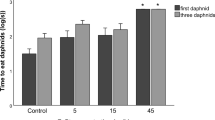
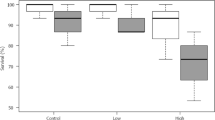
Abstract
Roundup® is one of the most widely marketed glyphosate-based herbicides in the world. There are many different formulations of this brand that differ from each other in glyphosate concentration, salts and adjuvants, including surfactants, which are labelled as “inert” compounds. Several studies have shown that these formulations are highly toxic to fish, even compared with pure glyphosate. However, mechanisms underlying this toxicity are not fully understood. In this context, this study evaluated the effects of exposure to Roundup Original® (RO), Roundup Transorb® (RT), and Roundup WG® (RWG) on the behavioural patterns of the livebearer Jenynsia multidentata. This fish naturally inhabits agricultural areas in southern Brazil and Argentina where glyphosate is used extensively. In the experiment, animals were exposed to the herbicides for 96 h, at the environmentally relevant concentration of 0.5 mg/L of glyphosate. Swimming performance, anxiety, aggressiveness, long-term memory and male sexual activity were recorded. The formulation RWG negatively affected swimming performance, thigmotaxia and long-term memory consolidation. Conversely, RT reduced the sexual performance of males. These results confirm that Roundup® formulations are extremely harmful and also that they have different targets of toxicity, affecting behaviours that are essential for fish survival.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Amé M, Baroni M, Galanti L, Bocco J, Wunderlin D (2009) Effects of microcystin–LR on the expression of P-glycoprotein in Jenynsia multidentata. Chemosphere. 74(9):1179–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.068
Annett R, Habibi H, Hontela A (2014) Impact of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on the freshwater environment: impact of glyphosate-based herbicides. J Appl Toxicol 34(5):458–479. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2997
Ballesteros M, Bianchi G, Carranza M, Bistoni M (2007) Endosulfan acute toxicity and histomorphological alterations in Jenynsia multidentata (Anablepidae, Cyprinodontiformes). J Environ Sci Health B 42(4):351–357. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601230701309577
Ballesteros M, Wunderlin D, Bistoni M (2009) Oxidative stress responses in different organs of Jenynsia multidentata exposed to endosulfan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(1):199–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.01.008
Bizarra A, Manfredi S, Pilastro A (2000) Sexual competition, coercive mating and mate assessment in the one-sided livebearer, Jenynsia multidentata: are they predictive of sexual dimorphism? Ethology. 106(11):961–978. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0310.2000.00620.x
Bonansea R, Wunderlin D, Amé M (2016) Behavioral swimming effects and acetylcholinesterase activity changes in Jenynsia multidentata exposed to chlorpyrifos and cypermethrin individually and in mixtures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 129:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.03.043
Braz-Mota S, Sadauskas-Henrique H, Duarte R, Val A, Almeida-Val V (2015) Roundup® exposure promotes gills and liver impairments, DNA damage and inhibition of brain cholinergic activity in the Amazon teleost fish Colossoma macropomum. Chemosphere. 135:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.042
Bridi D, Altenhofen S, Gonzalez J, Reolon G, Bonan C (2017) Glyphosate and Roundup® alter morphology and behavior in zebrafish. Toxicology. 392:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2017.10.007
Caballero-Gallardo K, Olivero-Verbel J, Freeman J (2016) Toxicgenomics to evaluate endocrine disrupting effects of environmental chemicals using the zebrafish model. Curr Genomics 17(6):515–527. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202917666160513105959
Calcagno E, Durando P, Valdés M, Franchioni L, Bistoni M (2016) Effects of carbamazepine on cortisol levels and behavioral responses to stress in the fish Jenynsia multidentata. Physiol Behav 158:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.02.025
Castro M, Lima J, Salomão de Freitas D, De Souza VR, Dummer N, De Aguiar R, Dos Santos L, Marins L, Geracitano L, Monserrat J, Barros D (2009) Behavioral and neurotoxic effects of arsenic exposure in zebrafish (Danio rerio, Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 150(3):337–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2009.05.017
Cattani D, Cavalli V, Rieg C, Domingues J, Dal-Cim T, Tasca C, Mena Barreto Silva F, Zamoner A (2014) Mechanisms underlying the neurotoxicity induced by glyphosate-based herbicide in immature rat hippocampus: involvement of glutamate excitotoxicity. Toxicology. 320:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2014.03.001
Cazenave J, Wunderlin D, Bistoni M, Amé M, Krause E, Pflugmacher S, Wiegand C (2005) Uptake, tissue distribution and accumulation of microcystin-RR in Corydoras paleatus, Jenynsia multidentata and Odontesthes bonariensis. J Aquat Toxicol 75(2):178–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.08.002
Chivittz C, Pinto D, Ferreira R, Sopezki M, Fillmann G, Zanette J (2016) Responses of the CYP1A biomarker in Jenynsia multidentata and Phalloceros caudimaculatus and evaluation of a CYP1A refractory phenotype. Chemosphere. 144:925–931
Cortés D, Ramírez E, Giraldo H (2016) Histopathological alterations of olfactory bulbs of white cachama to a commercial presentation glyphosate (Roundup® Activo). Revista Facultad De Ciencias Básicas 11(2):8–17. https://doi.org/10.18359/rfcb.1294
Croft D, James R, Ward A, Mawdsley BM, Krause J (2005) Assortative interactions and social networks in fish. Oecologia 143(2):211–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-004-1796-8
Defarge N, Takács E, Lozano V, Mesnage R, Spiroux de Vendômois J, Séralini G, Székács A (2016) Co-formulants in glyphosate-based herbicides disrupt aromatase activity in human cells below toxic levels. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(3):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13030264
Diotel N, Page Y, Mouriec K, Tong S, Pellegrini E, Vaillant C, Anglade I, Brion F, Pakdel F, Chung B, Kah O (2010) Aromatase in the brain of teleost fish: expression, regulation and putative functions. Front Neuroendocrinol 31(2):172–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2010.01.003
Egan R, Bergner C, Hart P, Cachat J, Canavello P, Elegante M, Elkhayat I, Bartels B, Tien A, Tien D, Mohnot S, Beeson E, Glasgow E, Amri H, Zukowska Z, Kalueff A (2009) Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav Brain Res 205(1):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.06.022
Galindo-Villegas J, Sosa-Lima F (2002) Gonopodial system review and a new fish record of Poeciliopsis infans (Cyprinodontiformes: Poeciliidae) for Lake Patzcuaro, Michoacan, Central Mexico. Ver Biol Trop 50:1151–1157
Garcia A, Vieira J, Winemiller K, Raseira M (2004) Reproductive cycle and spatiotemporal variation in abundance of the one-sided livebearer Jenynsia multidentata, in Patos Lagoon, Brazil. Hydrobiologia. 515(1-3):39–48. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000027316.59258.a0
Gasnier C, Dumont C, Benachour N, Clair E, Chagnon M, Séralini G (2009) Glyphosate-based herbicides are toxic and endocrine disruptors in human cell lines. Toxicology. 262(3):184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.06.006
Gerlai R, Lahav M, Guo S, Rosenthal A (2000) Drinks like a fish: zebra fish (Danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67(4):773–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-3057(00)00422-6
Giesy J, Dobson S, Solomon K (2000) Ecotoxicological risk assessment for Roundup® Herbicide. In: Ware G (ed) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer, New York, pp 35–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1156-3_2
Glusczak L, Dos Santos MD, Crestani M, Braga da Fonseca M, Araújo F, Duarte M, Vieira V (2006) Effect of glyphosate herbicide on acetylcholinesterase activity and metabolic and hematological parameters in piava (Leporinus obtusidens). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 65(2):237–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.07.017
Glusczak L, Miron D, Moraes B, Simões R, Schetinger M, Morsch V, Loro V (2007) Acute effects of glyphosate herbicide on metabolic and enzymatic parameters of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 146(4):519–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.06.004
Grier H, Taylor R (1998) Testicular maturation and regression in the common snook. J Fish Biol 53(3):521–542
Griffiths S (2003) Learned recognition of conspecifics by fishes. Fish Fish 4(3):256–268. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1467-2979.2003.00129.x
Hamdani E, Doving K (2007) The functional organization of the fish olfactory system. Prog Neurobiol 82(2):80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2007.02.007
Harayashiki C, Varela-Junior A, de Souza Machado AA, Cabrera L, Primel E, Bianchini A, Corcini C (2013) Toxic effects of the herbicide Roundup in the guppy Poecilia viviparaacclimated to fresh water. Aquat Toxicol 142– 143:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.08.006
Haro J, Bistoni M (2007) Peces de Córdoba. (Ed) Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina, pp 266.
Hued A, Bistoni M (2005) Development and validation of a Biotic Index for evaluation of environmental quality in the central region of Argentina. Hydrobiologia. 543(1):279–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-7893-1
Hued A, Oberhofer S, Bistoni M (2012) Exposure to a commercial glyphosate formulation (Roundup®) alters normal gill and liver histology and affects male sexual activity of Jenynsia multidentata (Anablepidae, Cyprinodontiformes). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62(1):107–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-011-9686-7
Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis – IBAMA (2014) Comercialização IBAMA 2014 - Portal de Dados Abertos Sobre Agrotóxicos. http://dados.contraosagrotoxicos.org/pt_PT/dataset/comercializacao-ibama-2014. Accessed 17 Feb 2020.
International Agency for Research on Cancer - IARC (2015) evaluation of five organophosphate insecticides and herbicides. IARC Monographs Vol. 112. https://www.iarc.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/MonographVolume112-1.pdf. Accessed 17 Feb 2020.
Isaac-Nahum V, Vazzoler A (1987) Biologia reprodutiva de Micropogonias furnieri (Desmarest,1823) (Teleostei, Siaenideae). 2. Relação gonadossomática, comprimento e peso dos ovários como indicadores do período de desova. Boletim do Instituto Oceanográfico 35(2):123–134. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0373-55241987000200003
Izquierdo I (2011) Memória. 2ª Ed. Artmed, Porto Alegre, Brazil. 133 p
James C (2015) Brief 51: 20th Anniversary (1996 to 2015) of the Global Commercialization of Biotech Crops and Biotech Crop Highlights in 2015. ISAAA. pp. 51-2015. http://www.isaaa.org/resources/publications/briefs/51/default.asp. Accessed 17 Feb 2020.
Kalueff A, Stewart A, Gerlai R (2014) Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35(2):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2013.12.002
Krause J, Butlin R, Peuhkuri N, Pritchard V (2000) The social organization of fish shoals: a test of the predictive power of laboratory experiments for the field. Camb Philos Soc Biol Rev 75(4):477–501
Lindeyer C, Langen E, Swaney W, Reader S (2015) Nonapeptide influences on social behaviour: effects of vasotocin and isotocin on shoaling and interaction in zebrafish. Behaviour 152(7-8):897–915. https://doi.org/10.1163/1568539X-00003261
Lopes F, Varela-Junior A, Corcini C, Da Silva A, Guazzelli V, Tavares G, Da Rosa C (2014) Effect of glyphosate on the sperm quality of zebrafish Danio rerio. Aquat Toxicol 155:322–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.07.006
Marigoudar S, Ahmed R, David M (2009) Cypermethrin induced respiratory and behavioural responses of the freshwater teleost, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Vet Arhiv 79(6):583–590
Maximino C, De Brito T, Da Silva BA, Herculano A, Morato S, Gouveia A (2010) Measuring anxiety in zebrafish: a critical review. Behav Brain Res 214(2):157–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2010.05.031
Melo F, Godoi F, Velasques R, Silveira A, Geihs M, Da Rosa C (2017) Effects of the herbicide Roundup on the polychaeta Laeonereis acuta: cholinesterases and oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.014
Modesto K, Martinez C (2010) Roundup® causes oxidative stress in liver and inhibits acetylcholinesterase in muscle and brain of the fish Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere. 78(3):294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.10.047
Moura F, Brentegani K, Gemelli A, Sinhorin A, Sinhorin V (2017) Oxidative stress in the hybrid fish jundiara (Leiarius marmoratus × Pseudoplatystoma reticulatum) exposed to Roundup Original®. Chemosphere. 185:445–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.030
Moustafa G, Shaaban F, Hadeed A, Elhady W (2016) Immunotoxicological, biochemical, and histopathological studies on Roundup and Stomp herbicides in Nile catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Vet World 9(6):638–647. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2016.638-647
Nakanishi S, Masu M (1994) Molecular diversity and functions of glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23(1):319–348. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.001535
Ortubay S, Lozada M, Cussac V (2002) Aggressive behaviour between Gymnocharacinus bergi (Pisces, Characidae) and other neotropical fishes from a thermal stream in Patagonia. Environ Biol Fish 63:341–346
Pérez G, Vera M, Miranda L (2011) Effects of herbicide glyphosate and glyphosate-based formulations on aquatic ecosystems. In: El-Ghany Hasaneen MNA (Ed) Herbicides—properties, synthesis and control of weeds, pp. 334–368. https://doi.org/10.5772/12877
Peruzzo P, Porta A, Ronco A (2008) Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ Pollut 156:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.01.015
Pinto D, Chivittz C, Ferreira R, Sopezki M, Zanette J (2015) Beta-naphthoflavone-induced CYP1A expression in the guppy Jenynsia multidentata: time-dependent response, anesthetic MS-222 effect and fin analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.11.023
Prut L, Belzung C (2003) The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol 463(1-3):3–33
Queiroz G, Silva M, Da Bianco R, Pinheiro A, Kaufmann V (2011) Glyphosate transport in runoff and leaching waters in agricultural soil. Quim Nova 34(2):190–195. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422011000200004
Quezada-Romegialli C, Vila I, Véliz D (2009) Nueva especie ictica invasora en aguas continentales de chile central: Jenynsia multidentata (Jenyns, 1842) (Cyprinodontiformes: Anablepidae). Gayana. 73:233–236. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-65382009000200007
Ranta E, Lindström K (1990) Assortative schooling in three-spined sticklebacks? Ann Zool Fenn 27(2):67–75
Rao J, Begum G, Pallela R, Usman P, Rao R (2005) Changes in behavior and brain acetylcholinesterase activity in mosquito fish, Gambusia affinis in response to the sub-lethal exposure to chlorpyrifos. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2(3):478–483
Relyea R, Jones D (2009) The toxicity of Roundup Original Max® to 13 species of larval amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 28(9):2004–2008. https://doi.org/10.1897/09-021.1
Roggio M, Guyón N, Hued A, Amé M, Valdés M, Giojalas L, Wunderlin D, Bistoni M (2014) Effects of the synthetic estrogen 17α-ethinylestradiol on aromatase expression, reproductive behavior and sperm quality in the fish Jenynsia multidentata. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92(5):579–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1185-2
Romano R, Romano M, Bernardi M, Furtado P, Oliveira C (2010) Prepubertal exposure to commercial formulation of the herbicide glyphosate alters testosterone levels and testicular morphology. Arch Toxicol 84(4):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-009-0494-z
Rosemberg D, Rico E, Mussulini B, Piato Â, Calcagnotto M, Bonan C, Dias R, Blaser R, Souza D, De Oliveira D (2011) Differences in spatio-temporal behavior of zebrafish in the open tank paradigm after a short-period confinement into dark and bright environments. PLoS One 6:e19397. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019397
Saif M, Chatterjee D, Buske C, Gerlai R (2013) Sight of conspecific images induces changes in neurochemistry in zebrafish. Behav Brain Res 243:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.01.020
Salbego J, Pretto A, Gioda C, De Menezes C, Lazzari R, Radünz J, Baldisserotto B, Loro V (2010) Herbicide formulation with glyphosate affects growth, acetylcholinesterase activity, and metabolic and hematological parameters in piava (Leporinus obtusidens). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58(3):740–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9464-y
Sánchez J, Varela A, Corcini C, Da Silva J, Primel E, Caldas S, Klein R, Martins C (2017) Effects of Roundup formulations on biochemical biomarkers and male sperm quality of the livebearing Jenynsia multidentata. Chemosphere. 177:200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.147
Sánchez J, Da Costa Klosterhoff M, Romano L, Martins C (2018) Histological evaluation of vital organs of the livebearer Jenynsia multidentata (Jenyns, 1842) exposed to glyphosate: a comparative analysis of Roundup® formulations. Chemosphere. 217:914–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.020
Sandrini J, Rola R, Lopes F, Buffon H, Freitas M, Martins C, Da Rosa C (2013) Effects of glyphosate on cholinesterase activity of the mussel Perna perna and the fish Danio rerio and Jenynsia multidentata: In vitro studies. J Aquat Toxicol 130–131:171–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.01.006
Sandun K, Bandara N, Amarasinghe U (2015) Effect of glyphosate-based herbicide, RoundupTM on territory deference of male Oreochromis mossambicus (Osteichthyes, Cichlidae) associated with mating behaviour. Sri Lanka J Aquat Sci 20(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.4038/sljas.v20i1.7451
Scerbina T, Chatterjee D, Gerlai R (2012) Dopamine receptor antagonism disrupts social preference in zebrafish: a strain comparison study. Amino Acids 43(5):2059–2072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1284-0
Schulte P (2014) What is environmental stress? Insights from fish living in a variable environment. J Exp Biol 217(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.089722
Serra E, Medalha C, Mattioli R (1999) Natural preference of zebrafish (Danio rerio) for a dark environment. Braz J Med Biol Res 32(12):1551–1553. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-879x1999001200016
Silva M, Peralba M, Mattos M (2003) Determinação de glifosato e ácido aminometilfosfônico em águas superficiais do arroio passo do pilão. Pesticidas: Revista de Ecotoxicologia e Meio Ambiente 13:19–28. https://doi.org/10.5380/pes.v13i0.3161
Sinhorin V, Sinhorin A, Teixeira J, Miléski K, Hansen P, Moreira P, Kawashita N, Baviera A, Loro V (2014a) Effects of the acute exposition to glyphosate-based herbicide on oxidative stress parameters and antioxidant responses in a hybrid Amazon fish surubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.040
Sinhorin V, Sinhorin A, Teixeira J, Miléski P, Moeller P, Moreira P, Baviera A, Loro M (2014b) Metabolic and behavior changes in Surubim acutely exposed to a glyphosate-based herbicide. Arch Environ Toxicol Chem 67(4):659–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0073-z
Soares M, Cardoso S, Carvalho T, Maximino C (2018) Using model fish to study the biological mechanisms of cooperative behaviour: a future for translational research concerning social anxiety disorders? Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 82:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.11.014
Székács A, Darvas B (2012) Forty Years with Glyphosate. Herbicides - Properties, Synthesis and Control of Weeds 14:247–284. https://doi.org/10.5772/32491
Tsui M, Chu L (2003) Aquatic toxicity of glyphosate-based formulations: comparison between different organisms and the effects of environmental factors. Chemosphere 52(7):1189–1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00306-0
Tzaskos D, Marcovicz C, Dias N, Rosso N (2012) Development of sampling for quantification of glyphosate in natural waters. Ciênc Agrotec 36(4):399–405. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542012000400003
Utne-Palm A, Hart P (2000) The effects of familiarity on competitive interactions between threespined sticklebacks. Oikos. 91(2):225–232. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0706.2000.910203.x
Vazzoler A, Caraciolo-Malta M, Amadio S (1989) Aspectos biológicos de peixes amazônicos. XII. Indicadores quantitativos do período de desovadas espécies do gênero Semaprochilodus (Characiformes, Prochilodontidae) do baixo Rio Negro, Amazonas, Brasil. Braz J Biol 49:175–181
Velasques R, Sandrini J, Da Rosa C (2016) Roundup ® in zebrafish: effects on oxidative status and gene expression. Zebrafish. 13(5):432–441. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2016.1259
Wang Y, Xu L, Tang M, Jiang H, Chen W, Zhang W, Wang R, Liu L (2016) Functional and integrative analysis of the proteomic profile of radish root under Pb exposure. Front Plant Sci 7:1871–1885. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01871
Ward A, Botham M, Hoare D, James R, Broom M, Godin J, Krause J (2002) Association patterns and shoal fidelity in the three–spined stickleback. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 269(1508):2451–2455. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2002.2169
Whitehead H, Dufault S (1999) Techniques for analyzing vertebrate social structure using identified individuals: review and recommendations. Adv Study Behav 28:33–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-3454(08)60215-6
World Health Organization - WHO (2005) Glyphosate and AMPA in Drinking-water background document for development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Sergiane for help with glyphosate measurements and Claudio Campos de Moraes for assistance with the herbicides.
Funding
The authors of the present study thank the Brazilian CNPq - National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (Process 449695/2014-0) for financial support. This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jessica Andrea Albañil Sanchéz and Camila De Martinez Gaspar Martins conceived the study and were in charge of the overall outline and planning. Camila De Martinez Gaspar Martins was responsible for obtaining financial support and managing it. Jessica Andrea Albañil Sanchéz performed all the experiments and analysed the results. Daniela Martí Barros, Maria de los Angeles Bistoni, Maria Laura Ballesteros and María Angelina Roggio provided critical feedback and helped shape the research. Jessica Andrea Albañil Sanchéz drafted this manuscript and designed the figures, and Camila De Martinez Gaspar Martins and Maria de los Angeles Bistoni contributed to finalizing the manuscript and its revisions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures with animals presented here complied with ethical standards (CEUA-FURG, reference Pq015/2013).
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez, J.A.A., Barros, D.M., de los Angeles Bistoni, M. et al. Glyphosate-based herbicides affect behavioural patterns of the livebearer Jenynsia multidentata. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 29958–29970 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11958-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11958-8