Abstract
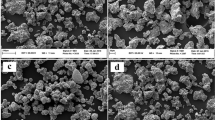
Open cell steel foams were successfully fabricated through the powder metallurgy route using urea granules as the water leachable space holder in the present study. The influence of different amounts of phosphorus (0, 0.5wt%, 1wt%, 2wt%, and 4wt%) was investigated on the cell morphology, porosity, microstructure of cell walls, and mechanical properties of steel foams. The cell morphology and microstructure of the cell walls were evaluated using an optical microscope equipped with image processing software and a scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer. In addition, the compression tests were conducted on the steel foams using a universal testing machine. Based on microscopic images, the porous structure consists of spherical cells and irregularly shaped pores that are distributed in the cell walls. The results indicated that by increasing the phosphorus content, the porosity increases from 71.9% to 83.2%. The partially distributed ferrite and fine pearlite was observed in the microstructure of the cell walls, and α-Fe and Fe3P eutectic extended between the boundaries of agglomerated iron particles. Furthermore, elastic and long saw-toothed plateau regions were observed before fracture in the compressional stress—strain curves. According to the results, by increasing the phosphorus content from 0 to 4wt%, the plateau region of the stress—strain curves shifts to the right and upward. Therefore, increasing phosphorus content causes improvement in the mechanical properties of steel foams.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ashby, T. Evans, N.A. Fleck, J.W. Hutchinson, H.N.G. Wadley, and L.J. Gibson, Metal Foams: A Design Guide, Elsevier Inc, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2000.
H.P. Degischer and B. Kriszt, Handbook of Cellular Metals, Production, Processing, Applications, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, 2002.
J. Banhart, Manufacture, characterization and application of cellular metals and metal foams, Prog. Mater. Sci., 46(2001), No. 6, p. 559.
Y. Bienvenu, Application and future of solid foams, C.R. Phys., 15(2014), No. 8–9, p. 719.
N. Gupta and P.K. Rohatgi, Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams: Processing, Microstructure, Properties and Applications, DEStech Publications, 2014.
A.J. Otaru, Review on processing and fluid transport in porous metals with a focus on bottleneck structures, Met. Mater. Int., 26(2020), No. 4, p. 510.
R. Kumar, H. Jain, S. Sriram, A. Chaudhary, A. Khare, V.A.N. Ch, and D.P. Mondal, Lightweight open cell aluminum foam for superior mechanical and electromagnetic interference shielding properties, Mater. Chem. Phys., 240(2020), art. No. 122274.
C.J. Liu, Y.X. Zhang, and J. Li, Impact responses of sandwich panels with fibre metal laminate skins and aluminium foam core, Compos. Struct., 182(2017), p. 183.
C. Liu, Y.X. Zhang, and L. Ye, High velocity impact responses of sandwich panels with metal fibre laminate skins and aluminium foam core, Int. J. Impact Eng., 100(2017), p. 139.
I. Duarte, M. Vesenjak, L. Krstulović-Opara, and Z. Ren, Crush performance of multifunctional hybrid foams based on an aluminium alloy open-cell foam skeleton, Polym. Test., 67(2018), p. 246.
J.H. Fan, J.J. Zhang, Z.H. Wang, Z.Q. Li, and L.M. Zhao, Dynamic crushing behavior of random and functionally graded metal hollow sphere foams, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 561(2013), p. 352.
L.B. Li, Z.J. Zheng, J.L. Yu, and F.Y. Lu, Deformation and perforation of sandwich panels with aluminum-foam core at elevated temperatures, Int. J. Impact Eng., 109(2017), p. 366.
L. Jing, Z.H. Wang, and L.M. Zhao, The dynamic response of sandwich panels with cellular metal cores to localized impulsive loading, Composite Part B, 94(2016), p. 52.
J.J. Wu, C.G. Li, D.B. Li, and M.C. Gui, Damping and sound absorption properties of particle reinforced Al matrix composite foams, Compos. Sci. Technol., 63(2003), No. 3–4, p. 569.
H. Huisseune, S. de Schampheleire, B. Ameel, and M. de Paepe, Comparison of metal foam heat exchangers to a finned heat exchanger for low Reynolds number applications, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 89(2015), p. 1.
D.Y. Kim, T.H. Sung, and K.C. Kim, Application of metal foam heat exchangers for a high-performance liquefied natural gas regasification system, Energy, 105(2016), p. 57.
C.J. Tseng, Y.J. Heush, C.J. Chiang, Y.H. Lee, and K.R. Lee, Application of metal foams to high temperature PEM fuel cells, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 41(2016), No. 36, p. 16196.
S.T. Kolaczkowski, S. Awdry, T. Smith, D. Thomas, L. Torkuhl, and R. Kolvenbach, Potential for metal foams to act as structured catalyst supports in fixed-bed reactors, Catal. Today, 273(2016), p. 221.
J. Seok, K.M. Chun, S. Song, and J. Lee, An empirical study of the dry soot filtration behavior of a metal foam filter on a particle number concentration basis, Energy, 76(2014), p. 949.
I. Garcia, E. Gracia-Escosa, M. Bayod, A. Conde, M.A. Arenas, J. Damborenea, A. Romero, and G. Rodríguez, Sustainable production of titanium foams for biomedical applications by Concentrated Solar Energy sintering, Mater. Lett., 185(2016), p. 420.
S. Kashef, A. Asgari, T.B. Hilditch, W.Y. Yan, V.K. Goel, and P.D. Hodgson, Fracture toughness of titanium foams for medical applications, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 29–30, p. 7689.
J. Banhart, Production of metal foams, [in] P.W.R. Beaumont and C.H. Zweben, eds., Comprehensive Composite Materials II, 2nd ed., Elsevier, 2018, p. 347.
S. Kim, and C.W. Lee, A review on manufacturing and application of open-cell metal foam, Procedia Mater. Sci., 4(2014), p. 305.
B.H. Smith, S. Szyniszewski, J.F. Hajjar, B.W. Schafer, and S.R. Arwade, Steel foam for structures: A review of applications, manufacturing and material properties, J. Constr. Steel. Res., 71(2012), p. 1.
M.H. Golabgir, R. Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi, O. Torabi, H. Tajizadegan, and A. Jamshidi, Fabrication and evaluation of oxidation resistance performance of open-celled Fe(Al) foam by space-holder technique, Adv. Powder. Technol., 25(2014), No. 3, p. 960.
B. Xie, Y.Z. Fan, T.Z. Mu, and B. Deng, Fabrication and energy absorption properties of titanium foam with CaCl2 as a space holder, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 708(2017), p. 419.
B.Q. Li, Z.Q. Li, and X. Lu, Effect of sintering processing on property of porous Ti using space holder technique, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 25(2015), No. 9, p. 2965.
S.F. Aida, M.N. Hijrah, A.H. Amirah, H. Zuhailawati, and A.S. Anasyida, Effect of NaCl as a space holder in producing open cell A356 aluminium foam by gravity die casting process, Procedia Chem., 19(2016), p. 234.
G.Z. Jia, Y. Hou, C.X. Chen, J.L. Niu, H. Zhang, H. Huang, M.P. Xiong, and G.Y. Yuan, Precise fabrication of open porous Mg scaffolds using NaCl templates: Relationship between space holder particles, pore characteristics and mechanical behavior, Mater. Des., 140(2018), p. 106.
Y. Torres, J.J. Pavón, and J.A. Rodríguez, Processing and characterization of porous titanium for implants by using NaCl as space holder, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 212(2012), No. 5, p. 1061.
E. Ruperez, J.M. Manero, K. Riccardi, Y.P. Li, C. Aparicio, and F.J. Gil, Development of tantalum scaffold for orthopedic applications produced by space-holder method, Mater. Des., 83(2015), p. 112.
I. Unver, H.O. Gulsoy, and B. Aydemir, Ni-625 superalloy foam processed by powder space-holder technique, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 22(2013), No. 12, p. 3735.
D.R. Tian, Y.H. Pang, L. Yu, and L. Sun, Production and characterization of high porosity porous Fe-Cr-C alloys by the space holder leaching technique, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 23(2016), No. 7, p. 793.
H. Bafti and A. Habibolahzadeh, Production of aluminum foam by spherical carbamide space holder technique-processing parameters, Mater. Des., 31(2010), No. 9, p. 4122.
S.A. Hosseini, R. Yazdani-Rad, A. Kazemzadeh, and M. Alizadeh, A comparative study on the mechanical behavior of porous titanium and NiTi produced by a space holder technique, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 23(2014), No. 3, p. 799.
M. Sharma, G.K. Gupta, O.P. Modi, B.K. Prasad, and A.K. Gupta, Titanium foam through powder metallurgy route using acicular urea particles as space holder, Mater. Lett., 65(2011), No. 21–22, p. 3199.
G. Adamek and J. Jakubowicz, Tantalum foam made with sucrose as a space holder, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 53(2015), p. 51.
A. Mansourighasri, N. Muhamad, and A.B. Sulong, Processing titanium foams using tapioca starch as a space holder, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 212(2012), No. 1, p. 83.
E.E. Asik and Ş. Bor, Fatigue behavior of Ti-6Al-4V foams processed by magnesium space holder technique, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 621(2015), p. 157.
T. Aydoğmuş, E.T. Bor, and Ş. Bor, Phase transformation behavior of porous TiNi alloys produced by powder metallurgy using magnesium as a space holder, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 42(2011), No. 9, p. 2547.
T. Shimizu, K. Matsuzaki, H. Nagai, and N. Kanetake, Production of high porosity metal foams using EPS beads as space holders, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 558(2012), p. 343.
J. Kadkhodapour, H. Montazerian, M. Samadi, S. Schmauder, and A. Abouei Mehrizi, Plastic deformation and compressive mechanical properties of hollow sphere aluminum foams produced by space holder technique, Mater. Des., 83(2015), p. 352.
N. Bekoz and E. Oktay, Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties of low alloy steel foams, Mater. Des., 51(2013), p. 212.
N. Bekoz and E. Oktay, High temperature mechanical properties of low alloy steel foams produced by powder metallurgy, Mater. Des., 53(2014), p. 482.
I. Mutlu and E. Oktay, Processing and properties of highly porous 17-4 PH stainless steel, Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 50(2011), No. 1–2, p. 73.
M. Mirzaei and M.H. Paydar, Fabrication and characterization of core-shell density-graded 316L stainless steel porous structure, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 28(2019), No. 1, p. 221.
Q. Pang, Z.L. Hu, and G.R. Wang, Effect of Ce content on mechanical properties of Ce/Cr coated open-cell Ni-Cr-Fe alloy foams, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 27(2017), No. 5, p. 1052.
M. Mirzaei and M.H. Paydar, A novel process for manufacturing porous 316L stainless steel with uniform pore distribution, Mater. Des., 121(2017), p. 442.
N. Bekoz and E. Oktay, Effects of carbamide shape and content on processing and properties of steel foams, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 212(2012), No. 10, p. 2109.
H.Ö. Gulsoy and R.M. German, Sintered foams from precipitation hardened stainless steel powder, Powder Metall., 51(2008), No. 4, p. 350.
H. Sazegaran and M. Hojati, Effects of copper content on microstructure and mechanical properties of open-cell steel foams, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 26(2019), No. 5, p. 588.
H. Okamoto, The Fe-P (iron-phosphorus) system, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagram, 11(1990), No. 4, p. 404.
Y. Yin, Z.M. Li, and S.M. Zhai, The phase diagram of the Fe-P binary system at 3 GPa and implications for phosphorus in the lunar core, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 254(2019), p. 54.
H. Sazegaran, A. Feizi, and M. Hojati, Effect of Cr contents on the porosity percentage, microstructure, and mechanical properties of steel foams manufactured by powder metallurgy, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 72(2019), No. 10, p. 2819.
A.A.S. Abosbaia, S.C. Mitchell, M. Youseffi, and A.S. Wronski, Liquid phase sintering, heat treatment and properties of ultrahigh carbon steel, Powder Metall., 54(2011), No. 5, p. 592.
M. Turkmen, Effect of carbon content on microstructure and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy steels, Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 55(2016), No. 3–4, p. 164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sazegaran, H., Nezhad, S.M.M. Cell morphology, porosity, microstructure and mechanical properties of porous Fe-C-P alloys. Int J Miner Metall Mater 28, 257–265 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-1995-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-1995-2