Abstract
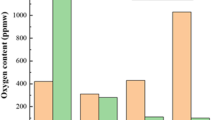
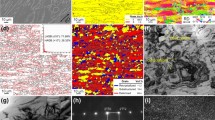
In this research, the effect of multiple remelting on microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of (TiZr)1(VFeCrMn)2.1 alloy was studied. The alloy was melted using a VIM furnace. This process was repeated three times. The microstructure was evaluated by SEM and XRD analysis, and the hydrogen storage properties were measured by Sieverts method. The results indicated that the microstructure contains predominant C14 Laves, BCC solid solution and titanium oxide phases. The homogenous microstructure and fine BCC phase distribution was obtained by remelting. The volume fraction of BCC phase was decreased from 26 to 18% during remelting. PCT curves revealed that increasing remelting times results in decreasing slope and hysteresis factors. The values of alloys slope factor for single, double and triple melting are 0.57, 0.26 and 0.21, respectively. Therefore, hydrogen storage properties of the alloy are improved as a result of homogenous microstructure and appropriate content of phases during the remelting process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ulmer U, Dieterich M, Pohl A, Dittmeyer R, Linder M, and Fichtner M, Int J Hydrog Energy 42 (2017) 20103.
Broom D P, Hydrogen Storage Materials, Green Energy and Technology, Springer, London (2011), p 1.
Kazemipour M, Salimijazi H, Saidi A, and Saatchi A, Int J Hydrog Energy 39 (2014) 12784.
Prachi R P, and Mahesh M W, Adv Energy Power 4 (2016) 11.
Guo X, Wang S, Liu X, Li Z, Lü F, Mi J, Hao L, and Jiang L, Rare Met 30 (2011) 227.
Yu X, Wu Z, Xia B, and Xu N, J Alloys Compd 372 (2004) 272.
Young K H, Batteries 4 (2018) 9.
Zhang Y, Zhang T, Li J, Li R, Yu Y, and Lu Y, Met Mater Int 25 (2019) 814.
Chen X, Chen R, Ding X, Li X, Ding H, Su Y, Gou J, and Fu H, Int J Hydrog Energy 43 (2018) 19567.
Ma P, Wu E, and Li W, Int J Hydrog Energy 39 (2014) 13569.
Teliz E, Díaz V, Piganelli V, Faccio R, and Zinola C F, J Electrochem Soc 165 (2018) A3389.
Young K, Ouchi T, Yang J, and Fetcenko M, Int J Hydrog Energy 36 (2011) 11137.
Kazemipour M, Salimijazi H, Saidi H, Saatchi A, Mostaghimi J, and Pershin L, Int J Hydrog Energy 40 (2015) 15569.
Pei P, Song X, Liu J, Chen G, Qin X, and Wang B, Int J Hydrog Energy 34 (2009) 8094.
Yu X, Wu Z, Li F, Xia B, and Xu N, Appl Phys Lett 84 (2004) 3199.
Kim J H, Han K S, Hwang K T, Kim B G, and Kang Y M, Int J Hydrog Energy 38 (2013) 6215.
Semboshi S, Masahashi N, Konno T J, Sakurai M, and Hanada S, J Alloys Compd 379 (2004) 290.
Young K, Fetcenko M, Li F, and Ouchi T, J Alloys Compd 464 (2008) 238.
Zhang Y H, Li P, Wang X L, Lin Y F, and Qu X H, J Alloys Compd 364 (2004) 289.
Iba H, and Akiba E, J Alloys Compd 231 (1995) 508.
Wong D, Young K, and Ng K, Model Simul Mater Sci 24 (2016) 085007.
Hang Z, Xiao X, Tan D, He Z, Li W, Li S, Chen C, and Chen L, Int J Hydrog Energy 35 (2010) 3080.
Huang T, Wu Z, Sun G, and Xu N, Intermetallics 15 (2007) 593.
Pickering L, Ti–V–Mn Based Metal Hydrides for Hydrogen Storage and Compression Applications, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, England (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taghizadeh, M., Abbasi, S.M., Seifollahi, M. et al. The Effect of Remelting on Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Ti–Mn–V Alloy. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 811–816 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02178-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02178-2