Abstract
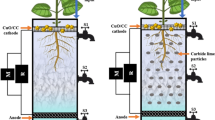
In this study, the performance of carbon cloth (CC) modified with iodine (I2) doped polythiophene nanoparticles (PTh-NP) as an anode was investigated in a double chamber microbial fuel cell (MFC) for the purpose of simultaneous power generation and lead (Pb2+) removal using Shewanella putrefaciens as the biocatalyst. The CC with I2 doped PTh-NP displayed good electrochemical characteristics compared to pristine CC and the CC with undoped PTh-NP. A further increase in the electrical conductivity using the modified CC with biofilm was observed, which matured after 51 h, as evident from cyclic voltametry. The removal of lead for concentrations, viz., 20 ppm, 30 ppm, and 40 ppm, was analyzed. The optimum concentration was found to be 30 ppm with a maximum power density of 0.84 W/m2 and a current density of 1.45 A/m2 at an optimum resistance of 250 ohms. At the end of the process, total organic carbon (TOC) and Pb2+ removal of 95.1% and 89.6%, respectively, were obtained at the optimum concentration. Hence, this study demonstrates the possibility of utilizing MFC for treating low concentrated metal wastewater.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma, T.; Mohana Reddy, A.L.; Chandra, T.S.; Ramaprabhu, S.: Development of carbon nanotubes and nanofluids based microbial fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 33, 6749–6754 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.05.112
Santoro, C.; Arbizzani, C.; Erable, B.; Ieropoulos, I.: Microbial fuel cells: from fundamentals to applications: A review. J. Power Sources 356, 225–244 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.03.109
Zhao, F.; Slade, R.C.T.; Varcoe, J.R.: Techniques for the study and development of microbial fuel cells: an electrochemical perspective. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 1926 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b819866g
Das, S.; Mangwani, N.: Recent developments in microbial fuel cells: a review. J Sci Ind. Res. (India) 69, 727–731 (2010)
Liang, P.; Wang, H.; Xia, X.: Carbon nanotube powders as electrode modifier to enhance the activity of anodic biofilm in microbial fuel cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 3000–3004 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.12.002
Mustakeem, M.: Electrode materials for microbial fuel cells: nanomaterial approach. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 4, 1–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40243-015-0063-8
Kang, Y.L.; Ibrahim, S.; Pichiah, S.: Synergetic effect of conductive polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) with different structural configuration of anode for microbial fuel cell application. Bioresour. Technol. 189, 364–369 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.04.044
Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Ding, L.: Effect of conductive polymers coated anode on the performance of microbial fuel cells (MFCs) and its biodiversity analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 4169–4176 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.04.018
Qiao, Y.; Bao, S.J.; Li, C.M.: Nanostructured polyaniline/titanium dioxide composite anode for microbial fuel cells. ACS Nano 2, 113–119 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn700102s
Chi, M.: Graphite felt anode modified by electropolymerization of nano-polypyrrole to improve microbial fuel cell (MFC) production of bioelectricity. J Microb. Biochem. Technol. 1, 10–13 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-5948.S12-004
Sumisha, A.; Haribabu, K.: Modification of graphite felt using nano polypyrrole and polythiophene for microbial fuel cell applications-a comparative study. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43, 3308–3316 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.12.175
Dharma, K.; Atsushi, M.; Kohtaro, O.; Takakazu, : Iodine Doping of Poly(thiophene-2,5-diyl) and Poly(3-alkylthiophene-2,5-diyl)s in Aqueous Media. Polym. J. 30, 860–862 (1998)
Sumisha, A.; Jiben, A.; Aswathy, A.; Haribabu, K.: Reduction of copper and generation of energy in double chamber microbial fuel cell using Shewanella putrefaciens. Separ. Sci. Technol. 55, 2391–2399 (2020)
Handan, U.; Kemal, B.; Yusuf, K.; Avni, C.; Faruk, A.: Biosorption of lead (II) from aqueous solution by cone biomass of Pinus sylvestris. Desalination 154, 233–238 (2003)
Biswas, S.; Mishra, U.: Continuous fixed-bed column study and adsorption modeling: removal of lead ion from aqueous solution by charcoal originated from chemical carbonization of rubber wood sawdust. J. Chem. 2015, 1–9 (2015)
Li, X.G.; Li, J.; Huang, M.R.: Facile optimal synthesis of inherently electroconductive polythiophene nanoparticles. Chem. A Eur. J. 15, 6446–6455 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200900181
Ringeisen, B.R.; Ray, R.; Little, B.: A miniature microbial fuel cell operating with an aerobic anode chamber. J. Power Sources 165, 591–597 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.10.026
Sumisha, A.; Anju, K.; Srinivas, P.; Haribabu, K.: Energy generation in single chamber microbial fuel cell from pure and mixed culture bacteria by copper reduction. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45, 7719–7724 (2020)
Senthilkumar, B.; Thenamirtham, P.; Kalai Selvan, R.: Structural and electrochemical properties of polythiophene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 9063–9067 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.05.100
Gök, A.; Omastová, M.; Yavuz, A.G.: Synthesis and characterization of polythiophenes prepared in the presence of surfactants. Synth. Met. 157, 23–29 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2006.11.012
Sakthivel, S.; Boopathi, A.: Synthesis and preparation of polythiophene thin film by spin coating method. J. Chem. Chem. Sci. 4, 150–155 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2005.10.019
Bazaka, K.; Jacob, M.: Effects of iodine doping on optoelectronic and chemical properties of polyterpenol thin films. Nanomaterials 7, 1–16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7010011
Kramer, J.; Soukiazian, S.; Mahoney, S.; Hicks-Garner, J.: Microbial fuel cell biofilm characterization with thermogravimetric analysis on bare and polyethyleneimine surface modified carbon foam anodes. J. Power Sources 210, 122–128 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.03.022
Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jin, M.: Copper removal and microbial community analysis in single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 253, 372–377 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.046
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajendran, R., Dhakshina Moorthy, G.P., Krishnan, H. et al. A Study on Polythiophene Modified Carbon Cloth as Anode in Microbial Fuel Cell for Lead Removal. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 6695–6701 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05402-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05402-3