Abstract
Rationale
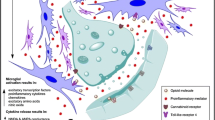
Opioid and GABAA receptors are both located in central nociceptive pathways, and compounds that activate these receptors have pain-relieving properties. To date, the interactive effects of concurrent administration of these compounds in preclinical models of pain-like behaviors have not been assessed.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to examine the interactive effects of the μ-opioid agonist morphine and the α2GABAA and α3GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator methyl 8-ethynyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate (MP-III-024) in preclinical models of mechanical hyperalgesia and thermal nociception.
Methods
The antihyperalgesic and antinociceptive effects of morphine and MP-III-024 administered alone were assessed initially, followed by fixed-ratio mixtures of MP-III-024/morphine combinations. Drug interaction data were analyzed using isobolographic and dose-addition analyses. All studies were conducted in male CD-1 mice.
Results
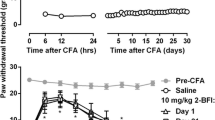
In the assay of mechanical hyperalgesia, each compound produced dose-dependent antihyperalgesic effects, whereas only morphine was effective on thermal nociception. Fixed-ratio mixtures of MP-III-024/morphine were also dose-dependently effective in both procedures. These drug combination studies revealed that morphine and MP-III-024 produced supra-additive (synergistic) effects in both assays, depending on their relative proportions.
Conclusions
These results demonstrate an interaction between α2GABAA and α3GABAA receptor- and μ-opioid receptor-mediated signals and suggest that combination therapy may be useful for the treatment of pain-related disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benyamin R, Trescot AM, Datta S, Buenaventura R, Adlaka R, Sehgal N, Glaser SE, Vallejo R (2008) Opioid complications and side effects. Pain Physic 11(2 Suppl):S105–S120
Biggerstaff A, Kivell B, Smith JL, Mian MY, Golani LK, Rashid F, Sharmin D, Knutson DE, Cerne R, Cook JM, Witkin JM (2020) The α2,3-selective potentiators of GABAA receptors, KRM-II-81 and MP-III-80, produce anxiolytic-like effects and block chemotherapy-induced hyperalgesia in mice without tolerance development. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 196:172996
Chudomel O, Herman H, Nair K, Moshé SL, Galanopoulou AS (2009) Age- and gender-related differences in GABAA receptor-mediated postsynaptic currents in GABAergic neurons of the substantia nigra reticulata in the rat. Neuroscience 163(1):155–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.06.025
Davies M (2003) The role of GABAA receptors in mediating the effects of alcohol in the central nervous system. J Psychiat Neurosci : JPN 28(4):263–274
de Lucas AG, Ahring PK, Larsen JS, Rivera-Arconada I, Lopez-Garcia JA, Mirza NR, Munro G (2015) GABAA α5 subunit-containing receptors do not contribute to reversal of inflammatory-induced spinal sensitization as indicated by the unique selectivity profile of the GABAA receptor allosteric modulator NS16085. Biochem Pharmacol 93(3):370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2014.12.010
Di Lio A, Benke D, Besson M, Desmeules J, Daali Y, Wang ZJ et al (2011) HZ166, a novel GABAA receptor subtype-selective benzodiazepine site ligand, is antihyperalgesic in mouse models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 60(4):626–632
Egerton A, Modinos G, Ferrera D, McGuire P (2017) Neuroimaging studies of GABA in schizophrenia: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Transl Psychiatry 7(6):e1147–e1147
Fischer BD, Miller LL, Henry FE, Picker MJ, Dykstra LA (2008) Increased efficacy of μ-opioid agonist-induced antinociception by metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists in C57BL/6 mice: comparison with (−)-6-phosphonomethyl-deca-hydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (LY235959). Psychopharmacology 198(2):271–278
Fischer BD, Licata SC, Edwankar RV, Wang ZJ, Huang S, He X, Yu J, Zhou H, Johnson EM Jr, Cook JM, Furtmüller R, Ramerstorfer J, Sieghart W, Roth BL, Majumder S, Rowlett JK (2010) Anxiolytic-like effects of 8-acetylene imidazobenzodiazepines in a rhesus monkey conflict procedure. Neuropharmacology 59:612–618
Fischer BD, Atack JR, Platt DM, Reynolds DS, Dawson GR, Rowlett JK (2011) Contribution of GABA(A) receptors containing α3 subunits to the therapeutic-related and side effects of benzodiazepine-type drugs in monkeys. Psychopharmacology 215(2):311–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2142-y
Fischer BD, Schlitt RJ, Hamade BZ, Rehman S, Ernst M, Poe MM, Li G, Kodali R, Arnold LA, Cook JM (2017) Pharmacological and antihyperalgesic properties of the novel α2/3 preferring GABAA receptor ligand MP-III-024. Brain Res Bull 131:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.03.001
Gessner PK, Cabana BE (1970) A study of the interaction of the hypnotic effects and of the toxic effects of chloral hydrate and ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 174(2):247–259
Jamison RN, Mao J (2015) Opioid Analgesics. Mayo Clin Proc 90(7):957–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.04.010
Knabl J, Witschi R, Hösl K, Reinold H, Zeilhofer UB, Ahmadi S, Brockhaus J, Sergejeva M, Hess A, Brune K, Fritschy JM, Rudolph U, Möhler H, Zeilhofer HU (2008) Reversal of pathological pain through specific spinal GABAA receptor subtypes. Nature 451(7176):330–334
Knabl J, Zeilhofer UB, Crestani F, Rudolph U, Zeilhofer HU (2009) Genuine antihyperalgesia by systemic diazepam revealed by experiments in GABAA receptor point-mutated mice. Pain 141(3):233–238
Le Merrer J, Becker JA, Befort K, Kieffer BL (2009) Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol Rev 89(4):1379–1412. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00005.2009
Lewter LA, Fisher JL, Siemian JN, Methuku KR, Poe MM, Cook JM, Li JX (2017) Antinociceptive effects of a novel α2/α3-subtype selective GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. ACS Chem Neurosci 8(6):1305–1312
Li C, Lei Y, Tian Y, Xu S, Shen X, Wu H, Bao S, Wang F (2019) The etiological contribution of GABAergic plasticity to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 15:1744806919847366. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806919847366
McCurdy CR, Prisinzano TE, Abraham DJ (2003) Opioid Receptor Ligands, Burger's Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, Hoboken
Munro G, Lopez-Garcia JA, Rivera-Arconada I, Erichsen HK, Nielsen EØ, Larsen JS, Mirza NR (2008) Comparison of the novel subtype-selective GABAA receptor-positive allosteric modulator NS11394 [3′-[5-(1-hydroxy-1-methyl-ethyl)-benzoimidazol-1-yl]-biphenyl-2-carbonitrile] with diazepam, zolpidem, bretazenil, and gaboxadol in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327(3):969–981
Paul J, Yévenes GE, Benke D, Di Lio A, Ralvenius WT, Witschi R, Scheurer L, Cook JM, Rudolph U, Fritschy JM, Zeilhofer HU (2014) Antihyperalgesia by α2-GABAA receptors occurs via a genuine spinal action and does not involve supraspinal sites. Neuropsychopharmacology 39(2):477–487. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.221
Poe MM, Methuku KR, Li G, Verma AR, Teske KA, Stafford DC, Arnold LA, Cramer JW, Jones TM, Cerne R, Krambis MJ, Witkin JM, Jambrina E, Rehman S, Ernst M, Cook JM, Schkeryantz JM (2016) Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A (GABAA) Receptor Ligand That Combines Outstanding Metabolic Stability, Pharmacokinetics, and Anxiolytic Efficacy. J Med Chem 59:10800–10806
Ralvenius WT, Benke D, Acuña MA, Rudolph U, Zeilhofer HU (2015) Analgesia and unwanted benzodiazepine effects in point-mutated mice expressing only one benzodiazepine-sensitive GABAA receptor subtype. Nat Commun 6:6803
Rudolph U, Knoflach F (2011) Beyond classical benzodiazepines: novel therapeutic potential of GABA A receptor subtypes. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(9):685–697
Shang Y, Filizola M (2015) Opioid receptors: Structural and mechanistic insights into pharmacology and signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 763(Pt B):206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.012
Siemian JN, Obeng S, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li JX (2016) Antinociceptive interactions between the imidazoline I2 receptor agonist 2-BFI and opioids in rats: role of efficacy at the μ-opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 357(3):509–519
Tallarida RJ (2000) Drug Synergism and Dose-Effect Data Analysis. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton
Tallarida RJ (2002) The interaction index: a measure of drug synergism. Pain 98:163–168
Witkin JM, Cerne R, Davis PG, Freeman KB, do Carmo JM, Rowlett JK, Methuku KR, Okun A, Gleason SD, Li X, Krambis MJ, Poe M, Li G, Schkeryantz JM, Jahan R, Yang L, Guo W, Golani LK, Anderson WH, Catlow JT, Jones TM, Porreca F, Smith JL, Knopp KL, Cook JM (2019) The α2,3-selective potentiator of GABAA receptors, KRM-II-81, reduces nociceptive-associated behaviors induced by formalin and spinal nerve ligation in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 180:22–31
Witschi R, Punnakkal P, Paul J, Walczak JS, Cervero F, Fritschy JM, Kuner R, Keist R, Rudolph U, Zeilhofer HU (2011) Presynaptic alpha2-GABAA receptors in primary afferent depolarization and spinal pain control. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 31(22):8134–8142. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6328-10.2011
Zeilhofer HU, Wildner H, Yévenes GE (2012) Fast synaptic inhibition in spinal sensory processing and pain control. Physiol Rev 92:193–235
Zhu Q, Sun Y, Mao L, Liu C, Jiang B, Zhang W, Li JX (2016) Antinociceptive effects of sinomenine in a rat model of postoperative pain. Br J Pharmacol 173(10):1693–1702
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by internal funds from Rowan University and Cooper Medical School of Rowan University. We also acknowledge the NIH for generous financial support (DA041560, DA043204, NS076517), the Milwaukee Institute for Drug Discovery and the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee’s Shimadzu Laboratory for Advanced and Applied Analytical Chemistry for help with spectroscopy, and the National Science Foundation (Division of Chemistry, CHE-1625735).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The corresponding author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.A., Keck, T.M., Poe, M.M. et al. Synergistic antihyperalgesic and antinociceptive effects of morphine and methyl 8-ethynyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate (MP-III-024): a positive allosteric modulator at α2GABAA and α3GABAA receptors. Psychopharmacology 238, 1585–1592 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05791-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05791-1