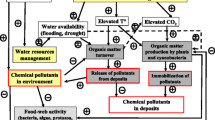
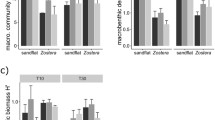
Abstract
Climatic fluctuations are among the most important factors that cause changes in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. This review considers the principal mechanisms of the influence of climate changes on the structure and functioning of ecosystems of water bodies and shows the need to take these mechanisms into account when developing strategies for conserving the biological resources of aquatic ecosystems. Climatic fluctuations affect aquatic ecosystems through changes in temperature, surface runoff of nutrients and other substances and their ratios, the intensity of water mixing during the circulation period, and other mechanisms. Additional nutrients received in rainy periods from the catchment area and directly with precipitation stimulate the growth of primary producers and cause the risk of the further eutrophication of water bodies. An increase in temperature promotes the growth of potentially toxic phytoplankton species and exacerbates the problem of green tides, the massive development of multicellular algae in the coastal zone. Organic substances coming from the catchment area during wet periods stimulate a microbial loop in aquatic ecosystems. In shallow lakes, climate fluctuations can cause changes in food webs and the ecological regime. Climate-induced changes in the composition of producer communities often weaken pelagic–benthic relationships in aquatic ecosystems. In some cases, climate changes have contributed to the invasions of alien species. The natural dynamics of ecosystems affected by climate fluctuations deserves close attention and requires the development of special adaptive management of aquatic biological resources. In some cases, it is necessary to take more severe measures for the protection and restoration of water bodies, which would take into account adverse changes in natural factors.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abell, J.M., Özkundakci, D., Hamilton, D.P., and Jones, J.R., Latitudinal variation in nutrient stoichiometry and chlorophyll-nutrient relationships in lakes: a global study, Fundam. Appl. Limnol., 2012, vol. 181, pp. 1‒14.
Alimov, A.F., Bogatov, V.V., and Golubkov, S.M., Produktsionnaya gidrobiologiya (Production Hydrobiology), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 2013.
Bariĉa, J., Kling, H., and Gibson, J., Experimental manipulation of algal bloom composition by nitrogen addition, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1980, vol. 37, pp. 1175‒1183.
Bogatov, V.V. and Fedorovskiy, A.S., Freshwater ecosystems of the southern region of the Russian Far East are undergoing extreme environmental change, Knowl. Manage. Aquat. Ecosyst., 2016, vol. 417. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae/2016021
Bogatov, V.V. and Fedorovskiy, A.S., Osnovy rechnoi gidrologii i gidrobiologii (Principles of River Hydrology and Hydrobiology), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2017.
Boulion, V.V., Effect of geographical factors on the biological productivity of lake ecosystems: modeling and forecast, Contemp. Probl. Ecol., 2017, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 111–118. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425517020020
Boulion, V.V., Modeling the biotic energy flow in the plankton community of the lake type ecosystem with the involvement of microorganisms, Inland Water Biol., 2019, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 259–266.
Chukov, S.N., Golubkov, M.S., and Ryumin, A.G., Intrahorizon differentiation of the structural-functional parameters of the humic acids from a typical chernozem, Eurasian Soil Sci., 2010, vol. 43, pp. 1255–1262. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229310110086
Eggleton, T., Future physical changes, in Climate Change Impacts on Fisheries and Aquaculture. A Global Analysis, Chichester: Wiley, 2018, vol. 1, pp. 23–44.
Elliott, J.A., Jones, I.D., and Thackeray, S.J., Testing the sensitivity of phytoplankton communities to changes in water temperature and nutrient load, in a temperate lake, Hydrobiologia, 2006, vol. 559, pp. 401‒411.
Eriksson Wiklund, A.-K., Dahlgren, K., Sunderlin, B., and Andersson, A., Effects of warming and shifts of pelagic food web structure on benthic productivity in a coastal marine system, Mar. Ecol.: Prog. Ser., 2009, vol. 396, pp. 13‒25.
Gentry, L.E., David, M.B., Royer, T.V., Mitchell, C.A., and Starks, K.M., Phosphorus transport pathways to streams in tile-drained agricultural watersheds, J. Environ. Qual., 2007, vol. 36, pp. 408–415.
Gladyshev, M.I. and Gubelit, Yu.I., Green tides: new consequences of the eutrophication of natural waters (invited review), Contemp. Probl. Ecol., 2019, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 109–125. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425519020057
Golubkov, M.S., Primary production of plankton and decomposition of organic matter in saline lakes of the Crimea Peninsula, Inland Water Biol., 2012, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 322–327.
Golubkov, M.S. and Golubkov, S.M., Climatic factors and hydrobiological regimes of shallow salt lakes, in Dinamika biologicheskogo raznoobraziya i bioresursov kontinental’nykh vodoemov (Dynamics of Biological Diversity and Biological Resources of Continental Reservoirs), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 2012, pp. 113‒126.
Golubkov, M.S. and Golubkov, S.M., The effect of weather conditions on eutrophication in the Neva River Estuary, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2018, vol. 480, pp. 110–113. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0012496618030122
Golubkov, M. and Golubkov, S., Eutrophication in the Neva Estuary (Baltic Sea): response to temperature and precipitation patterns, Mar. Freshwater Res., 2020, vol. 71, no. 6, pp. 583–595.
Golubkov, M., Nikulina, V., and Golubkov, S., Effects of environmental variables on midsummer dinoflagellate community in the Neva estuary (Baltic Sea), Oceanologia, 2019, vol. 61, pp. 197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceano.2018.09.001
Golubkov, S.M., Trophodynamics of continental water reservoirs: from a balance approach to the dynamic variability of ecosystems, Izv. Samar. Nauchn. Tsentra, Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2006, no. 5, pp. 18‒25.
Golubkov, S. and Alimov, A., Ecosystem of the Neva estuary (Baltic Sea): natural dynamics or response to anthropogenic impacts? Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2010, vol. 61, pp. 198–204.
Golubkov, S., Kemp, R., Golubkov, M., Balushkina, E., Litvinchuk, L., and Gubelit, Y., Biodiversity and the functioning of hypersaline lake ecosystems from Crimea Peninsula (Black Sea), Fundam. Appl. Limnol., 2007, vol. 169, no. 1, pp. 79–87. https://doi.org/10.1127/1863-9135/2007/0169-0079
Golubkov, S.M., Maksimov, A.A., Golubkov, M.S., and Litvinchuk, L.F., Dynamics of biological diversity and biological resources of the ecosystem of the eastern part of the Gulf of Finland affected by regional climate changes and invasive species, in Dinamika biologicheskogo raznoobraziya i bioresursov kontinental’nykh vodoemov (Dynamics of Biological Diversity and Biological Resources of Continental Reservoirs), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 2012, pp. 278‒293.
Golubkov, S., Golubkov, M., Tiunov, A., and Nikulina, V. Long-term changes in primary production and mineralization of organic matter in the Neva estuary (Baltic Sea), J. Mar. Syst., 2017, vol. 171, pp. 73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.12.009
Golubkov, S.M., Shadrin, N.V., Golubkov, M.S., Balushkina, E.V., and Litvinchuk, L.F., Food chains and their dynamics in ecosystems of shallow lakes with different water salinities, Russ. J. Ecol., 2018a, vol. 49, no. 5, pp. 442–448. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425519020057
Golubkov, S.M., Berezina, N.A., Gubelit, Y.I., Demchuk, A.S., Golubkov, M.S., and Tiunov, A.V., A relative contribution of carbon from green tide algae Cladophora glomerata and Ulva intestinalis in the coastal food webs in the Neva estuary (Baltic Sea), Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2018b, vol. 126, pp. 43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.10.032
Golubkov, S.M., Belyakov, V.P., Golubkov, M.S., Litvinchuk, L.F., Petukhov, V.A., and Gubelit, Yu.I., Energy flows and phosphorus turnover in the system of shallow reservoir under anthropogenic stress, Russ. J. Ecol., 2019a, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 560–566. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413619060055
Golubkov, S.M., Golubkov, M., and Tiunov, A.V., Anthropogenic carbon as a basal resource in the benthic food webs in the Neva Estuary (Baltic Sea), Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2019b, vol. 146, pp. 190–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.06.037
Golubkov, S.M., Balushkina, E.V., and Golubkov, M.S., Restoration of zoobenthic communities and water quality in the river ecosystem after a decrease in the level of organic pollution, Contemp. Probl. Ecol., 2020, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 146–155. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425520020031
Gubelit, Yu.I., Climatic impact on community of filamentous macroalgae in the Neva estuary (eastern Baltic Sea), Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2015, vol. 91, pp. 166–172.
Holopainen, R., Lehtiniemi, M., Meier, H.E.M., Albertsson, J., Gorokhova, E., Kotta, J., and Viitasalo, M., Impacts of changing climate on the non-indigenous invertebrates in the northern Baltic Sea by end of the twenty-first century, Biol. Invasions, 2016, vol. 18, pp. 3015–3032.
Hurrell, J.W., Decadal trends in the North Atlantic oscillation: regional temperatures and precipitation, Science, 1995, vol. 269, pp. 676‒679.
Huttunen, I., Lehtonen, H., Huttunen, M., Piirainen, V., Korppoo, M., Veijalainen, N., Viitasalo, M., and Vehviläinen, B., Effects of climate change and agricultural adaptation on nutrient loading from Finnish catchments to the Baltic Sea, Sci. Total Environ., 2015, vol. 529, pp. 168–181.
Jansson, M., Hickler, T., Jonsson, A., and Karlsson, J., Links between terrestrial primary production and bacterial production and respiration in lakes in a climate gradient in subarctic Sweden, Ecosystems, 2008, vol. 11, pp. 367–376.
Järvinen, M., Lehtinen, S., and Arvola, L., Variations in phytoplankton assemblage in relation to environmental and climatic variation in a boreal lake, Verh. Int. Verein. Limnol., 2006, vol. 29, pp. 1841–1844.
Jeppesen, E., Kronvang, B., Meerhoff, M., Sondergaard, M., Hansen, K.M., Andersen, H.E., Lauridsen, T.L., Beklioglu, M., Ozen, A.O., and Olesen, J.E., Climate change effects on runoff, catchment phosphorus loading and lake ecological state, and potential adaptations, J. Environ. Qual., 2009, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 1030–1041.
Karlsson, J., Berggren, M., Ask, J., Bystrom, P., Jonsson, A., Laudon, H., and Jansson, M., Terrestrial organic matter support of lake food webs: evidence from lake metabolism and stable hydrogen isotopes of consumers, Limnol. Oceanogr., 2012, vol. 57, pp. 1042–1048.
Klais, R., Tamminen, T., Kremp, A., Spilling, K., An, B.W., Hajdu, S., and Olli, K., Spring phytoplankton communities shaped by interannual weather variability and dispersal limitation: mechanisms of climate change effects on key coastal primary producers, Limnol. Oceanogr., 2013, vol. 58, pp. 753–762.
Kopylov, A.I., Lazareva, V.I., Mineeva, N.M., Maslennikova, T.S., and Stroinov, Ya.V., influence of anomalous high water temperatures on the development of the plankton community in the Middle Volga reservoirs in summer 2010, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2012, vol. 442, pp. 11–13. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0012496612010012
Lin, Q., Xu, L., Hou, J., Liu, Z., Jeppesen, E., and Hanet, B.-P., Responses of trophic structure and zooplankton community to salinity and temperature in Tibetan lakes: Implication for the effect of climate warming, Water Res., 2017, vol. 124, pp. 618–629.
Maximov, A.A., Long-term variability of climatic factors and dynamics of benthic animal communities, in Dinamika biologicheskogo raznoobraziya i bioresursov kontinental’nykh vodoemov (Dynamics of Biological Diversity and Biological Resources of Continental Reservoirs), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 2012, pp. 126‒138.
Maximov, A.A., Mezhgodovaya i mnogoletnyaya dinamika makrobentosa na primere verhsiny Finskogo zaliva (Interannual and Long-Term Dynamics of Macrozoobenthos by Example of the Top of Gulf of Finland), St. Petersburg: Nestor-Istoriya, 2018.
Maximov, A.A., Berezina, N.A., Golubkov, S.M., and Nikulina, V.N., Long-term climatic changes of the productivity of the northern lake ecosystem, in Dinamika biologicheskogo raznoobraziya i bioresursov kontinental’nykh vodoemov (Dynamics of Biological Diversity and Biological Resources of Continental Reservoirs), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 2012, pp. 138‒144.
Markensten, H., Climate effects on early phytoplankton biomass over three decades modified by the morphometry in connected lake basins, Hydrobiologia, 2006, vol. 559, pp. 319‒329.
Melack, J.M. and Jellison, R., Limnological conditions in Mono Lake: contrasting monomixis and meromixis in the 1990s, Hydrobiologia, 1998, vol. 384, pp. 21‒29.
Mittelbach, G.G., Turner, A.M., Hall, D.J., Rettig, J.E., and Osenberg, C.W., Perturbation and resilience—a long-term, whole-lake study of predator extinction and reintroduction, Ecology, 1995, vol. 76, no. 8, pp. 2347‒2360.
Naz, B.S., Kao, S.-C., Ashfaq, M., Gao, H., Rastogi, D., and Gangrade, S., Effects of climate change on streamflow extremes and implications for reservoir inflow in the United States, J. Hydrol., 2018, vol. 556: P. 359–370.
Nõges, P., van de Bund, W., Cardoso, A.C., and Heiskanen, A.-S. Impact of climate variability on parameters used in typology and ecological quality assessment of surface waters—implication on the Water Framework Directive, Hydrobiologia, 2007, vol. 584, pp. 373‒379.
Padisák, J., Molnár, G., Soróczki-Pintér, É., Hajnal, É., and George, D.G., Four consecutive dry years in Lake Balaton (Hungary): consequences for phytoplankton biomass and composition, Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol., 2006, vol. 29, pp. 1153‒1159.
Rast, W. and Thornton, J.A., The phosphorus loading concept and OECD Eutrophication Program: origin, application and capabilities, in The Lake Handbook, Vol. 2: Lake Restoration and Rehabilitation, Oxford: Blackwell, 2005, pp. 354‒385.
Rip, W.J., Ouboter, M.R.L., and Los, H.J., Impact of climatic fluctuations on Characeae biomass in a shallow, restored lake in the Netherlands, Hydrobiologia, 2007, vol. 584, pp. 415‒424.
Roberts, W.M., Gonzalez-Jimenez, J.L., Doody, D.G., Jordan, P., and Daly, K., Assessing the risk of phosphorus transfer to high ecological status rivers: integration of nutrient management with soil geochemical and hydrological conditions, Sci. Total Environ., 2017, vol. 589, pp. 25–35.
Rogozin, D.Yu., Meromikticheskie ozera Severo-Minusinskoi kotloviny: zakonomernosti stratifikatsii i ekologiya fototrofnykh sernykh bakterii (Meromictic Lakes of the North Minusinsk Depression: Stratification Pattern and Ecology of Phototrophic Sulfur Bacteria), Krasnoyarsk: Inst. Fiz., Sib. Otd., Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2019.
Rogozin, D.Y., Tarnovsky, M.O., Belolipetskii, V.M., Zykov, V.V., Zadereev, E.S., Tolomeev, A.P., Drobotov, A.V., Barkhatov, Y.V., Gaevsky, N.A., Gorbaneva, T.B., Kolmakova, A.A., and Degermendzhi, A.G., Disturbance of meromixis in saline Lake Shira (Siberia, Russia): Possible reasons and ecosystem response, Limnologica, 2017, vol. 66, pp. 12–23.
Ruosteenoja, K., Räisänen, J., and Pirinen, P., Projected changes in thermal seasons and the growing season in Finland, Int. J. Climatol., 2011, vol. 31, pp. 1473–1487.
Salmaso, N., Decet, F., and Cordella, P., Spring mixing depth affects the interannual variations in phytoplankton abundance and composition in deep lakes. A case study from Lake Garda (Northern Italy), Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol., 2003, vol. 28, pp. 1486‒1489.
Schoumans, O.F., Bouraoui, F., Kabbe, C., Oenema, O., and van Dijk, K.C., Phosphorus management in Europe in a changing world, Ambio, 2015, vol. 44, pp. 180–192.
Simona, M., Winter and spring mixing depths affect the trophic status and composition of phytoplankton in the northern meromictic basin of Lake Lugano, J. Limnol., 2003, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 190–206.
Shadrin, N.V. and Anufriieva, E.V., Climate change impact on the marine lakes and their Crustaceans: the case of marine hypersaline Lake Bakalskoye (Ukraine), Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 2013, vol. 13, pp. 603–611.
Shadrin, N.V. and Anufriieva, E.V., Structure and trophic relations in hypersaline environments, Biol. Bull. Rev., 2020, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 48–56.
Sharov, A.N., Berezina, N.A., Nazarova, L.E., Poliakova, T.N., and Chekryzheva, T.A., Links between biota and climate-related variables in the Baltic region using Lake Onega as an example, Oceanologia, 2014, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 291‒306.
Sharpley, A.N., Bergström, L., Aronsson, H., Bechmann, M., Bolster, C.H., Börling, K., Djodjic, F., Jarvie, H.P., Schoumans, O.F., Stamm, C., Tonderski, K.S., Ulén, B., Uusitalo, R., and Withers, P.J.A., Future agriculture with minimized phosphorus losses to waters: research needs and direction, Ambio, 2015, vol. 44, suppl. 2, pp. S163–S179.
Spilling, K., Olli, K., Lehtoranta, J., Kremp, A., Tedesco, L., Tamelander, T., Klais, R., Peltonen, H., and Tamminen, T., Shifting diatom—dinoflagellate dominance during spring bloom in the Baltic Sea and its potential effects on biogeochemical cycling, Front. Mar. Sci., 2018, vol. 5, art. ID 327. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00327
Stenseth, N.C., Mysterud, A., Ottersen, G., Hurrell, J.W., Chan, K.-S., and Lima, M., Ecological effects of climate fluctuations, Science, 2002, vol. 297, pp. 1292–1296.
Teutschbein, C., Sponseller, R.A., Grabs, T., Blackburn, M., Boyer, E.W., Hytteborn, J.K., and Bishop, K., Future riverine inorganic nitrogen load to the Baltic Sea from Sweden: an ensemble approach to assessing climate change effects, Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 2017, vol. 31, pp. 1674–1701.
Thompson, R., Kamenik, C., and Schmid, R., Ultra-sensitive lakes and climate change, J. Limnol., 2005, vol. 64, no. 2, pp. 139–152.
Uusitalo, R., Närvänen, A., Kaseva, A., Launto-Tiuttu, A., Heikkinen, J., Joki-Heiskala, P., Rasa, K., and Salo, T., Conversion of dissolved phosphorus in runoff by ferric sulfate to a form less available to algae: field performance and cost assessment, Ambio, 2015, vol. 44, pp. 286–296.
Vtoroi otsenochnyi doklad Rosgidrometa ob izmenenii klimata i ikh posledstviyakh na territorii Rossiiskoi Federatsii. Obshchee rezyume (The Second Roshydromet Assessment Report on Climate Change and Its Consequences in the Russian Federation: General Summary), Frolov, A.V., Moscow: Rosgidromet, 2014. http://voeikovmgo.ru/ download/2014/od/od2.pdf.
Wen, Y., Schoups, G., and van de Giesen, N., Organic pollution of rivers: combined threats of urbanization, livestock farming and global climate change, Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, no. 43289, pp. 1–9.
Weyhenmeyer, G., Blenckner, T., and Pettersson, K., Changes of the plankton spring outburst related to the North Atlantic Oscillation, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1999, vol. 44, no. 7, pp. 1788–1792.
Wilk-Woźniak, E., Amirowicz, A., Pociecha, A., and Gąsiorowski, M., The effect of water balance of a man-made lacustrine ecosystem on the food web: does flushing affect the carbon signature of plankton and benthos? Ecohydrology, 2016, vol. 9, pp. 765–772.
Williams, W.D., Environmental threats to salt lakes and the likely status of inland saline ecosystems in 2025, Environ. Conserv., 2002, vol. 29, pp. 154–167.
Williamson, T.J., Vanni, M.J., and Renwick, W.H., Spatial and temporal variability of nutrient dynamics and ecosystem metabolism in a hyper-eutrophic reservoir differ between a wet and dry year, Ecosystems, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-020-00505-8
Withers, P.J.A. and Jarvie, H.P., Delivery and cycling of phosphorus in rivers: a review, Sci. Total Environ., 2008, vol. 400, pp. 379–395.
Zadereev, E.S., Tolomeev, A.P., Drobotov, A.V., and Kolmakova, A.A., Impact of weather variability on spatial and seasonal dynamics of dissolved and suspended nutrients in water column of meromictic Lake Shira, Contemp. Probl. Ecol., 2014, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 384–396. https://doi.org/10.1134/S199542551404012X
Zillén, L., Conley, D. J., Andrén, T., Andrén, E., and Björck, S., Past occurrences of hypoxia in the Baltic Sea and the role of climate variability, environmental change and human impact, Earth-Sci. Rev., 2008, vol. 91, pp. 77–92.
Funding
This review was prepared within the framework of the state subject no. АААА-А19-119020690091-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by K. Lazarev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golubkov, S.M. Effect of Climatic Fluctuations on the Structure and Functioning of Ecosystems of Continental Water Bodies. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 14, 1–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425521010030
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425521010030