1685/00/3606-0568525.00
Sarma B, Tikekar NM, Chandran KSRavi (2012) Kinetics of growth of superhard boride layers during solid state diffusion of boron into titanium Ceram Int 38:6795–6805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.05.077
Moscicki T, Psiuk R, Słomińska H, Levintant-Zayonts N, Garbiec D, Pisarek M, Bazarnik P, Nosewicz S, Chrzanowska-Giżyńsk J (2020) Influence of overstoichiometric boron and titanium addition on the properties of RF magnetron sputtered tungsten borides. Surf Coat Technol 390:125689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125689
Mishra SK, Gokuul V, Paswan S (2014) Alumina-titanium diboride in situ composite by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) dynamic compaction: effect of compaction pressure during synthesis. Int J Refract Met H 43:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.10.018
Ebrahimi A, Esfahani H, Fattah-alhosseini A, Imantalab O (2019) Electrochemical properties of commercially pure Ti with TiB/TiB2 coatings in Hanks balanced salt solution. J Mater Eng Perform 28:1456–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-03930-6
Masanta M, Shariff SM, Choudhury ARoy (2016) Microstructure and properties of TiB2–TiC–Al2O3 coating prepared by laser assisted SHS and subsequent cladding with micro-/nano-TiO2 as precursor constituent. Mater Des 90:307–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.135
Morsi K, Patel VV (2007) Processing and properties of titanium–titanium boride (TiBw) matrix composites—a review. J Mater Sci 42:2037–2047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0776-2
Jiang Z, Rhine WE (1993) Preparation of titanium diboride from the borothermic reduction of TiO2, TiOx(OH)y, Ti(O-n-Bu)4-derived polymers. J Eur Ceram Soc 12:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/0955-2219(93)90011-F
Hernández MF, Suárez G, Cipollone M, Conconi MS, Aglietti EF, Rendtorff NM (2017) Formation, microstructure and properties of aluminum borate ceramics obtained from alumina and boric acid. Ceram Int 43(2):2188–2195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.11.002
Hernández MF, Suárez G, Cipollone M, Aglietti EF, Rendtorff NM (2017) Mechanical behavior and microstructure of porous needle: aluminum borate (Al18B4O33) and Al2O3-Al18B4O33 composites. Ceram Int 43:11759–11765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.06.011
Esfahani H, Abdollahzadeh A, Dabir F, Samar MahsaRasouli (2020) Enhanced surface protection of in-738lc ni based alloy by metallic borides and aluminium borate coating via short time powder pack method. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 56(3):567–574. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205120030144
Wang Y, Feng J, Wang Z, Song X, Cao J (2016) Joining of Al2O3 by epitaxial growth of aluminum borate whiskers for high-temperature applications. Mater Lett 163:231–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.10.079
Guo D, Zhao Y, Ling C, Li J, Jin H (2018) Vacuum freeze-drying assisted preparation of spherical AlB2 powders with ultrafine microstructure. Ceram Int 44(6):6451–6455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.040
Cheng Ding J, Fei Zhang T, Moon Yun J, Ho Kim K, Wang QMin (2018) Effect of Cu addition on the microstructure and properties of TiB2 films deposited by a hybrid system combining high power impulse magnetron sputtering and pulsed dc magnetron sputtering. Surf Coat Technol 344:441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.03.026
Yang J, Wang Q, Wang T (2017) A novel synthesis route of titania–alumina composite aerogels with potassium titanate as the precursor. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83:527–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4433-9
Rebholz C, Leyland A, Schneider JM, Voevodin AA, Matthews A (1999) Structure, hardness and mechanical properties of magnetron sputtered titanium–aluminium boride films. Surf Coat Technol, 120– 121:412–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(99)00490-9
Nedfors N, Mráz S, Palisaitis J, Persson POÅ, Lind H, Kolozsvari S, Schneider JM, Rosen J (2019) Influence of the Al concentration in Ti-Al-B coatings on microstructure and mechanical properties using combinatorial sputtering from a segmented TiB2/AlB2 target. Surf Coat Technol 364:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.02.060
Ghugare AD, Dhanalakshmi R, Vinu R (2020) Preparation and characterization of nanoboron for slurry fuel applications. Adv Powder Technol 31:1851–1867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.02.018
Liang D, Xiao R, Liu J, Wang Y (2019) Ignition and heterogeneous combustion of aluminum boride and boron–aluminum blend. Aerosp Sci Technol 84:1081–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2018.11.046
Adil S, Murty BS (2019) Effect of milling on the oxidation kinetics of aluminium+boron mixture and nanocrystalline aluminium boride (AlB12). Thermochim Acta 678:178306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2019.178306
Buchilin NV, Stroganova EE, Mikhailenko NYU, Sarkisov PD, Paleari A (2013) Crystallization-controlled pore retention in calcium-phosphate glassceramics from powder sintering of CaO–P2O5–B2O3–Al2O3–TiO2–ZrO2 glass. J Non-Cryst Solids 373–374:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.04.037
Tauch D, Russel C (2007) Glass-ceramics in the system BaO/TiO2(ZrO2)/Al2O3/B2O3 and their thermal expansion. J Non-Cryst Solids 353:2109–2114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.03.016
Tautkus S, Ishikawa K, Ramanauskas R, Kareiva A (2020) Zinc and chromium co-doped calcium hydroxyapatite: sol-gel synthesis, characterization, behaviour in simulated body fluid and phase transformations. J Solid State Chem 284:121202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2020.121202
Biedunkiewicz A (2011) Manufacturing of ceramic nanomaterials in Ti–Si–C–N system by sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 59:448–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2237-2
Altaf AA, Ahmed M, Hamayun M, Kausar S, Waqar M, Badshah A (2020) Titania nano-fibers: a review on synthesis and utilities. Inorg Chim Acta 501:119268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2019.119268
Someswararao MV, Pradeep D, Dubey RS, Subbarao PSV (2019) Experimental investigation of electrospun titania nanofibers: an applied voltage influence. Mater Today Proc 18:384–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.315
Esfahani H, Jose R, Ramakrishna S (2017) Electrospun ceramic nanofiber mats today: synthesis, properties, and applications. Materials 10(11):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111238
Osali S, Esfahani H, Dabir F, Tajaslan P (2019) Structural and electro-optical properties of electrospun Cu-Doped ZnO thin films. Solid State Sci 98:106038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.106038
Prabhakaran MP, Zamani M, Felice B, Ramakrishna S (2015) Electrospraying technique for the fabrication of metronidazole contained PLGA particles and their release profile. Mat Sci Eng C Mater 56(1):66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.06.018
Dai H, Gong J, Kim H, Lee D (2002) A novel method for preparing ultra-fine alumina-borate oxide fibres via an electrospinning technique. Nanotechnology 13:674–677. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/13/5/327
Ozdemir M, Celik E, Cocen U (2013) Effect of viscosity on the production of alumina borate nanofibers via electrospinning. Mater Technol 47:735–738
Song X, Liu W, Xu S, Wang J, Liu B, Cai Q, Tang S, Ma Y (2018) Microstructure and elastic modulus of electrospun Al2O3-SiO2-B2O3 composite nanofibers with mullite-type structure prepared at elevated temperatures. J Eur Ceram Soc 38(1):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.08.007
Liu J, Blanpain B, Wollants P, XPS A (2008) Study of atmospheric plasma sprayed TiB2 coatings. Key Eng Mater 368-372:1347–1350. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.368-372.1347
Yuan J, Zhang Z, Yang M, Guo F, Men X, Liu W (2017) TiB2 reinforced hybrid-fabric composites with enhanced thermal and mechanical properties for high-temperature tribological applications. Tribol Int 115:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.05.006
Chichi SAM, Hamidon MN, Ertugrul M, Mamat MS, Jaafar H, Aris N (2020) Influence of B2O3 addition on the properties of TiO2 thick film at various annealing temperatures for hydrogen sensing. J Elec Mater 49:3340–3349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08059-0
Wang J, Sha L, Yang Q, Wang Y, Yang D (2005) Synthesis of aluminium borate nanowires by sol–gel method. Mater Res Bull 40:1551–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2005.04.016
Raghavan V (2005) Al-B-Ti (Aluminum-Boron-Titanium). J Phase Equilib Diff 26(2):173–174. https://doi.org/10.1361/15477030523058
Duan XF, Wang JF, Lieber CM (2000) Synthesis and optical properties of gallium arsenide nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 76:1116. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.125956
Zhang E, Zeng G, Zeng S (2002) Oxidation behavior of in situ TiB short fibre reinforced Ti-6Al-1.2B alloy in air. J Mater Sci 37:4063–4071. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020019431992
Zhang J, Meng F, Todd RI, Fu Z (2010) The nature of grain boundaries in alumina fabricated by fast sintering. Scr Mater 62(9):658–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.01.019
Zhou M, Sui Y, Jiang Y (2020) Growth behavior of aluminum borate whiskers on zirconia toughened alumina (ZTA) particle surface. Ceram Int 46(7):8839–8844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.128
Samsonov GV, Kovenskaya II BA (1977) The nature of the chemical bond in borides. In: Matkovich VI (eds.) Boron and refractory borides. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Xu SC, Wang LD, Zhao PT, Li WL, Xue ZW, Fei WD (2012) Fiber texture evolution of hot-rolled aluminum matrix composite reinforced by aluminum borate whisker. Mat Sci Eng A Struct 533:82–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.11.038
Mayrhofer PH, Mitterer C, Wen JG, Greene JE, Petrov I (2005) Self-organized nanocolumnar structure in superhard TiB2 thin films. Appl Phys Lett 86:131909. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1887824
Hu B, Zhang Q, Niu L, Liu J, Rao J, Zhou X (2015) Microsphere assembly of boron-doped Rutile TiO2 nanotubes with enhanced photoelectric performance. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 26:8915–8921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3573-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All persons who meet authorship criteria are listed as authors, and all authors certify that they have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content, including participation in the concept, design, analysis, writing, or revision of the manuscript. Furthermore, each author certifies that this material or similar material has not been and will not be submitted to or published in any other publication before its appearance in the Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology. Z.G.: writing—original draft preparation, investigation. H.E.: conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, validation, writing—review and editing, supervision. Y.M.: conceptualization, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghadimi, Z., Esfahani, H. & Mazaheri, Y. Control on nanostructured quaternary Ti–Al–O–B composite synthesized via electrospinning method, from nanoparticles to nanowhiskers. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 98, 127–137 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05487-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05487-0