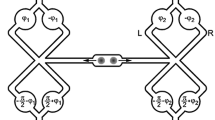
Abstract
The possibility of masking an accelerated two-qubit system by using a minimum number of qubits is discussed. It is shown that the information may be masked in either entangled local states or product non-local separable states. We examine that each partition of these states satisfies the masking conditions. Due to the presence of non-local separable partition, one may consider that it is a type of quantum data hiding scheme. The local/non-local information encoded in the masked entangled state is robust against the decoherence of the acceleration process. The possibility of estimating the acceleration parameter via the entangled/separable masked state increases as the initial entanglement value increases. The efficiency of the masking process is examined by quantifying the fidelity of the accelerated state and its subsystems. It is shown that the fidelity of the masked state is maximum at small initial acceleration, while the minimum fidelity is more than 96%.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beige, A., Englert, B.-G., Kurtsiefer, C., Weinfurter, H.: Secure communication with a publicly known key. Acta Phys. Pol. A 101, 357–368 (2002)
Jiang, D., Chen, Y., Gu, X., Xie, L., Chen, L.: Deterministic secure quantum communication using a single d-level system. Sci. Rep. 7, 44934 (2017)
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74(1), 145–195 (2002)
Fink, M., Rodriguez, A., Handsteiner, J., Ziarkash, A., Steinlechner, F., Scheidl, T., Fuentes, I., Pienaar, J., Ralph, T.C., Ursin, R.: Experimental test of photonic entanglement in accelerated reference frames. Nat. Commun. 8(1), 1–6 (2017)
Schumacher, B.: Quantum coding. Phys. Rev. A 51(4), 2738–2747 (1995)
Modi, K., Pati, A.K., Sen, A., Sen, U.: Masking quantum information is impossible. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120(23), 230501 (2018)
Ghosh, T., Sarkar, S., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Masking of quantum information is possible (2019). arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.00938
Li, M.S., Wang, Y.L.: Masking quantum information in multipartite scenario. Phys. Rev. A 98(6), 062306 (2018)
Liang, X.B., Li, B., Fei, S.M., Fan, H.: Impossibility of masking a set of quantum states of nonzero measure. Phys. Rev. A 101(4), 042321 (2020)
Liang, X.B., Li, B., Fei, S.M.: Complete characterization of qubit masking. Phys. Rev. A 100(3), 030304 (2019)
Lie, S.H., Kwon, H., Kim, M.S., Jeong, H.: Unconditionally secure qubit commitment scheme using quantum maskers (2019). arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.12304
Li, M.-S., Modi, K.: Probabilistic and approximate masking of quantum information. Phys. Rev. A 102, 022418 (2020)
Fuentes, I., Mann, R.B.: Alice falls into a black hole: entanglement in noninertial frames. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(12), 120404 (2005)
Alsing, P.M., Fuentes, I., Mann, R.B., Tessier, T.E.: Entanglement of dirac fields in noninertial frames. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 74(3), 1–15 (2006)
Moradi, S.: Distillability of entanglement in accelerated frames. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 79(6), 064301 (2009)
Landulfo, A.G.S., Matsas, G.E.A.: Sudden death of entanglement and teleportation fidelity loss via the Unruh effect. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 80(3), 032315 (2009)
Martín-Martínez, E., León, J.: Quantum correlations through event horizons: fermionic versus bosonic entanglement. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 81(3), 032320 (2010)
Metwally, N.: Entanglement of simultaneous and non-simultaneous accelerated qubit-qutrit systems. Quantum Inf. Comput. 16(5–6), 530–542 (2016)
Shi, J., Chen, J., He, J., Wu, T., Ye, L.: Inevitable degradation and inconsistency of quantum coherence in a curved space-time. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 300 (2019)
Metwally, N.: Usefulness classes of traveling entangled channels in noninertial frames. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 27(28), 1350155 (2013)
Hamdoun, H., Sagheer, A.: Information security through controlled quantum teleportation networks. Digit. Commun. Netw. 6, 463–470 (2020)
Metwally, N., Sagheer, A.: Quantum coding in non-inertial frames. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(3), 771–780 (2014)
Bradler, K., Hayden, P., Panangaden, P.: Private information via the Unruh effect. J. High Energy Phys. 8, 2008 (2009)
Yu, T., Eberly, J.H.: Evolution from entanglement to decoherence of bipartite mixed “X” states. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7(5–6), 459–468 (2007)
Martín-Martínez, E., Fuentes, I.: Redistribution of particle and antiparticle entanglement in noninertial frames. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 83(5), 1 (2011)
Shi, J.-D., Wang, D., Ye, L.: Comparative explorations of the revival and robustness for quantum dynamics under decoherence channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 1649–1659 (2016)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722 (1996)
Shi, Jia Dong, Wang, Dong, Ma, Wen Chao, Ye, Liu: Enhancing quantum correlation in open-system dynamics by reliable quantum operations. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 3569–3579 (2015)
Metwally, N.: Quantum filtering of accelerated qubit-qutrit system. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 178, 524–531 (2019)
Shi, J.-D., Xu, S., Ma, W.-C., Song, X.-K., Ye, L.: Purifying two-qubit entanglement in nonidentical decoherence by employing weak measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 1387–1397 (2015)
Metwally, N.: Protecting the handled information in Smart Cities by freezing the accelerated information. ILT, Smart Cities Symposium, Bahrain 2018 (2018) (6 pp.). https://doi.org/10.1049/cp.2018.1416
Shi, J., Wang, Y., Liu, C., He, J., Yu, L., Tao, W.: Freezing and revival of quantum coherence in decoherent reservoir. Quantum Inf. Process. 19, 385 (2020)
Peres, A.: Separability criterion for density matrices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(8), 1413–1415 (1996)
Horodecki, R., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, P.: Teleportation, Bell’s inequalities and inseparability. Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid State Phys. 222(1–2), 21–25 (1996)
Yao, Y., Xiao, X., Ge, L., Wang, X.G., Sun, C.P.: Quantum fisher information in noninertial frames. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 89(4), 1–7 (2014)
Metwally, N.: Enhancing entanglement, local and non-local information of accelerated two-qubit and two-qutrit systems via weak-reverse measurements. Eur. Phys. Lett. 116(6), 60006 (2016)
Abd-Rabbou, M.Y., Metwally, N., Ahmed, M.M.A., Obada, A.S.F.: Suppressing the information losses of accelerated qubit-qutrit system. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 17(4), 1950032 (2019)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the referee for their reports which have improved our results. This work is supported by the Academy of Scientific research and Technology (ASRT), Egypt ScienceUp Grant No. 6538.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelwahab, A.G., Ghwail, S.A., Metwally, N. et al. The concealment of accelerated information is possible. Quantum Inf Process 20, 71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03009-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03009-z