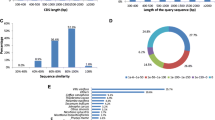
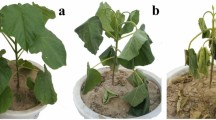
Abstract
Cynanchum thesioides, a member of the Asclepiadaceae family, are plants that have been used in traditional Chinese medicine and their latex contains succinic acid which has an important medicinal value. To identify candidate genes involved in succinic acid biosynthesis and accumulation, we analyzed transcriptome data from C. thesioides under drought stress using Illumina sequencing technology. A total of 146 and 172 unique genes were annotated as encoding enzymes involved in the succinic acid biosynthesis of C. thesioides and C. thesioides var. australe and the number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was 40 and 32, respectively. As drought stress increased, nine genes were significantly up-regulated and seven genes were significantly down-regulated in C. thesioides. In C. thesioides var. australe seven genes were up-regulated and nine were down-regulated. Enzymes participating in succinic acid biosynthesis were ATP citrate (pro-S)-lyase, succinate dehydrogenase, aconitate hydratase, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, glutamate synthase, fumarate hydratase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, glutamate dehydrogenase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, 4-aminobutyrate transaminase, malate dehydrogenase, and glutamate decarboxylase and their activities relating to succinic acid synthesis were determined. RNA-seq sequencing was used in our study. The genes involved in biosynthesis and accumulation of succinic acid in C. thesioides were predicted. Succinic acid content was positively correlated with MDH (BMK_Unigene_033366), but negatively correlated with GAD (BMK_Unigene_096180 and BMK_Unigene_030468), SDH (BMK_Unigene_142841). These results provide an important resource for further research on succinic acid of C. thesioides and other homologous species.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACLY:
-
ATP Citrate (pro-S)-lyase
- SDH:
-
Succinate dehydrogenase
- ACO:
-
Aconitate hydratase
- OGDH:
-
2-Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase
- CS:
-
Citrate synthase
- GLT:
-
Glutamate synthase
- FH:
-
Fumarate hydratase
- SUCLA:
-
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
- SSADH:
-
Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase
- GDH:
-
Glutamate dehydrogenase
- IDH:
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- GABA-T:
-
4-Aminobutyrate transaminase
- MDH:
-
Malate dehydrogenase
- GAD:
-
Glutamate decarboxylase
- CT:
-
Cynanchum thesioides (Freyn) K. Schum.
- CA:
-
Cynanchum thesioides (Freyn) K. Schum. var. australe (Maxim.) Tsiang et P. T. Li
- CK:
-
Control
- LS:
-
Mild drought stress
- MS:
-
Moderate drought stress
- SS:
-
Severe drought stress
References
Allen RS, Miller JAC, Chitty JA, Fist AJ, Gerlach WL, Larkin PJ (2008) Metabolic engineering of morphinan alkaloids by over-expression and RNAi suppression of salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase in opium poppy. Plant Biotechnol J 6(1):22–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2007.00293.x
Al-Quraan NA, Al-Share AT (2016) Characterization of the γ-aminobutyric acid shunt pathway and oxidative damage in Arabidopsis thaliana pop 2 mutants under various abiotic stresses. Biol Plant 60:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-015-0563-5
Al-Quraan N, Locy R, Singh N (2011) Implications of paraquat and hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress treatments on the GABA shunt pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin mutants. Plant Biotechnol Rep 5:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-011-0174-3
Ansari MI, Lee RH, Chen SCG (2005) A novel senescence-associated gene encoding γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA):pyruvate transaminase is upregulated during rice leaf senescence. Physiol Plant 123(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2004.00430.x
Araújo WL, Adriano N-N, Sandra T, Victoria IB, Alisdair RF (2008) Inhibition of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase in potato tuber suggests the enzyme is limiting for respiration and confirms its importance in nitrogen assimilation. Plant Physiol 148:1782–1796. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.126219
Araújo WL, Tohge T, Nunes-Nesi A, Daloso DM, Nimick M, Krahnert I (2012a) Phosphonate analogs of 2-oxoglutarate perturb metabolism and gene expression in illuminated Arabidopsis leaves. Front Plant Sci 3:114–133. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00114
Araújo WL, Tohge T, Osorio S, Lohse M, Balbo I, Krahnert I, Sienkiewicz-Porzucek A (2012b) Antisense inhibition of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in tomato demonstrates its importance for plant respiration and during leaf senescence and fruit maturation. Plant Cell 24:2328–2351. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.099002
Bouché N, Fait A, Bouchez D, Møller SG, Fromm H (2003) Mitochondrial succinic-semialdehyde dehydrogenase of the γ-aminobutyrate shunt is required to restrict levels of reactive oxygen intermediates in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(11):6843–6848. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1037532100
Boyer JS (1982) Plant productivity and environment. Science 218:443–448. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.218.4571.443
Cheng K, Zhao X, Zeng J, Zhang J (2012) Biotechnological production of succinic acid: current state and perspectives. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 6(3):302–318. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1327
Cheng K, Wang G, Zeng J, Zhang J (2013) Improved succinate production by metabolic engineering. Biomed Res Int 2013:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/538790
Elisabetta M, Alfredo T, Luigi C, Giuseppe F (2011) Metabolism of γ-aminobutyric acid during cold acclimation and freezing and its relationship to frost tolerance in barley and wheat. J Exp Bot 57:3755–3766. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erl141
Fait A, Fromm H, Walter D, Galili G, Fernie AR (2008) Highway or byway: the metabolic role of the GABA shunt in plants. Trends Plant Sci 13(1):14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.10.005
Fait A, Nesi AN, Angelovici R, Lehmann M, Pham PA, Song L, Haslam RP, Napier JA (2011) Targeted enhancement of glutamate-to-γ-aminobutyrate conversion in Arabidopsis seeds affects carbon-nitrogen balance and storage reserves in a development-dependent manner. Plant Physiol 3(157):1026–1042. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.179986
Hamanishi ET, Barchet GL, Dauwe R, Mansfield SD, Campbell MM (2015) Poplar trees reconfigure the transcriptome and metabolome in response to drought in a genotype- and time-of-day-dependent manner. BMC Genom 16(1):329–345. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1535-z
Han EH, Cho K, Goo Y, Kim M, Shin YW, Kim YH, Lee SW (2016) Development of molecular markers, based on chloroplast and ribosomal DNA regions, to discriminate three popular medicinal plant species, Cynanchum wilfordii, Cynanchum auriculatum, and Polygonum multiflorum. Mol Biol Rep 43:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-3959-1
Hsiao TC (1973) Plant response to water stress. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 24:519–570. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.24.060173.002511
Jenner HL, Winning BM, Millar AH, Tomlinson KL, Leaver CJ, Hill SA (2001) NAD Malic enzyme and the control of carbohydrate metabolism in Potato Tubers. Plant Physiol 126(3):1139–1150. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.126.3.1139
Kinnersley AM, Turano FJ (2000) Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and plant responses to stress. Crit Rev Plant Sci 19(6):479–509. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680091139277
Konno K, Hirayama C, Yasui H, Okada S, Sugimura M, Yukuhiro F, Tamura Y, Hattori M, Shinbo H, Nakamura M (2010) GABA, β-alanine and glycine in the digestive juice of privet-specialist insects: convergent adaptive traits against plant iridoids. J Chem Ecol 36(9):983–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-010-9824-y
Kowluru A (2001) Adenine and guanine nucleotide-specific succinyl-CoA synthetases in the clonal beta-cell mitochondria: implications in the beta-cell high-energy phosphate metabolism in relation to physiological insulin secretion. Diabetologia 44(1):89–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001250051584
Li B, Fang X, Chu FH, Xu B, Bi SL, Zhang Z (2016) Screening succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors: an established model and its application in Tall Gastrodia Tuber. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med 39:664–669
Liu X, Hu X, Jin L, Shi C, Liu Y, Peng S (2014) Identification and transcript analysis of two glutamate decarboxylase genes, CsGAD1 and CsGAD2, reveal the strong relationship between CsGAD1 and citrate utilization in citrus fruit. MolBiolRep 41:6253–6262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3506-x
Men Y, Wang D, Li B, Su Y, Chen G (2018) Effects of drought stress on the antioxidant system, osmolytes and secondary metabolites of Saposhnikovia divaricata seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 40:191–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2762-0
Navarre DA (2000) Nitric oxide modulates the activity of tobacco aconitase. Plant Physiol 122:573–582. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.2.573
Nayyar H, Kaur R, Kaur S, Singh R (2014) γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) imparts partial protection from heat stress injury to rice seedlings by improving Leaf Turgor and upregulating osmoprotectants and antioxidants. J Plant Growth Regul 33:408–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-013-9389-6
Pessarakli M, Haghighi M, Sheibanirad A (2015) Plant responses under environmental stress conditions. Adv Plants Agric Res 2:73–85. https://doi.org/10.15406/apar.2015.02.00073
Renault H, Roussel V, Amrani El A, Arzel M, Renault D, Bouchereau A, Deleu C (2010) The Arabidopsis pop2–1mutant reveals the involvement of GABA transaminase in salt stress tolerance. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):20–36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-20
Renault H, El Amrani A, Palanivelu R, Updegraff EP, Yu A, Renou J-P, Preuss D (2011) GABA accumulation causes cell elongation defects and a decrease in expression of genes encoding secreted and cell wall-related proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 52(5):894–908. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcr041
Schreiber JM, Pearl PL, Dustin I, Wiggs E, Barrios E, Wassermann EM, Gibson KM, Theodore WH (2016) Biomarkers in a taurine trial for succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. JIMD Rep 30:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2015_524
Shelp BJ, Bown A, Mclean MD (1999) Metabolism and functions of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Trends Plant Sci 4:446–452. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.115.1.1
Song J, Zhang H, Duan C, Cui X (2018) Exogenous application of succinic acid enhances tolerance of Larix olgensis seedling to lead stress. J Forestry Res 29(6):1–12
Stuart SD, Schauble A, Gupta S, Kennedy AD, Keppler BR, Bingham PM, Zachar Z (2014) A strategically designed small molecule attacks alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in tumor cells through a redox process. Cancer Metab 2(1):4–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-3002-2-4
Sun C, Gao X, Fu J, Zhou J, Wu X (2015) Metabolic response of maize (Zea mays L.) plants to combined drought and salt stress. Plant Soil 388(1):99–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2309-0
Sunita A, Ramesh SD, Tyerman MG, Xu B (2017) γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) signalling in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:1577–1603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2415-7
Toyokura K, Watanabe K, Oiwaka A, Kusano M, Tameshige T, Tatematsu K (2011) Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase is involved in the robust patterning of Arabidopsis leaves along the adaxial-abaxial axis. Plant Cell Physiol 52(8):1340–1353. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcr079
Upadhyaya H, Panda SK, Dutta BK (2008) Variation of physiological and antioxidative responses in tea cultivars subjected to elevated water stress followed by rehydration recovery. Acta Physiol Plant 30:457–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-008-0143-9
Vijayakumari K, Puthur JT (2016) γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) priming enhances the osmotic stress tolerance in Piper nigrum Linn. plants subjected to PEG-induced stress. Plant Growth Regul 78:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0074-6
Wang WG, Tang SS, Lu Y (2017) GC determination of 12 organic acids in foods. PTCA 53:1313–1317
Wink M (2010) Functions and biotechnology of plant secondary metabolites, vol 39. Annual Plant Reviews
Yao S, Zheng L, Zhao S, Xiong S (2006) Effect of germination conditions on γ-aminobutyric acid content of germinated brown rice. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 22:211–215
Yin Y, Yang R, Gu Z (2014) Calcium regulating growth and GABA metabolism pathways in germinating soybean (Glycine max L.) under NaCl stress. Eur Food Res Technol 239:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2214-z
Yue K (2012) A brief discussion on the pharmacology and medicine of some effective components in Cynanchum thesioides (Freyn) K. Schum. J Inner Mongolia Univ Nationalities 18(2):26–27
Yue J, Du C, Ji J, Xie T, Chen W, Chang E, Chen L, Jiang Z, Shi S (2018) Inhibition of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity affects adventitious root growth in poplar via changes in GABA shunt. Planta 248:963–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2929-3
Zeikus JG, Jain MK, Elankovan P (1999) Biotechnology of succinic acid production and markets for derived industrial products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051431
Zhang H, Wu Z, Suo Y, Wang J, Zheng L, Wang Y (2017) Gene expression and flavonol biosynthesis are induced by ultraviolet-B and salt stresses in Reaumuria trigyna. Biol Plant 61:246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-017-0725-8
Zhang X, Yang Z, Li Z, Zhang F, Hao L (2019) De novo transcriptome assembly and co-expression network analysis of Cynanchum thesioides: identification of genes involved in resistance to drought stress. Gene 710(2019):375–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.055
Zhang X, Yang Z, Zhang F, Hao L, Zhao H, Wang C, Long X (2020) Effect of drought stress on succinic acid biosynthesis in Cynanchum thesioides. J Northwest A F Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 48(04):137–145
Funding
This study was supported by Applied Technology Research and Development Fund of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (2019GC237); Inner Mongolia Agricultural University special plant and animal species breeding (YZGC2017016); Science Fund of Inner Mongolia of China (2020MS03085, 2015MS0359); PhD Start-up Fund of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (BT09-17). All funding played a role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LZH and ZRY supervised the experiment. XYZ, ZL and HYZ performed the experiment work and prepared the figures and tables. XYZ wrote the manuscript. FLZ edited the final version of the manuscript. XYZ and FLZ contributed equally to this work. All authors have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12374_2021_9301_MOESM2_ESM.doc
Supplementary file2 (DOC 148 KB) Table S2. Correlation analysis of index related succinic acid synthesis of C. thesioides. Note: * indicates a significant correlation at the 0.05 level. ** indicates a significant correlation at the 0.01 level. The top right represents C. thesioides and the bottom left represents C. thesioides var. australe
12374_2021_9301_MOESM3_ESM.xls
Supplementary file3 (XLS 350 KB) Table S3. Correlation between succinic acid and GABA concentration and related expression of enzyme genes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhang, F., Li, Z. et al. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Cynanchum thesioides Under Drought Stress Reveals Candidate Genes Involved in Succinic Acid Biosynthesis. J. Plant Biol. 66, 283–295 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-021-09301-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-021-09301-w