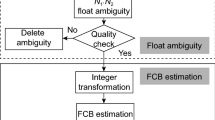
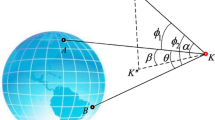
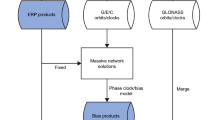
Abstract
While precise point positioning ambiguity resolution (PPP AR) is a valuable tool of the multi-constellation global navigation satellite system (multi-GNSS), phase biases are critical to implement PPP AR. Multi-frequency phase biases and satellite attitude files are provided freely by Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), which are estimated based on GeoForschungs Zentrum (GFZ) satellite rapid orbit and clock products. However, the temporal characteristics of these phase biases and their positioning performance in the multi-frequency and multi-GNSS PPP AR have not been investigated yet, especially in the low sun elevation and satellite maneuver period. We introduce the transformation between multi-frequency phase biases and integer recovery clock model. In this transformation, inter-frequency clock biases (IFCBs) and inconsistencies in satellite attitude model errors between GFZ and CNES products are well considered. Experiments with GPS/Galileo/BeiDou observations from 34 stations were performed in static and kinematic modes, and the multi-frequency phase residuals were analyzed in the low sun elevation. Our results show that the impact of IFCBs and inconsistencies in satellite attitude errors could be mitigated at the user ends by using phase biases and satellite attitude files. Under the condition of satellite reverse yaw maneuvers, the performance of kinematic PPP without phase biases or deleting maneuvering satellites would be degraded significantly until the end of satellite observation arc or the next reverse yaw maneuver occurs. By applying phase biases with PPP AR, the positioning accuracy could be improved by 34.4%, 23.1%, and 37.4% in the east (E), north (N), and up (U) directions, respectively. Therefore, we suggested that PPP users should apply phase biases and satellite attitude files when using the GFZ rapid orbit and clock products, especially for satellite maneuvers and low sun elevation.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The availability of multi-frequency phase biases and satellite attitude files is provided freely by CNES (www.ppp-wizard.net/ products/POST_PROCESSED). The rapid orbit and clock products are provided freely by GFZ (ftp://ftp.gfz-potsdam.de/pub/GNSS/products/mgnss). GNSS data, IGS SINEX weekly solutions files, and igs_2084.atx files are provided freely by IGS and MGEX (https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gps/data/daily).
References
Banville S, Geng J, Loyer S, Schaer S, Springer T, Strasser S (2020) On the interoperability of IGS products for precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution. J Geod 94(10):1–15
Cao X, Li J, Zhang S, Kuang K, Gao K, Zhao Q, Hu H (2018) Uncombined precise point positioning with triple-frequency GNSS signals. Adv Space Res 63(9):2745–2756
Collins P, Lahaye F, Herous P, Bisnath S (2008) Precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution using the decoupled clock model. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2008, Institute of Navigation. Savannah, Georgia, 16–19 September, pp 1315–1322
Dilssner F, Springer T, Enderle W (2011) GPS IIF yaw attitude control during eclipse season, AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, Dec 9, http://acc.igs.org/orbits/yaw-IIF_ESOC_agu11.pdf
Ge M, Gendt G, Rothacher M, Shi C, Liu J (2008) Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in Precise Point Positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J Geod 82(7):389–399
Geng J, Meng X, Dodson A, Teferle F (2010) Integer ambiguity resolution in precise point positioning: method comparison. J Geod 84(9):569–581
Geng J, Guo J, Chang H, Li X (2019) Toward global instantaneous decimeter-level positioning using tightly coupled multi-constellation and multi-frequency GNSS. J Geod 93:977–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1219-y
Guo J, Geng J (2018) GPS satellite clock determination in case of inter-frequency clock biases for triple-frequency precise point positioning. J Geod 92(10):1133–1142
Kouba J (2009) A simplified yaw-attitude model for eclipsing GPS satellites. GPS Solut 13(1):1–12
Kouba J, Héroux P (2001) Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solut 5(2):12–28
Kuang D, Desai S, Sibois A (2017) Observed features of GPS Block IIF satellite yaw maneuver and corresponding modeling. GPS Solut 21(2):739–745
Laurichesse D, Mercier F (2009) Integer ambiguity resolution on undifferenced GPS phase measurements and its application to PPP and satellite precise orbit determination. Navig J Inst Navig 56(2):135–149
Laurichesse D, Privat A (2015) An open-source PPP client implementation for the CNES PPP-WIZARD demonstrator. In: Proceedings ION GNSS 2015, Institute of Navigation, Tampa, USA, September 14–18, pp 2780–2789
Li P, Zhang X, Ren X, Zuo X, Pan Y (2016) Generating GPS satellite fractional cycle bias for ambiguity-fixed precise point positioning. GPS Solut 20(4):771–782
Li P, Zhang X, Guo F (2017) Ambiguity resolved precise point positioning with GPS and BeiDou. J Geod 91(1):25–40
Li P, Zhang X, Ge M, Schuh H (2018) Three-frequency bds precise point positioning ambiguity resolution based on raw observables. J Geod 92(12):1357–1369
Li X, Li X, Liu G, Feng G, Yuan Y, Zhang K, Ren X (2019) Triple-frequency PPP ambiguity resolution with multi-constellation GNSS: BDS and Galileo. J Geod 93(3):1105–1122
Liu X, Jiang W, Li Z, Chen H, Zhao W (2019) An analysis of inter-system biases in BDS/GPS precise point positioning. GPS Solut 23(4):1–14
Liu T, Jiang W, Laurichesse D, Chen H, Liu X, Wang J (2020) Assessing GPS/Galileo real-time precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution based on phase biases from CNES. Adv Space Res 66(4):810–825
Lou Y, Zheng F, Gu S, Liu Y (2015) The impact of non-nominal yaw attitudes of GPS Satellites on Kinematic PPP Solutions and their Mitigation Strategies. J Navgation 68(4):1–17
Loyer S, Banville S, Perosanz F, Mercier F (2017) Disseminating GNSS satellite attitude for improved clock correction consistency. Poster presented at the 2017 IGS Workshop, Paris
Malys S, Jensen PA (1990) Geodetic point positioning with GPS carrier beat phase data from the CASA UNO experiment. Geophys Res Lett 17(5):634–654
Montenbruck O, Hugentobler U, Dach R, Steigenberger P, Hauschild A (2012) Apparent clock variations of the Block IIF-1 (SVN62) GPS satellite. GPS Solut 16(3):303–313
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Prange L, Deng Z, Zhao Q, Perosanz F, Romero I, Noll C, Stuerze A, Weber G, Schmid R, Macleod K, Schaer S (2017) The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)-achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv Space Res 59(7):1671–1697
Pan L, Zhang X, Li X (2017) Characteristics of inter-frequency clock bias for Block IIF satellites and its effect on triple-frequency GPS precise point positioning. GPS Solut 21(2):811–822
Schaer S (2016) Bias-SINEX format and implications for IGS bias products. IGS Workshop. Australia, February, Sydney, pp 8–12
Shi J, Gao Y (2014) A comparison of three PPP integer ambiguity resolution methods. GPS Solut 18(4):349–528
Steigenberger P, Montenbruck O (2019) Consistency of MGEX Orbit and Clock Products. Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2019.12.005
Teunissen P (1995) The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J Geod 70(1–2):65–82
Wang C, Guo J, Zhao Q, Liu J (2018) Yaw attitude modeling for BeiDou I06 and BeiDou-3 satellites. GPS Solut 22(4):1–10
Wu J, Wu S (1993) Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscripta Geod 18(2):91–98
Xia F, Ye S, Chen D, Jiang N (2019) Observation of BDS-2 IGSO/MEOs yaw-attitude behavior during eclipse seasons. GPS Solut 23(3):23–71
Zhang X, Li P (2016) Benefits of the third frequency signal on cycle slip correction. GPS Solut 20(3):434–460
Zhou F, Dong D, Li P, Li X, Schuh H (2019) Influence of stochastic modeling for inter-system biases on multi-GNSS undifferenced and uncombined precise point positioning. GPS Solut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0852-0
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102(B3):5005–5017
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge IGS MGEX for providing GNSS data. We also acknowledge the GFZ and CNES for providing precise products. This research was funded by Natural Science Innovation Group Foundation of China (No. 41721003), National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 41525014), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1503600), National Dam Safety Research Center (Grant No. CX2019B05), National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 41704030), and Opening Foundation of Hunan Engineering and Research Center of Natural Resource Investigation and Monitoring (2020-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Chen, H., Chen, Q. et al. Characteristics of phase bias from CNES and its application in multi-frequency and multi-GNSS precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 25, 58 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01100-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01100-7