Abstract
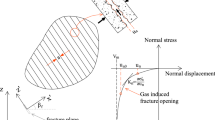
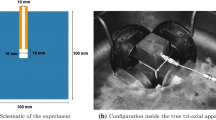
A thermodynamically consistent phase field model that accounts for initial stress state is proposed in this paper to simulate the gas migration process in saturated bentonite. The energy contribution due to the fracturing process is included in Coussy’s thermodynamic framework for unsaturated porous media. The possible effect of the interfaces between different phases on the driving force functional for phase field and the effective stress has been identified from the proposed thermodynamic framework. In addition, the initial stress state is innovatively accounted for in the phase field model by introducing a fictitious strain tensor that is calculated from its corresponding initial stress tensor. It is the sum of the fictitious strain tensor and the strain tensor due to elastic deformation that governs the evolution of the phase field. The simulated results showed that the effect of the swelling pressure (regarded as the initial effective stress for a high swelling clay) on the fracture initiation has been well described by the proposed method. Specifically, the effect of either isotropic or anisotropic stress state on the fracturing process can be well reflected by the phase field approach based on Rankine-type fracture criterion. In contrast, the phase field approach based on the Griffith fracture criterion is more appropriate for the isotropic stress state than the anisotropic stress state because of the Poisson’s effect. Moreover, the gas pressure required to trigger the fracturing process needs to exceed the sum of the porewater pressure and the initial stress. The effect of the boundary condition on the evolution of fluid pressure and total stress has been qualitatively captured. It is found that the boundary with higher stiffness leads to a higher gas pressure in the developed fracture and a higher water pressure and total stress in the surrounding porous matrix. In addition, some key experimental findings, such as the preferential gas flow, the build-up of porewater pressure, the almost fully saturated state and the localized consolidation, have been qualitatively captured by the developed phase field model.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Code Availability
All models and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Achanta, S., Cushman, J.H., Okos, M.R.: On multicomponent, multiphase thermomechanics with interfaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 32(11), 1717–1738 (1994)
Alonso, E.E., Vaunat, J., Gens, A.: Modelling the mechanical behaviour of expansive clays. Eng. Geol. 54(1–2), 173–183 (1999)
Amarasiri, A.L., Kodikara, J.K.: Numerical modeling of desiccation cracking using the cohesive crack method. Int. J. Geomech. 13(3), 213–221 (2011)
Arnedo, D., Alonso, E.E., Olivella, S.: Gas flow in anisotropic claystone: modelling triaxial experiments. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods. Geomech. 37(14), 2239–2256 (2013)
Bennethum, L.S., Murad, M.A., Cushman, J.H.: Modified Darcy’s law, Terzaghi’s effective stress principle and Fick’s law for swelling clay soils. Comput. Geotech. 20(3–4), 245–266 (1997)
Borja, R.I.: On the mechanical energy and effective stress in saturated and unsaturated porous continua. Int. J Solids Struct. 43(6), 1764–1786 (2006)
Borja, R.I., Koliji, A.: On the effective stress in unsaturated porous continua with double porosity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 57(8), 1182–1193 (2009)
Bourdin, B., Francfort, G.A., Marigo, J.J.: Numerical experiments in revisited brittle fracture. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48(4), 797–826 (2000)
Cajuhi, T., Sanavia, L., De Lorenzis, L.: Phase-field modeling of fracture in variably saturated porous media. Comput. Mech. 61, 299–318 (2018)
Carrier, B., Granet, S.: Numerical modeling of hydraulic fracture problem in permeable medium using cohesive zone model. Eng. Fract. Mech. 79, 312–328 (2012)
Chapuis, R.P., Aubertin, M.: On the use of the Kozeny Carman equation to predict the hydraulic conductivity of soils. Can. Geotech. J. 40(3), 616–628 (2003)
Chen, B., Sun, Y., Barboza, B.R., Barron, A.R., Li, C.: Phase-field simulation of hydraulic fracturing with a revised fluid model and hybrid solver. Eng. Fract. Mech. 229, 106928 (2020)
Choo, J., Borja, R.I.: Stabilized mixed finite elements for deformable porous media with double porosity. Comput. Method Appl. Mater 293, 131–154 (2015)
Choo, J., Sun, W.: Cracking and damage from crystallization in pores: coupled chemo-hydro-mechanics and phase-field modeling. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 335, 347–379 (2018)
Choo, J., Sun, W.: Coupled phase-field and plasticity modeling of geological materials: from brittle fracture to ductile flow. Comput Method Appl M 330, 1–32 (2018a)
Choo, J., Sun, W.: Cracking and damage from crystallization in pores: coupled chemo-hydro-mechanics and phase-field modeling. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 335, 47–379 (2018b)
Choo, J., White, J.A., Borja, R.I.: Hydromechanical modeling of unsaturated flow in double porosity media. Int. J. Geomech. 16(6), D4016002 (2016)
Coussy, O.: Poromechanics. Wiley, New York (2004)
Coussy, O.: Revisiting the constitutive equations of unsaturated porous solids using a Lagrangian saturation concept. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 31(15), 1675–1694 (2007)
Cueto-Felgueroso, L., Juanes, R.: A phase-field model of two-phase Hele–Shaw flow. J. Fluid Mech. 758, 522–552 (2014)
Cuss, R.J., Harrington, J.F., Noy, D.J., Graham, C.C., Sellin, P.: Evidence of localised gas propagation pathways in a field-scale bentonite engineered barrier system; results from three gas injection tests in the large scale gas injection test (Lasgit). Appl Clay Sci 102, 81–92 (2014)
Dagher, E., Nguyen, T., Sedano, J.I.: Development of a mathematical model for gas migration (two-phase flow) in natural and engineered barriers for radioactive waste disposal. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 482(SP482), 14 (2018)
Daniels, K.A., Harrington, J.: The response of compact bentonite during a 1-D gas flow test. British Geological Survey. OR/17/067 (2017)
De Lorenzis, L., McBride, A., Reddy, B.: Phase-field modelling of fracture in single crystal plasticity. GAMM-Mitteilungen 39(1), 7–34 (2016)
Doughty, C.: Modeling geologic storage of carbon dioxide: comparison of non-hysteretic and hysteretic characteristic curves. Energy Convers. Manage 48(6), 1768–1781 (2007)
Espinoza, D.N., Santamarina, J.C.: Clay interaction with liquid and supercritical CO2: the relevance of electrical and capillary forces. Int J Greenh Gas Con 10, 351–362 (2012)
Fall, M., Nasir, O., Nguyen, T.S.: A coupled hydro-mechanical model for simulation of gas migration in host sedimentary rocks for nuclear waste repositories. Eng. Geol. 176, 24–44 (2014)
Fourar, M., Lenormand, R.: A viscous coupling model for relative permeabilities in fractures. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers (1998)
Gens, A., Alonso, E.E.: A framework for the behavior of unsaturated expansive clays. Can. Geotech. J. 29(6), 1013–1032 (1992)
Gens Solé, A., Vállejan, B., Sánchez, M., Imbert, C., Villar, M.V., Van Geetl, M.: Hydromechanical behaviour of a heterogeneous compacted soil: experimental observations and modelling. Géotechnique 61(5), 367–386 (2011)
Gerard, P., Harrington, J., Charlier, R., Collin, F.: Modelling of localised gas preferential pathways in claystone. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 67, 104–114 (2014)
Graham, C.C., Harrington, J.F., Cuss, R.J., Sellin, P.: Gas migration experiments in bentonite: implications for numerical modelling. Min. Mag. 76(8), 3279–3292 (2012)
Graham, C.C., Harrington, J.F., Sellin, P.: Gas migration in pre-compacted bentonite under elevated pore-water pressure conditions. Appl. Clay Sci. 132–133, 353–365 (2016)
Gui, Y., Hu, W., Zhao, Z., Zhu, X.: Numerical modelling of a field soil desiccation test using a cohesive fracture model with Voronoi tessellations. Acta Geotech. 13, 87–102 (2017)
Guo, G., Fall, M.: Modelling of dilatancy-controlled gas flow in saturated bentonite with double porosity and double effective stress concepts. Eng. Geol. 243, 253–271 (2018)
Guo, G., Fall, M.: Modelling of preferential gas flow in heterogeneous and saturated bentonite based on phase field method. Comput. Geotech. 116, 103206 (2019)
Guo, G., Fall, M.: A double pore structure model for gas migration in saturated bentonite accounting for damaging effects and hysteresis of permeability, submitted for publication (2020)
Gurtin, M.E.: Generalized Ginzburg–Landau and Cahn–Hilliard equations based on a microforce balance. Phys. D 92(3), 178–192 (1996)
Harrington, J.,Horseman, S.: Gas migration in KBS-3 buffer bentonite, Sensitivity of Test Parameters to Experimental Boundary ConditionsSwedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Company, Stockholm (Sweden) (2003)
Harrington, J., Milodowski, A., Graham, C., Rushton, J., Cuss, R.: Evidence for gas-induced pathways in clay using a nanoparticle injection technique. Min. Mag 76(8), 3327–3336 (2012)
Harrington, J.F., Graham, C.C., Cuss, R.J., Norris, S.: Gas network development in a precompacted bentonite experiment: evidence of generation and evolution. Appl. Clay Sci. 147, 80–89 (2017)
Harrington, J., Graham, C., Cuss, R., Norris, S.: Gas network development in compact bentonite: key controls on the stability of flow pathways. Geofluids 2019, 1–19 (2019)
Heider, Y., Sun, W.: A phase field framework for capillary-induced fracture in unsaturated porous media: drying-induced vs. hydraulic cracking. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 359, 112647 (2020)
Horseman, S.T., Harrington, J.F., Sellin, P.: Gas migration in clay barriers. Eng. Geol. 54(1–2), 139–149 (1999)
Jain, A., Juanes, R.: Preferential mode of gas invasion in sediments: grain-scale mechanistic model of coupled multiphase fluid flow and sediment mechanics. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 114(B8), 1–19 (2009)
Juanes, R., Spiteri, E., Orr, F., Blunt, M.: Impact of relative permeability hysteresis on geological CO2 storage. Water Resour. Res. 42(12), 1–13 (2006)
Killough, J.: Reservoir simulation with history-dependent saturation functions. Soc. Petrol. Eng. J. 16(01), 37–48 (1976)
Lee, S., Wheeler, M.F., Wick, T.: Pressure and fluid-driven fracture propagation in porous media using an adaptive finite element phase field model. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 305, 111–132 (2016)
Lenhard, R., Parker, J.: A model for hysteretic constitutive relations governing multiphase flow: 2. Permeability-saturation relations. Water Resour. Res. 23(12), 2197–2206 (1987)
Li, W., Wei, C.: Stabilized low-order finite elements for strongly coupled poromechanical problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 115(5), 531–548 (2018)
Liu, J.F., Skoczylas, F., Talandier, J.: Gas permeability of a compacted bentonite-sand mixture: coupled effects of water content, dry density, and confining pressure. Can. Geotech. J. 52(8), 1159–1167 (2015)
Liu, J.-F., Song, Y., Skoczylas, F., Liu, J.: Gas migration through water-saturated bentonite–sand mixtures, COx argillite, and their interfaces. Can. Geotech. J. 53(1), 60–71 (2016)
Luckner, L., Vangenuchten, M.T., Nielsen, D.R.: A consistent set of parametric models for the 2-phase flow of immiscible fluids in the subsurface. Water Resour. Res. 25(10), 2187–2193 (1989)
Mahjoub, M., Rouabhi, A., Tijani, M., Granet, S., M’jahad, S., Talandier, J. : Numerical study of Callovo-Oxfordian argillite expansion due to gas injection. Int. J. Geomech. 18(1), 04017134 (2017)
Marschall, P., Horseman, S., Gimmi, T.: Characterisation of gas transport properties of the Opalinus Clay, a potential host rock formation for radioactive waste disposal. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 60(1), 121–139 (2005)
Mauthe, S., Miehe, C.: Hydraulic fracture in poro-hydro-elastic media. Mech. Res. Commun. 80, 69–83 (2017)
Miehe, C., Mauthe, S.: Phase field modeling of fracture in multi-physics problems. Part III. Crack driving forces in hydro-poro-elasticity and hydraulic fracturing of fluid-saturated porous media. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 304, 619–655 (2016)
Miehe, C., Welschinger, F., Hofacker, M.: Thermodynamically consistent phase-field models of fracture: variational principles and multi-field FE implementations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 83(10), 1273–1311 (2010a)
Miehe, C., Hofacker, M., Welschinger, F.: A phase field model for rate-independent crack propagation: robust algorithmic implementation based on operator splits. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 199(45–48), 2765–2778 (2010b)
Miehe, C., Schänzel, L.-M., Ulmer, H.: Phase field modeling of fracture in multi-physics problems. Part I. Balance of crack surface and failure criteria for brittle crack propagation in thermo-elastic solids. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 294, 449–485 (2015)
Mikelić, A., Wheeler, M.F., Wick, T.: Phase-field modeling of a fluid-driven fracture in a poroelastic medium. Comput. Geosci. 19(6), 1171–1195 (2015)
Mohammadnejad, T., Khoei, A.: Hydro-mechanical modeling of cohesive crack propagation in multiphase porous media using the extended finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 37(10), 1247–1279 (2013a)
Mohammadnejad, T., Khoei, A.: An extended finite element method for hydraulic fracture propagation in deformable porous media with the cohesive crack model. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 73, 77–95 (2013b)
Mualem, Y.: A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 12(3), 513–522 (1976)
Na, S., Sun, W.: Computational thermomechanics of crystalline rock, Part I: a combined multi-phase-field/crystal plasticity approach for single crystal simulations. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 338, 657–691 (2018)
Nguyen, T., Le, A.: Simultaneous gas and water flow in a damage-susceptible bedded argillaceous rock. Can. Geotech. J. 52(1), 18–32 (2014)
Nguyen, V.P., Lian, H., Rabczuk, T., Bordas, S.: Modelling hydraulic fractures in porous media using flow cohesive interface elements. Eng. Geol. 225(8), 68–82 (2017)
Olivella, S., Alonso, E.E.: Gas flow through clay barriers. Geotechnique 58(3), 157–176 (2008)
Parker, J., Lenhard, R.: A model for hysteretic constitutive relations governing multiphase flow: 1. Saturation-pressure relations. Water Resour. Res. 23(12), 2187–2196 (1987)
Qi, S., Vanapalli, S.K.: Simulating hydraulic and mechanical responses of unsaturated expansive soil slope to rainfall: Case Study. Int. J. Geomech. 18(6), 05018002 (2018)
Rodwell, W.R., Harris, A.W., Horseman, S.T., Lalieux, P., Muller, W., Amaya, L.O.,Pruess, K.: Gas migration and twophase flow through engineered and geological barriers for a deep repository for radioactive waste. Nuclear Energy Agency (1999)
Salimzadeh, S., Khalili, N.: A three-phase XFEM model for hydraulic fracturing with cohesive crack propagation. Comput. Geotech. 69, 82–92 (2015)
Sánchez, M., Gens, A., Villar, M.V., Olivella, S.: Fully coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical double-porosity formulation for unsaturated soils. Int. J. Geomech. 16(6), D4016015 (2016)
Santillán, D., Juanes, R., Cueto-Felgueroso, L.: Phase field model of fluid-driven fracture in elastic media: immersed-fracture formulation and validation with analytical solutions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 122(4), 2565–2589 (2017)
Santillán, D., Juanes, R., Cueto-Felgueroso, L.: Phase-field model of hydraulic fracturing in poroelastic media: fracture propagation, arrest and branching under fluid injection and extraction. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 123(3), 2127–2155 (2018)
Shin, H., Santamarina, J.: Desiccation cracks in saturated fine-grained soils: particle-level phenomena and effective-stress analysis. Géotechnique 61(11), 961 (2011)
Snow, D.T.: Anisotropie permeability of fractured media. Water Resour. Res. 5(6), 1273–1289 (1969)
Song, X., Ye, M., Wang, K.: Strain localization in a solid-water-air system with random heterogeneity via stabilized mixed finite elements. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 112(13), 1926–1950 (2017)
Spiteri, E.J., Juanes, R.: Impact of relative permeability hysteresis on the numerical simulation of WAG injection. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 50(2), 115–139 (2006)
Tamayo-Mas, E., Harrington, J., Shao, H., Dagher, E., Lee, J., Kim, K., Rutqvist, J., Lai, S., Chittenden, N., Wang, Y.: Numerical modelling of gas flow in a compact clay barrier for DECOVALEX-2019. In: Proceeding of the 2nd international discrete fracture network engineering conference, Seattle, Washington, USA, 20–22 June 2018, pp ARMA-DFNE-18-0623. ARMA (2018)
Taron, J., Elsworth, D.: Thermal–hydrologic–mechanical–chemical processes in the evolution of engineered geothermal reservoirs. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 46(5), 855–864 (2009)
Taron, J., Elsworth, D., Min, K.-B.: Numerical simulation of thermal-hydrologic-mechanical-chemical processes in deformable, fractured porous media. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 46(5), 842–854 (2009)
van Genuchten, M.T.: A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44(5), 892–898 (1980)
Wang, J.J., Zhu, J.G., Chiu, C.F., Zhang, H.: Experimental study on fracture toughness and tensile strength of a clay. Eng. Geol. 94(1–2), 65–75 (2007)
Wheeler, M.F., Wick, T., Lee, S.: IPACS: integrated phase-field advanced crack propagation simulator. An adaptive, parallel, physics-based-discretization phase-field framework for fracture propagation in porous media. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 367, 113124 (2020)
White, J.A., Borja, R.I.: Stabilized low-order finite elements for coupled solid-deformation/fluid-diffusion and their application to fault zone transients. Comput. Method Appl. Mater. 197(49–50), 4353–4366 (2008)
Wilson, Z.A., Borden, M.J., Landis, C.M.: A phase-field model for fracture in piezoelectric ceramics. Int. J. Fract. 183(2), 135–153 (2013)
Wiseall, A., Cuss, R., Graham, C., Harrington, J.: The visualization of flow paths in experimental studies of clay-rich materials. Min. Mag. 79(6), 1335–1342 (2015)
Xu, W.J., Shao, H., Hesser, J., Wang, W., Schuster, K., Kolditz, O.: Coupled multiphase flow and elasto-plastic modelling of in-situ gas injection experiments in saturated claystone (Mont Terri Rock Laboratory). Eng. Geol. 157, 55–68 (2013)
Xu, L., Ye, W.M., Ye, B., Chen, B., Chen, Y.G., Cui, Y.J.: Investigation on gas migration in saturated materials with low permeability. Eng. Geol. 197, 94–102 (2015)
Xu, L., Ye, W.M., Chen, B., Chen, Y.G., Cui, Y.J.: Experimental investigations on thermo-hydro-mechanical properties of compacted GMZ01 bentonite-sand mixture using as buffer materials. Eng. Geol. 213, 46–54 (2016)
Xu, L., Ye, W., Chen, Y., Chen, B., Cui, Y.: A new approach for determination of gas breakthrough in saturated materials with low permeability. Eng. Geol. 241, 121–131 (2018)
Ye, W.M., Xu, L., Chen, B., Chen, Y.G., Ye, B., Cui, Y.J.: An approach based on two-phase flow phenomenon for modeling gas migration in saturated compacted bentonite. Eng. Geol. 169, 124–132 (2014)
Yin, P., Vanapalli, S.K.: Model for predicting tensile strength of unsaturated cohesionless soils. Can. Geotech. J. 55(9), 1313–1333 (2018)
Zheng, L., Rutqvist, J., Xu, H., Kim, K., Voltolini, M., Cao, X.: Investigation of coupled processes and impact of high temperature limits in argillite rock: FY17 Progress. Ernest Orlando Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA (2017)
Zhou, S., Zhuang, X., Rabczuk, T.: A phase-field modeling approach of fracture propagation in poroelastic media. Eng. Geol. 240, 189–203 (2018)
Zhou, S., Zhuang, X., Rabczuk, T.: Phase field method for quasi-static hydro-fracture in porous media under stress boundary condition considering the effect of initial stress field. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 107, 102523 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the financial support from Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the China Scholarship Council and the University of Ottawa. Moreover, the authors extend their appreciations to CMC Microsystems that provides the computational resources for this study.
Funding
The authors are grateful to the financial support from Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the China Scholarship Council and the University of Ottawa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no potential conflicts of interests and competing interests.
Availability of Data and Material
All data, models, materials and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, G., Fall, M. A Thermodynamically Consistent Phase Field Model for Gas Transport in Saturated Bentonite Accounting for Initial Stress State. Transp Porous Med 137, 157–194 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01555-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01555-9