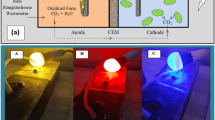
Abstract
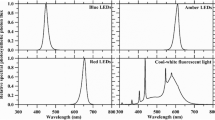
In this study, the red LED with wavelength range of 625 ~ 627.5 nm and the blue LED with wavelength range of 464 ~ 467 nm are chosen as the light source in order to increase the lipid content of microalgae as well as to reduce the energy consumption. The highest lipid weight of Scenedesmus obliquus is achievedwith 5000lux light intensity, 12L:12D of photoperiod and blue continuous LED light which consuming 53.4 times less energy in term of the total lipid content per unit than that of tricolor energy-saving lamp. In addition, the highest biomass and lipid weight of Chlorella pyrenoidosa are achieved with 5000lux of light intensity, 8L:16D of photoperiod and red continuous LED light, which is 0.73 g/L and 0.552 g/L respectively. And it consumes 29.4 times less energy consumption for units of the total lipid content than that of tricolor energy-saving lamp. Furthermore, continuous LED light improves effect of municipal wastewater treatment as the better light source for Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa comparing with intermittent LED light.
Graphic Abstract




source and intermittent LED light source

source on municipal wastewater treatment of microalgae a TN b TP c NH4+–N d COD e pH

source on municipal wastewater treatment of microalgae a TN b TP c NH4+–N d COD
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salama, E., Hwang, J., El-Dalatony, M.M., Kurade, M.B., Kabra, A.N., Abou-Shanab, R.A.I., Kim, K., Yang, I., Govindwar, S.P., Kim, S., Jeon, B.: Enhancement of microalgal growth and biocomponent-based transformations for improved biofuel recovery: a review. Bioresource Technol. 258, 365–375 (2018)
Choo, M.Y., Oi, L.E., Show, P.L., Chang, J.S., Ling, T.C., Ng, E.P., Phang, S.M., Juan, J.C.: Recent progress in catalytic conversion of microalgae oil to green hydrocarbon: a review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 79, 116–124 (2017)
Zhou, X., Jin, W., Tu, R., Guo, Q., Han, S., Chen, C., Wang, Q., Liu, W., Jensen, P.D., Wang, Q.: Optimization of microwave assisted lipid extraction from microalga Scenedesmus obliquus grown on municipal wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 221, 502–508 (2019)
Su, Y.J., Song, K.H., Zhang, P.D., Su, Y.Q., Cheng, J., Chen, X.: Progress of microalgae biofuel’s commercialization. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 74, 402–411 (2017)
Cao, S., Zhou, X., Jin, W.B., Wang, F., Tu, R.J., Han, S.F., Chen, H.Y., Chen, C., Xie, G.J., Ma, F.: Improving of lipid productivity of the oleaginous microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa via atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP). Bioresource Technol. 244, 1400–1406 (2017)
Tu, R., Jin, W., Han, S., Zhou, X., Wang, J., Wang, Q., He, Z., Ding, W., Che, L., Feng, X.: Enhancement of microalgal lipid production in municipal wastewater: fixation of CO2 from the power plant tail gas. Biomass Bioenerg. 131 (2019).
Han, S., Jin, W., Abomohra, A.E., Tu, R., Zhou, X., He, Z., Chen, C., Xie, G.: Municipal wastewater enriched with trace metals for enhanced lipid production of the biodiesel-promising microalga Scenedesmus obliquus. Bioenerg Res. 12, 1127–1133 (2019)
Wang, Q., Jin, W., Zhou, X., Guo, S., Gao, S., Chen, C., Tu, R., Han, S., Jiang, J., Feng, X.: Growth enhancement of biodiesel-promising microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa in municipal wastewater by polyphosphate-accumulating organisms. J Clean Prod. 240 (2019).
Zhou, X., Jin, W., Wang, Q., Guo, S., Tu, R., Han, S., Chen, C., Xie, G., Qu, F., Wang, Q.: Enhancement of productivity of Chlorella pyrenoidosa lipids for biodiesel using co-culture with ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in municipal wastewater. Renew Energy. 151, 598–603 (2020)
Feng, X., Chen, Y., Lv, J., Han, S., Tu, R., Zhou, X., Jin, W., Ren, N.: Enhanced lipid production by Chlorella pyrenoidosa through magnetic field pretreatment of wastewater and treatment of microalgae-wastewater culture solution: magnetic field treatment modes and conditions. Bioresource Technol. 306 (2020)
Pienkos, P.T., Laurens, L., Aden, A.: Making biofuel from microalgae. Am. Sci. 99, 474–481 (2011)
Abomohra, A.E., Jin, W., El-Sheekh, M.: Enhancement of lipid extraction for improved biodiesel recovery from the biodiesel promising microalga Scenedesmus obliquus. Energy Convers. Manag. 108, 23–29 (2016)
Hu, Z., Ma, X., Li, L., Wu, J.: The catalytic pyrolysis of microalgae to produce syngas. Energy Convers. Manag. 85, 545–550 (2014)
Silva, C.E.D.F., Bertucco, A.: Bioethanol from microalgae and cyanobacteria: a review and technological outlook. Process Biochem. 51, 1833–1842 (2016)
Aziz, M.: Integrated hydrogen production and power generation from microalgae. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41, 104–112 (2016)
Han, S., Jin, W., Tu, R., Wu, W.: Biofuel production from microalgae as feedstock: current status and potential. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 35, 255–268 (2015)
Tu, R., Jin, W., Xi, T., Yang, Q., Han, S., Abomohra, A.E.: Effect of static magnetic field on the oxygen production of Scenedesmus obliquus cultivated in municipal wastewater. Water Res. 86, 132–138 (2015)
Cheah, W.Y., Ling, T.C., Show, P.L., Juan, J.C., Chang, J.S., Lee, D.J.: Cultivation in wastewaters for energy: a microalgae platform. Appl. Energy 179, 609–625 (2016)
Cao, W.X., Wang, X., Sun, S.Q., Hua, C.W., Zhao, Y.J.: Simultaneously upgrading biogas and purifying biogas slurry using cocultivation of Chlorella vulgaris and three different fungi under various mixed light wavelength and photoperiods. Bioresource Technol. 241, 701–709 (2017)
Fozer, D., Kiss, B., Lorincz, L., Szekely, E., Mizsey, P., Nemeth, A.: Improvement of microalgae biomass productivity and subsequent biogas yield of hydrothermal gasification via optimization of illumination. Renew. Energ. 138, 1262–1272 (2019)
Wondraczek, L., Gruendler, A., Reupert, A., Wondraczek, K., Schmidt, M.A., Pohnert, G., and Nolte, S.: Biomimetic light dilution using side-emitting optical fiber for enhancing the productivity of microalgae reactors. Sci. Rep. 9 (2019)
Gupta, S., Pawar, S.B., Pandey, R.A., Kanade, G.S., Lokhande, S.K.: Outdoor microalgae cultivation in airlift photobioreactor at high irradiance and temperature conditions: effect of batch and fed-batch strategies, photoinhibition, and temperature stress. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 42, 331–344 (2019)
Xu, H., Liu, X., Mei, Z., Lin, J., Aaron, S., Du, H.: Effects of various light-emitting diode (LED) wavelengths on the growth of Scenedesmus Obliquus Fachb-12 and accumulation of Astaxanthin. Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 88, 335–348 (2019)
Tennessen, D.J., Singsaas, E.L., Sharkey, T.D.: Light-emitting-diodes as a light-source for photosynthesis research. Photosynth. Res. 39, 85–92 (1994)
Lababpour, A., Hada, K., Shimahara, K., Katsuda, T., Katoh, S.: Effects of nutrient supply methods and illumination with blue light emitting diodes (LEDs) on astaxanthin production by Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 98, 452–456 (2004)
Shu, C., Tsai, C., Liao, W., Chen, K., Huang, H.: Effects of light quality on the accumulation of oil in a mixed culture of Chlorella sp and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 87, 601–607 (2012)
Kim, T., Lee, Y., Han, S., Hwang, S.: The effects of wavelength and wavelength mixing ratios on microalgae growth and nitrogen, phosphorus removal using Scenedesmus sp for wastewater treatment. Bioresource Technol. 130, 75–80 (2013)
Chirivella-Martorell, J., Briz-Redon, A., Serrano-Aroca, A.: Modelling of biomass concentration, multi-wavelength absorption and discrimination method for seven important marine microalgae species. Energies 11 (2018)
Kendirlioglu, G., Cetin, A.K.: Effect of different wavelengths of light on growth, pigment content and protein amount of Chlorella vulgaris. Fresen Environ. Bull. 26, 359–365 (2017)
Wagner, I., Steinweg, C., Posten, C.: Mono- and dichromatic LED illumination leads to enhanced growth and energy conversion for high-efficiency cultivation of microalgae for application in space. Biotechnol. J. 11, 1060–1071 (2016)
Wang, S., Stiles, A.R., Guo, C., Liu, C.: Microalgae cultivation in photobioreactors: an overview of light characteristics. Eng. Life Sci. 14, 550–559 (2014)
Folch, J., Lees, M., Stabley, G.: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides form animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1957)
Wei, Y.: Study on Cultivation Of Oil - Producing Stragglers from Municipal Sewage. Harbin Institute of Technology (2010) (in Chinese)
Lu, S.: Selection and Optimization of Cultivation Conditions of High-Fat Algae Cultivated with Municipal Sewage. Harbin Institute of Technology (2010) (in Chinese)
Ma, W., Chen, L., Wei, L., Wang, Q.: Excitation energy transfer between photosystems in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. J. Lumin. 128, 546–548 (2008)
Yan, C., Zheng, Z.: Performance of mixed LED light wavelengths on biogas upgrade and biogas fluid removal by microalga Chlorella sp. Appl. Energ. 113, 1008–1014 (2014)
Ravelonandro, P.H., Ratianarivo, D.H., Joannis-Cassan, C., Isambert, A., Raherimandimby, M.: Influence of light quality and intensity in the cultivation of Spirulina platensis from Toliara (Madagascar) in a closed system. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 83, 842–848 (2008)
Wang, Z., Zhao, Y., Ge, Z., Zhang, H., Sun, S.: Selection of microalgae for simultaneous biogas upgrading and biogas slurry nutrient reduction under various photoperiods. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 91, 1982–1989 (2016)
Zamani, N., Noshadi, M., Amin, S., Niazi, A., Ghasemi, Y.: Effect of alginate structure and microalgae immobilization method on orthophosphate removal from wastewater. J. Appl. Phycol. 24, 649–656 (2012)
Converti, A., Casazza, A.A., Ortiz, E.Y., Perego, P., Del Borghi, M.: Effect of temperature and nitrogen concentration on the growth and lipid content of Nannochloropsis oculata and Chlorella vulgaris for biodiesel production. Chem. Eng. Process. 48, 1146–1151 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51878215), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2018A030313185), Key Areas Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, China (2019B110205001), Demonstration Project for Marine Economic Development in Shenzhen to Dr. Zhangli HU, China's State Oceanic Administration, and Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Project (KJYY20171011144235970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Z., Han, W., Jin, W. et al. Cultivation of Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa in Municipal Wastewater Using Monochromatic and White LED as Light Sources. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 4873–4883 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01359-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01359-4