Abstract
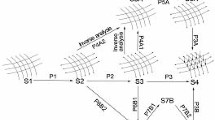
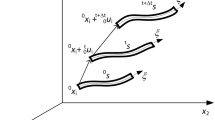
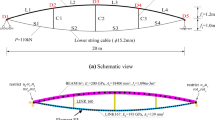
The analysis of cable structures is one of the most challenging problems for civil and mechanical engineers. Because they have highly nonlinear behavior, it is difficult to find solutions to these problems. Thus far, different assumptions and methods have been proposed to solve such structures. The dynamic relaxation method (DRM) is an explicit procedure for analyzing these types of structures. To utilize this scheme, investigators have suggested various stiffness matrices for a cable element. In this study, the efficiency and suitability of six well-known proposed matrices are assessed using the DRM. To achieve this goal, 16 numerical examples and two criteria, namely, the number of iterations and the analysis time, are employed. Based on a comprehensive comparison, the methods are ranked according to the two criteria. The numerical findings clearly reveal the best techniques. Moreover, a variety of benchmark problems are suggested by the authors for future studies of cable structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Underwood P. Computational Method for Transient Analysis. North Holland, 1983
Day A S. An Introduction to Dynamic Relaxation. The Engineer, 1965
Bunce J W. A note on the estimation of critical damping in dynamic relaxation. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1972, 4(2): 301–303
Cassell A C, Hobbs R E. Numerical stability of dynamic relaxation analysis of non-linear structures. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1976, 10(6): 1407–1410
Qiang S. An adaptive dynamic relaxation method for nonlinear problems. Computers & Structures, 1988, 30(4): 855–859
Zhang L G, Yu T X. Modified adaptive dynamic relaxation method and its application to elastic-plastic bending and wrinkling of circular plates. Computers & Structures, 1989, 33(2): 609–614
Zhang L C, Kadkhodayan M, Mai Y W. Development of the MADR method. Computers & Structures, 1994, 52(1): 1–8
Rezaiee-Pajand M. Nonlinear analysis of truss structures using dynamic relaxation. International Journal of Engineering, 2006, 19: 11–22
Kadkhodayan M, Alamatian J, Turvey G J. A new fictitious time for the dynamic relaxation (DXDR) method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2008, 74(6): 996–1018
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Alamatian J. The dynamic relaxation method using new formulation for fictitious mass and damping. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 2010, 34(1): 109–133
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Sarafrazi S R. Nonlinear structural analysis using dynamic relaxation method with improved convergence rate. International Journal of Computational Methods, 2010, 7(4): 627–654
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Sarafrazi S R. Nonlinear dynamic structural analysis using dynamic relaxation with zero damping. Computers & Structures, 2011, 89(13–14): 1274–1285
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Sarafrazi S R, Rezaiee H. Efficiency of dynamic relaxation methods in nonlinear analysis of truss and frame structures. Computers & Structures, 2012, 112–113: 295–310
Alamatian J. Displacement-based methods for calculating the buckling load and tracing the post-buckling regions with Dynamic Relaxation method. Computers & Structures, 2013, 114–115: 84–97
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Rezaee H. Fictitious time step for the kinetic dynamic relaxation method. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2014, 21(8): 631–644
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Estiri H. Computing the structural buckling limit load by using dynamic relaxation method. International Journal of Non-linear Mechanics, 2016, 81: 245–260
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Estiri H. Finding equilibrium paths by minimizing external work in dynamic relaxation method. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2016, 40(23–24): 10300–10322
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Estiri H. Mixing dynamic relaxation method with load factor and displacement increments. Computers & Structures, 2016, 168: 78–91
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Estiri H. A comparison of large deflection analysis of bending plates by dynamic relaxation. Periodica Polytechnica. Civil Engineering, 2016, 60(4): 619–645
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Estiri H. Comparative analysis of three-dimensional frames by dynamic relaxation methods. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2018, 25(6): 451–466
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Alamatian J, Rezaee H. The state of the art in Dynamic Relaxation methods for structural mechanics Part 1: Formulations. Iranian Journal of Numerical Analysis and Optimization, 2017, 7(2): 65–86
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Alamatian J, Rezaee H. The state of the art in Dynamic Relaxation methods for structural mechanics Part 2: Applications. Iranian Journal of Numerical Analysis and Optimization, 2017, 7(2): 87–114
Labbafi S F, Sarafrazi S R, Kang T H K. Comparison of viscous and kinetic dynamic relaxation methods in form-finding of membrane structures. Advances in Computational Design, 2017, 2(1): 71–87
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Mohammadi-Khatami M. A fast and accurate dynamic relaxation scheme. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering, 2019, 13(1): 176–189
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Estiri H, Mohammadi-Khatami M. Creating better dynamic relaxation methods. Engineering Computations, 2019, 36(5): 1483–1521
Ozdemir H. A finite element approach for cable problems. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1979, 15(5): 427–437
Pevrot A H, Goulois A M. Analysis of cable structures. Computers & Structures, 1979, 10(5): 805–813
Monforton G R, El-Hakim N M. Analysis of truss-cable structures. Computers & Structures, 1980, 11(4): 327–335
Jayaraman H B, Knudson W C. A curved element for the analysis of cable structures. Computers & Structures, 1981, 14(3–4): 325–333
Lewis W J, Jones M S, Rushton K R. Dynamic relaxation analysis of the non-linear static response of pretensioned cable roofs. Computers & Structures, 1984, 18(6): 989–997
Kmet S, Kokorudova Z. Nonlinear analytical solution for cable truss. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2006, 132(1): 119–123
Deng H, Jiang Q F, Kwan A S K. Shape finding of incomplete cable-strut assemblies containing slack and prestressed elements. Computers & Structures, 2005, 83(21–22): 1767–1779
Andreu A, Gil L, Roca P. A new deformable catenary element for the analysis of cable net structures. Computers & Structures, 2006, 84(29–30): 1882–1890
Yang Y B, Tsay J Y. Geometric nonlinear analysis of cable structures with a two-node cable element by generalized displacement control method. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 2007, 07(04): 571–588
Chen Z H, Wu Y J, Yin Y, Shan C. Formulation and application of multi-node sliding cable element for the analysis of Suspen-Dome structures. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 2010, 46(9): 743–750
Thai H T, Kim S E. Nonlinear static and dynamic analysis of cable structures. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 2011, 47(3): 237–246
Vu T V, Lee H E, Bui Q T. Nonlinear analysis of cable-supported structures with a spatial catenary cable element. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 2012, 43(5): 583–605
Huttner M, Maca J, Fajman P. Numerical analysis of cable structures. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference: Computational Structures Technology. Stirlingshire: Civil-Comp Press, 2012
Ahmadizadeh M. Three-dimensional geometrically nonlinear analysis of slack cable structures. Computers & Structures, 2013, 128: 160–169
Temur R, Bekdaş G, Toklu Y C. Analysis of cable structures through total potential optimization using meta-heuristic algorithms. In: ACE2014, the 11th International Congress on Advances in Civil Engineering. 2014, 21–25
Hashemi S K, Bradford M A, Valipour H R. Dynamic response of cable-stayed bridge under blast load. Engineering Structures, 2016, 127: 719–736
Gale S, Lewis W J. Patterning of tensile fabric structures with a discrete element model using dynamic relaxation. Computers & Structures, 2016, 169: 112–121
Anitescu C, Atroshchenko E, Alajlan N, Rabczuk T. Artificial neural network methods for the solution of second order boundary value problems. Computers, Materials and Continua, 2019, 59(1): 345–359
Guo H, Zhuang X, Rabczuk T. A deep collocation method for the bending analysis of Kirchhoff plate. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2019, 59(2): 433–456
Rabczuk T, Ren H, Zhuang X. A nonlocal operator method for partial differential equations with application to electromagnetic waveguide problem. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2019, 59(1): 31–55
Torkamani M A M, Shieh J H. Higher-order stiffness matrices in nonlinear finite element analysis of plane truss structures. Engineering Structures, 2011, 33(12): 3516–3526
Hüttner M, Máca J, Fajman P. The efficiency of dynamic relaxation methods in static analysis of cable structures. Advances in Engineering Software, 2015, 89: 28–35
Rezaiee-Pajand M, Naserian R. Using more accurate strain for three-dimensional truss analysis. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2016, 17(1): 107–126
Lewis W J. The efficiency of numerical methods for the analysis of prestressed nets and pin-jointed frame structures. Computers & Structures, 1989, 33(3): 791–800
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaiee-Pajand, M., Mohammadi-Khatami, M. Nonlinear analysis of cable structures using the dynamic relaxation method. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 15, 253–274 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-020-0639-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-020-0639-y