Abstract
Our study aimed to investigate the effects of the new cardiotonic steroid BD-15 (γ-benzylidene derivatives) in the behavioral parameters, oxidative stress and the Na, K-ATPase activity in the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex and heart from rats to verify the safety and possible utilization in brain disorders. For this study, groups of male Wistar rats were used after intraperitoneal injection of 20, 100 and 200 µg/Kg with BD-15. The groups were treated for three consecutive days and the control group received 0.9% saline. BD-15 did not alter behavior of rats treated with different doses. An increase in the specific α2,3-Na, K-ATPase activity was observed for all doses of BD-15 tested in the hippocampus. However, in the prefrontal cortex, only the dose of 100 µg/Kg increased the activity of all Na, K-ATPase isoforms. BD-15 did not cause alteration in the lipid peroxidation levels in the hippocampus, but in the prefrontal cortex, a decrease of lipid peroxidation (~ 25%) was observed. In the hippocampus, GSH levels increased with all doses tested, while in the prefrontal cortex no changes were found. Subsequently, when the effect of BD-15 on cardiac tissue was analyzed, no changes were observed in the tested parameters. BD-15 at a dosage of 100 µg/Kg proved to be promising because it is considered therapeutic for brain disorders, since it increases the activity of the α3-Na, K-ATPase in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, as well as decreasing the oxidative stress in these brain regions. In addition, this drug did not cause changes in the tissues of the heart and kidneys, preferentially demonstrating specificity for the brain.
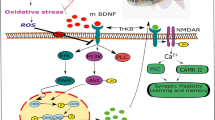
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari A, Topiwala MA, Gordon JA (2010) Synchronized activity between the ventral hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex during anxiety. Neuron 65:257–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.12.002
Alves SL et al (2015) gamma-Benzylidene digoxin derivatives synthesis and molecular modeling: evaluation of anticancer and the Na, K-ATPase activity effect. Bioorg Med Chem 23:4397–4404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.06.028
Bagrov AY, Shapiro JI, Fedorova OV (2009) Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: physiology, pharmacology, and novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Rev 61:9–38. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.108.000711
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52032-6
Cannon SC (2004) Paying the price at the pump: dystonia from mutations in a Na+/K+ -ATPase. Neuron 43:153–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.07.002
Carvalho DCM et al (2019) Marinobufagenin inhibits neutrophil migration and proinflammatory cytokines. J Immunol Res 2019:1094520. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1094520
Chauhan NB, Lee JM, Siegel GJ (1997) Na, K-ATPase mRNA levels and plaque load in Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 9:151–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02800498
Choleris E, Thomas AW, Kavaliers M, Prato FS (2001) A detailed ethological analysis of the mouse open field test: effects of diazepam, chlordiazepoxide and an extremely low frequency pulsed magnetic field. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:235–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-7634(01)00011-2
Clausen MV, Hilbers F, Poulsen H (2017) The structure and function of the Na, K-ATPase isoforms in health and disease. Front Physiol 8:371–371. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00371
de Lores Arnaiz GR, Ordieres MG (2014) Brain Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity in aging and disease. Int J Biomed Sci 10:85–102
de Souza GB et al (2019) Evaluation of neuroprotective activity of digoxin and semisynthetic derivatives against partial chemical ischemia. J Cell Biochem 120:17108–17122. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28971
Djordjevic J, Djordjevic A, Adzic M, Radojcic MB (2012) Effects of chronic social isolation on Wistar rat behavior and brain plasticity markers. Neuropsychobiology 66:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1159/000338605
Dobretsov M, Stimers JR (2005) Neuronal function and alpha3 isoform of the Na/K-ATPase. Front Biosci 10:2373–2396. https://doi.org/10.2741/1704
Ellis DZ, Rabe J, Sweadner KJ (2003) Global loss of Na K-ATPase and its nitric oxide-mediated regulation in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 23:43–51
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y (1925) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol chem 66:375
Garcia IJ, Kinoshita PF, Scavone C, Mignaco JA, Barbosa LA, Santos Hde L (2015) Ouabain modulates the lipid composition of hippocampal plasma membranes from rats with LPS-induced neuroinflammation. J Membr Biol 248:1191–1198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9840-7
Garcia IJP et al (2018) Ouabain attenuates the oxidative stress induced by lipopolysaccharides in the cerebellum of rats. J Cell Biochem 119:2156–2167. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26377
Garcia IJP, Kinoshita PF, Silva L (2019a) Ouabain attenuates oxidative stress and modulates lipid composition in hippocampus of rats in lipopolysaccharide-induced hypocampal neuroinflammation in rats. J Cell Biochem 120:4081–4091. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27693
Garcia IJP et al (2019b) New bufadienolides extracted from Rhinella marina inhibit Na, K-ATPase and induce apoptosis by activating caspases 3 and 9 in human breast and ovarian cancer cells. Steroids 152:108490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2019.108490
Grisar T, Guillaume D, Delgado-Escuet AV (1992) Contribution of Na+, K+-ATPase to focal epilepsy: a brief review. Epilepsy Res 12:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/0920-1211(92)90034-Q
Gustafsson S, Lindstrom V, Ingelsson M, Hammarlund-Udenaes M, Syvanen S (2018) Intact blood-brain barrier transport of small molecular drugs in animal models of amyloid beta and alpha-synuclein pathology. Neuropharmacology 128:482–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.002
Haux J, Klepp O, Spigset O, Tretli S (2001) Digitoxin medication and cancer; case control and internal dose-response studies. BMC Cancer 1:11–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-1-11
Johnson WM, Wilson-Delfosse AL, Mieyal JJ (2012) Dysregulation of glutathione homeostasis in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrients 4:1399–1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4101399
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillette JR (1974) Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 11:151–169. https://doi.org/10.1159/000136485
Kaur S, Rehni AK, Singh N, Jaggi AS (2009) Studies on cerebral protection of digoxin against ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice Yakugaku zasshi. J Pharm Soc Japan 129:435–443. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi.129.435
Kim W et al (2015) Antioxidant effects of Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract in the hippocampus of mercury-exposed rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:247–247. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0786-1
Kong D et al (2015) The effect of SCF and ouabain on small intestinal motility dysfunction induced by gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 32:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9702-9
Li Z, Xie Z (2009) The Na/K-ATPase/Src complex and cardiotonic steroid-activated protein kinase cascades. Pflugers Arch 457:635–644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0470-0
Lin S et al (2018) Bufadienolides induce p53-mediated apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett 15:1566–1572. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7457
Lu SC (2009) Regulation of glutathione synthesis. Mol Aspects Med 30:42–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2008.05.005
McCarty MF (2012) Marinobufagenin and cyclic strain may activate endothelial NADPH oxidase, contributing to the adverse impact of salty diets on vascular and cerebral health. Med Hypotheses 78:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2011.09.028
Modo M, Stroemer RP, Tang E, Veizovic T, Sowniski P, Hodges H (2000) Neurological sequelae and long-term behavioural assessment of rats with transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neurosci Methods 104:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-0270(00)00329-0
Morth JP et al (2007) Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump. Nature 450:1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06419
Moseley AE et al (2007) Deficiency in Na, K-ATPase alpha isoform genes alters spatial learning, motor activity, and anxiety in mice. J Neurosci 27:616–626. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4464-06.2007
Murata K, Kinoshita T, Ishikawa T, Kuroda K, Hoshi M, Fukazawa Y (2020) Region- and neuronal-subtype-specific expression of Na, K-ATPase alpha and beta subunit isoforms in the mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 528:2654. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.24924
Ohnishi T et al (2015) Na, K-ATPase α3 is a death target of Alzheimer patient amyloid-β assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:E4465–E4474. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1421182112
Oselkin M, Tian D, Bergold PJ (2010) Low-dose cardiotonic steroids increase sodium-potassium ATPase activity that protects hippocampal slice cultures from experimental ischemia. Neurosci Lett 473:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2009.10.021
Parreira GM et al (2018) Oxidative stress and Na, K-ATPase activity differential regulation in brainstem and forebrain of Wistar Audiogenic rats may lead to increased seizure susceptibility. Brain Res 1679:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.12.001
Pessôa MTC, Alves SLG, Taranto AG, Villar JAFP, Blanco G, Barbosa LA (2018) Selectivity analyses of γ-benzylidene digoxin derivatives to different Na, K-ATPase α isoforms: a molecular docking approach. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 33:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2017.1380637
Pessoa MTC et al (2020) 21-Benzylidene digoxin decreases proliferation by inhibiting the EGFR/ERK signaling pathway and induces apoptosis in HeLa cells. Steroids 155:108551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2019.108551
Pivovarov AS, Calahorro F, Walker RJ (2018) Na(+)/K(+)-pump and neurotransmitter membrane receptors. Invert Neurosci 19:1–1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-018-0221-7
Prassas I, Diamandis EP (2008) Novel therapeutic applications of cardiac glycosides. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:926–935. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2682
Radzyukevich TL, Lingrel JB, Heiny JA (2009) The cardiac glycoside binding site on the Na, K-ATPase α2 isoform plays a role in the dynamic regulation of active transport in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:2565–2570. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804150106
Rocha SC et al (2014) 21-Benzylidene digoxin: a proapoptotic cardenolide of cancer cells that up-regulates Na, K-ATPase and epithelial tight junctions. PLoS ONE 9:e108776. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108776
Shamraj OI, Lingrel JB (1994) A putative fourth Na+, K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit gene is expressed in testis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12952–12956. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.26.12952
Shih YL et al (2019) Ouabain promotes immune responses in WEHI-3 cells to generate leukemia mice through enhancing phagocytosis and natural killer cell activities in vivo. Environ Toxicol 34:659–665. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22732
Silva LND et al (2017) Differences of lipid membrane modulation and oxidative stress by digoxin and 21-benzylidene digoxin. Exp Cell Res 359:291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.07.017
Singh E, Devasahayam G (2020) Neurodegeneration by oxidative stress: a review on prospective use of small molecules for neuroprotection. Mol Biol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05354-1
Song HL, Demirev AV, Kim NY, Kim DH, Yoon SY (2019) Ouabain activates transcription factor EB and exerts neuroprotection in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 95:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2018.12.007
Tuncok Y, Hazan E, Oto O, Guven H, Catalyurek H, Kalkan S (1997) Relationship between high serum digoxin levels and toxicity. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 35:366–368
Vanmolkot KR et al (2006) Two de novo mutations in the Na, K-ATPase gene ATP1A2 associated with pure familial hemiplegic migraine. Eur J Hum Genet 14:555–560. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201607
Vasconcelos AR et al (2015) Effects of intermittent fasting on age-related changes on Na, K-ATPase activity and oxidative status induced by lipopolysaccharide in rat hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 36:1914–1923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.02.020
Vertes RP (2004) Differential projections of the infralimbic and prelimbic cortex in the rat. Synapse 51:32–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.10279
Vieira L et al (2018) 21Benzylidene digoxin, a novel digoxin hemi-synthetic derivative, presents an anti-inflammatory activity through inhibition of edema, tumour necrosis factor alpha production, inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and leucocyte migration. Int Immunopharmacol 65:174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.10.010
Walsh RN, Cummins RA (1976) The open-field test: a critical review. Psychol Bull 83:482–504
Wang Y et al (2014) Involvement of Na/K-ATPase in hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of the Src/ERK pathway in LLC-PK1 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 71:415–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.036
Wen L, Huang Y, Xie X (2014) Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of bufalin in rodents. Mediat Inflamm 2014:171839. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/171839
Zhang XH et al (2017) The combination of digoxin and GSK2606414 exerts synergistic anticancer activity against leukemia in vitro and in vivo. BioFactors 43:812–820. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1380
Acknowledgements
This study was partially funded by the FAPEMIG (Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais) APQ-00290-16, APQ-00855-19 and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) 401914/2016-0. We are grateful to Maria das Graças Carvalho for his contribution in correcting English. We would like to thank Dr. Hélio Batista dos Santos and Ralph Gruppi Thomé for their assistance in the histology experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parreira, G.M., Faria, J.A., Marques, S.M.S. et al. The γ-Benzylidene Digoxin Derivative BD-15 Increases the α3-Na, K-ATPase Activity in Rat Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex and no Change on Heart. J Membrane Biol 254, 189–199 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-021-00173-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-021-00173-2