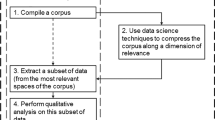
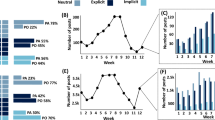
Abstract
How did the popularity of the Greek Prime Minister evolve in 2015? How did the predominant sentiment about him vary during that period? Were there any controversial sub-periods? What other entities were related to him during these periods? To answer these questions, one needs to analyze archived documents and data about the query entities, such as old news articles or social media archives. In particular, user-generated content posted in social networks, like Twitter and Facebook, can be seen as a comprehensive documentation of our society, and thus, meaningful analysis methods over such archived data are of immense value for sociologists, historians, and other interested parties who want to study the history and evolution of entities and events. To this end, in this paper we propose an entity-centric approach to analyze social media archives and we define measures that allow studying how entities were reflected in social media in different time periods and under different aspects, like popularity, attitude, controversiality, and connectedness with other entities. A case study using a large Twitter archive of 4 years illustrates the insights that can be gained by such an entity-centric and multi-aspect analysis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
http://www.internetlivestats.com/twitter-statistics/ (August 30, 2018).
https://www.nytimes.com/2016/03/31/us/politics/donald-trump-abortion.html (August 30, 2018).
References
Amigó, E., Carrillo de Albornoz, J., Chugur, I., Corujo, A., Gonzalo, J., Meij, E., de Rijke, M., Spina, D.: Overview of replab 2014: Author profiling and reputation dimensions for online reputation management. In: CLEF (2014)
Ardon, S., Bagchi, A., Mahanti, A., Ruhela, A., Seth, A., Tripathy, RM., Triukose, S.: Spatio-temporal analysis of topic popularity in Twitter. arXiv preprint arXiv:1111.2904 (2011)
Batrinca, B., Treleaven, P.C.: Social media analytics: a survey of techniques, tools and platforms. AI & SOCIETY 30(1), 89–116 (2015)
Blanco, R., Ottaviano, G., Meij, E.: Fast and space-efficient entity linking for queries. In: WSDM (2015)
Bruns, A., Stieglitz, S.: Towards more systematic Twitter analysis: metrics for tweeting activities. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 16(2), 91–108 (2013)
Bruns, A., Weller, K.: Twitter as a first draft of the present: and the challenges of preserving it for the future. In: WebSci (2016)
Celik, I., Abel, F., Houben, G.J.: Learning semantic relationships between entities in Twitter. In: ICWE (2011)
Chandrasekaran, B., Josephson, J.R., Benjamins, V.R.: What are ontologies, and why do we need them? IEEE Intell. Syst. Appl. 14(1), 20–26 (1999)
Chang, Y., Wang, X., Mei, Q., Liu, Y.: Towards twitter context summarization with user influence models. In: WSDM (2013)
Chang, Y., Tang, J., Yin, D., Yamada, M., Liu, Y.: Timeline summarization from social media with life cycle models. In: IJCAI (2016)
Chen, P.P.S.: The entity-relationship model toward a unified view of data. ACM Trans. Database Syst. (TODS) 1(1), 9–36 (1976)
Fafalios, P., Holzmann, H., Kasturia, V., Nejdl, W.: Building and querying semantic layers for web archives. In: 2017 ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries (JCDL), pp 1–10. IEEE (2017a)
Fafalios, P., Iosifidis, V., Stefanidis, K., Ntoutsi, E.: Multi-aspect entity-centric analysis of big social media archives. In: International Conference on Theory and Practice of Digital Libraries, pp 261–273. Springer (2017b)
Fafalios, P., Holzmann, H., Kasturia, V., Nejdl, W.: Building and querying semantic layers for web archives (extended version). Int. J. Digit. Libr. (2018a) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00799-018-0251-0
Fafalios, P., Iosifidis, V., Ntoutsi, E., Dietze, S.: Tweetskb: A public and large-scale rdf corpus of annotated tweets. In: European Semantic Web Conference, pp. 177–190. Springer (2018b)
Farzindar, A., Khreich, W.: A survey of techniques for event detection in twitter. Comput. Intell. 31(1), 132–164 (2015)
Garimella, K., Morales, G.D.F., Gionis, A., Mathioudakis, M.: Quantifying controversy on social media. ACM Trans. Soc. Comput. 1(1), 3 (2018)
Guille, A., Hacid, H., Favre, C., Zighed, D.A.: Information diffusion in online social networks: a survey. SIGMOD Rec. 42(2), 17–28 (2013)
Heath, T., Bizer, C.: Linked data: evolving the web into a global data space. Synth. Lect. Semant. Web Theory Technol. 1(1), 1–136 (2011)
Iosifidis, V., Ntoutsi, E.: Large scale sentiment learning with limited labels. In: KDD (2017)
Kucuktunc, O., Cambazoglu, B.B., Weber, I., Ferhatosmanoglu, H.: A large-scale sentiment analysis for Yahoo! answers. In: WSDM (2012)
Lehmann, J., Isele, R., Jakob, M., Jentzsch, A., Kontokostas, D., Mendes, P.N., Hellmann, S., Morsey, M., Van Kleef, P., Auer, S.: Dbpedia-a large-scale, multilingual knowledge base extracted from Wikipedia. Semant. Web 6(2), 167–195 (2015)
Li, J., Cardie, C.: Timeline generation: Tracking Individuals on Twitter. In: WWW (2014)
Meng, X., Wei, F., Liu, X., Zhou, M., Li, S., Wang, H.: Entity-centric topic-oriented opinion summarization in Twitter. In: KDD (2012)
Mohapatra, N., Iosifidis, V., Ekbal, A., Dietze, S., Fafalios, P.: Time-aware and corpus-specific entity relatedness. In: Workshop on Deep Learning for Knowledge Graphs and Semantic Technologies (DL4KGS)—In conjunction with ESWC 2018, Heraklion, Greece (2018)
Nakov, P., Ritter, A., Rosenthal, S., Sebastiani, F., Stoyanov, V.: Semeval-2016 task 4: Sentiment analysis in twitter. In: SemEval@ NAACL-HLT (2016)
Pang, B., Lee, L.: Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Found. Trends Inf. Retr. 2(1–2), 1–135 (2007)
Qazvinian, V., Rosengren, E., Radev, D.R., Mei, Q.: Rumor has it: Identifying misinformation in microblogs. In: EMNLP (2011)
Ren, Z., Liang, S., Meij, E., de Rijke, M.: Personalized time-aware tweets summarization. In: SIGIR (2013)
Rizzo, G., Basave, A.E.C., Pereira, B., Varga, A.: Making sense of microposts (#microposts2015) named entity recognition and linking (NEEL) challenge. CEUR-WS.org (2015)
Rizzo, G., van Erp, M., Plu, J., Troncy, R.: Making sense of microposts (#microposts2016) named entity recognition and linking (NEEL) challenge. CEUR-WS.org (2016)
Rosenthal, S., Farra, N., Nakov, P.: Semeval-2017 task 4: Sentiment analysis in twitter. In: SemEval (2017)
Roussakis, Y., Chrysakis, I., Stefanidis, K., Flouris, G., Stavrakas, Y.: A Flexible Framework for Understanding the Dynamics of Evolving RDF Datasets. In: ISWC (2015)
Saleiro, P., Soares, C.: Learning from the news: Predicting entity popularity on twitter. In: International Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis, pp. 171–182. Springer (2016)
Sebastiani, F.: An axiomatically derived measure for the evaluation of classification algorithms. In: ICTIR (2015)
Sedhai, S., Sun, A.: Hspam14: A collection of 14 million tweets for hashtag-oriented spam research. In: SIGIR (2015)
Shen, W., Wang, J., Han, J.: Entity linking with a knowledge base: issues, techniques, and solutions. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 27(2), 443–460 (2015)
Stefanidis, K., Koloniari, G.: Enabling Social Search in Time through Graphs. In: Web-KR@CIKM (2014)
Thelwall, M., Buckley, K., Paltoglou, G.: Sentiment strength detection for the social Web. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 63(1), 163–173 (2012)
Tran, T.A., Niederée, C., Kanhabua, N., Gadiraju, U., Anand, A.: Balancing novelty and salience: Adaptive learning to rank entities for timeline summarization of high-impact events. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 1201–1210. ACM (2015)
Weikum, G., Spaniol, M., Ntarmos, N., Triantafillou, P., Benczúr, A., Kirkpatrick, S., Rigaux, P., Williamson, M.: Longitudinal Analytics on Web Archive Data: It’s About Time! In: CIDR (2011)
Yao, J.g., Fan, F., Zhao, W.X., Wan, X., Chang, E., Xiao, J.: Tweet timeline generation with determinantal point processes. In: AAAI (2016)
Yu, S., Kak, S.: A survey of prediction using social media (2012). arXiv preprint arXiv:1203.1647
Zhang, L., Rettinger, A., Zhang, J.: A probabilistic model for time-aware entity recommendation. In: International Semantic Web Conference, pp. 598–614. Springer (2016)
Zhao, X.W., Guo, Y., Yan, R., He, Y., Li, X.: Timeline generation with social attention. In: SIGIR (2013)
Zimmer, M.: The Twitter Archive at the Library of Congress: challenges for information practice and information policy. First Monday (2015). https://doi.org/10.5210/fm.v20i7.5619
Acknowledgements
The work was partially funded by the European Commission for the ERC Advanced Grant ALEXANDRIA (No. 339233) and by the German Research Foundation (DFG) project OSCAR (Opinion Stream Classification with Ensembles and Active leaRners).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fafalios, P., Iosifidis, V., Stefanidis, K. et al. Tracking the history and evolution of entities: entity-centric temporal analysis of large social media archives. Int J Digit Libr 21, 5–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00799-018-0257-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00799-018-0257-7