Abstract
Nanofibers have attracted attention in the field of thermoelectric (TE) because of their remarkable properties; abundance, lightweight with the high-surface area-to-volume ratio, low thermal conductivity, mechanically stable, and non-toxic. In applications, like TE wearable device for energy harvesting, development of new composite nanofibers holds more significant potential with the targeted specifications. In our research, we have investigated for the first-time fiber nanocomposites for the application of wearable power generator in terms of TE energy. The electrospun technique attracts in the development of nanostructured materials in the field of thermoelectric power generation. The significance of this paper is to flourish the wearable device materials of 1D vanadium oxide/tin oxide (V2O5/SnO2) composite nanofibers synthesized using sol–gel method followed by electrospinning process. The structural and morphology properties of SnO2 fibers belong to tetragonal structure and nanocomposite relates to tetragonal (SnO2) and orthorhombic (V2O5) structure, diameter in the range of 100–400 nm. The high-surface area to volume ratio of nanofiber allowed more significant phonon scattering and enhance the efficiency. The nanofiber exhibits the outstanding TE properties of the Seebeck coefficient and power factor of 20–100 V/K and 0.3–1.6 µW/K2m at room temperature to 400 K, which is the highest among the fiber SnO2 and its composites. The nanofibers integration on wearable devices paves the way towards ultralight, thermally stable, tunable density and mechanically flexibile are unique, where nanocomposite offers a new opportunity to thermoelectric applications.

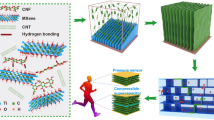
Schematic representation of fabrication process PVA-SnO2 NFs and PVA-V2O5/SnO2 NCF.
Highlights
-
Fabrication of 1D nanofibers, which increases phonon scattering and enhanced power factor.
-
The electrospun PVA-SnO2 and PVA-V2O5/SnO2 nanocomposites fiber for the first time was reported as a better thermoelectric material.
-
The exceptional power factor of 0.3 to 1.6 μW/K2m at room temperature to 400 K, which is the top-notch among the fiber SnO2 and its composites.
-
SnO2 composite nanofibers such integration paves the way towards ultralight, tunable density, thermally, and mechanically stable thermoelectric applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Veluswamy P, Sathiyamoorthy S, Chowdary K, Muthusamy O, Krishnamoorthy K, Takeuchi T, Ikeda H (2017) Morphology dependent thermal conductivity of ZnO nanostructures prepared via a green approach. J Alloy Compd 695:888–894
Choi H, Kim YJ, Song J, Kim CS, Lee GS, Kim S, Park J, Yim SH, Park SH, Hwang HR, Hong MH, Veluswamy P, Cho BJ (2019) UV‐curable silver electrode for screen‐printed thermoelectric generator. Adv Funct Mater 29:1901505
Zhang X, Zhao LD (2015) Thermoelectric materials: energy conversion between heat and electricity. J Materiomics 1:92–105
Agari Y, Ueda A, Omura Y, Nagai S (1997) Thermal diffusivity and conductivity of PMMA/PC blends. Polymer 38:801–807
Ju H, Park D, Kim J (2017) Hydrothermal transformation of SnSe crystal to Se nanorods in oxalic acid solution and the outstanding thermoelectric power factor of Se/SnSe composite. Sci Rep 7:18051
Dalola S, Faglia G, Comini E, Ferroni M, Soldano C, Zappa D, Ferrari V, Sberveglieri G (2011) Seebeck effect in ZnO nanowires for micropower generation. Procedia Eng 25:1481–1484
Soni A, Yanyuan Z, Ligen Yu, Aik MKK, Dresselhaus MS, Xiong Q (2012) Enhanced thermoelectric properties of solution grown Bi2Te3–xSexNanoplatelet composites. Nano Lett 12:1203–1209
Sharma J, Lizu M, Stewart M, Zygula K, Lu K, Chauhan R, Yan X, Guo Z, Wujcik EK, Wei S (2015) Multifunctional nanofibers towards active biomedical therapeutics. Polymers 7:186–219
Malliakas CD, Chung DY, Claus H, Kanatzidis MG (2016) Superconductivity in the narrow gap semiconductor RbBi11/3Te6. J Am Chem Soc 138:14694–14698
Iordanidis L, Bilc D, Mahanti SD, Kanatzidis MG (2003) Impressive structural diversity and polymorphism in the modular compounds ABi3Q5(A = Rb, Cs; Q = S, Se, Te). J Am Chem Soc 125:13741–13752
Xu B, Zhang J, Yu G, Ma S, Wang Y, Wang Y (2018) Thermoelectric properties of monolayer Sb2Te3. J Appl Phys 124:165104
Wang X, Wang H, Xiang B, Fu LW, Zhu H, Chai D, Zhu B, Yu Y, Gao N, Huang ZY, Zu FQ (2018) Thermoelectric performance of Sb2Te3-based alloys is improved by introducing PN junctions. Appl Mater Interfaces 10:23277–23284
Vieira EMF, Figueira J, Pires AL, Grilo J, Silva MF, Pereira AM, Goncalves LM (2019) Enhanced thermoelectric properties of Sb2Te3 and Bi2Te3 films for flexible thermal sensors. J Alloy Compd 774:1102–1116
Madelung O (1996) Semiconductors basic data. 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany
Lopez R, Boatner LA, Haynes TE, Feldman LC, Haglund Jr RF (2002) Synthesis and characterization of size-controlled vanadium dioxide nanocrystals in a fused silica matrix. J Appl Phys 92:4031–4036
Ishiguro K, Sasaki T, Arai T, Imai I (1958) Optical and electrical properties of tin oxide films. J Phys Soc Jpn 13:296–304
Charnock H, Yeo SA (1959) Thermoelectric e.m.f. of tin-cadmium alloys. J Sci Instrum 36:478–479
Nasirov YN, Feiziev YS (1967) Effect of small substitutions of tin by neodymium on thermoelectric properties of SnTe. Phys Stat Sol 24:K157–K159
Liu W, Kim HK, Chen S, Jie Q, Lv B, Yao M, Ren Z, Opeil CP, Wilson S, Chu CW, Ren Z (2015) In this issue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:1–2
Kadir RA, Zhenyu L, Sadek AZ, Rani RA, Zoolfakar AS, Field MR, Ou JZ, Chrimes AF, Zadeh KK (2014) Electrospun granular hollow SnO2 nanofibers hydrogen gas sensors operating at low temperatures. J Phys Chem C 118:3129–3139
Mali SS, Patil JV, Kim H, Hong CK (2018) Synthesis of SnO2 nanofibers and nanobelts electron transporting layer for efficient perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale 10:8275–8284
Xia X, Dong XJ, Wei QF, Cai YB, Lu KY (2012) Formation mechanism of porous hollow SnO2 nanofibers prepared by one-step electrospinning. EXPRESS Polym Lett 6:169–176
Byun JH, Katoch A, Choi SW, Kim JH, Kim SS (2014) A novel synthesis route for Pt-loaded SnO2 nanofibers and their sensing properties. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14:8253–8257
Gong J, Qiao H, Sigdel S, Elbohy H, Adhikari N, Zhou Z, Sumathy V, Wei Q, Qiao Q (2015) Characteristics of SnO2 nanofiber/TiO2 nanoparticle composite for dye-sensitized solar cells. AIP Adv 5:067134
Choi SW, Park JY, Kim SS (2009) Synthesis of SnO2–ZnO core–shell nanofibers via a novel two-step process and their gas sensing properties. Nanotechnology 20:465603
Li X, Ji Y, Huang JS, Li J, Huang J (2017) Microtubular SnO2/V2O5 composites derived from cellulose substance as cathode materials of lithium-ion batteries. Chem Select 2:7987
Subramaniam MP, Arunachalam G, Kandasamy R, Veluswamy P, Hiroya I (2018) Effect of pH and annealing temperature on the properties of tin oxide nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:658–666
Subramaniam MP, Arunachalam G, Kandasamy R (2018) Studies on the structural, morphological and optical properties of HCl assisted vanadium oxide/tin oxide nanocomposites prepared by sol-gel method. Appl Sur Sci 449:610–616
Haider A, Haider S, Kang IK (2018) A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab J Chem 11:1165–1188
Prakash MBN, Manjunath A, Somashekar R (2013) Studies on AC Electrical conductivity of CdCl2 doped PVA polymer electrolyte. Adv Cond Matter Phys 2013:6
Reddy AB, Manjula B, Jayaramudu T, Sadiku ER, Babu PA, Selvam SP (2016) 5-fluorouracil loaded chitosan–PVA/Na+MMT nanocomposite films for drug release and antimicrobial activity. Nano-Micro Lett 8:260–269
Liu Z, Hu Z, Liang J, Li S, Yang Y, Peng S, Qian Y (2004) Size-controlled synthesis and growth mechanism of monodisperse tellurium nanorods by a surfactant-assisted method. Langmuir 20:214–218
Horzum N, Mari M, Wagner M, Fortunato G, Popa AM, Demir MM, Landfester K, Crespy D, Espi RM (2015) Controlled surface mineralization of metal oxides on nanofibers. RSC Adv 5:37340–37345
Ray SS, Chen SS, Li CW, Nguyen NC, Nguyen HT (2016) A comprehensive review: electrospinning technique for fabrication and surface modification of membranes for water treatment application. RSC Adv 6:85495–85514
Haider S, Zeghayer YA, Ali FAA, Haider A, Mahmood A, Masry WAA, Imran M, Aijaz MO (2013) Highly aligned narrow diameter chitosan electrospun nanofibers. J Polym Res 20:105
Deitzel JM, Kleinmeyer J, Harris D, Tan NCB (2001) The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 42:261–272
Zhang L, Ge S, Zuo Y, Zhang B, Xi L (2010) Influence of oxygen flow rate on the morphology and magnetism of SnO2 nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 114:7541–7547
Yan L, Pan JS, Ong CK (2006) XPS studies of room temperature magnetic Co-doped SnO2 deposited on Si. Mater Sci Eng B 128:34–36
Akhter S, Allan K, Buchanan D, Cook JA, Campion A, White JM (1988) XPS and IR study of X-ray induced degradation of PVA polymer film. Appl Sur Sci 35:241–258
Suematsu K, Kodama K, Ma N, Yuasa M, Kida T, Shimano K (2016) Role of vanadium oxide and palladium multiple loading on the sensitivity and recovery kinetics of tin dioxide based gas sensors. RSC Adv 6:5169–5176
Ahsan M, Ahmad MZ, Tesfamichael T, Bell J, Wlodarski W, Motta N (2012) Low temperature response of nanostructured tungsten oxide thin films toward hydrogen and ethanol. Sens Actuat B 173:789–796
Mahan GD (2016) Introduction to thermoelectrics. APL Mater 4:104806
Dong X, Gan Y, Peng S, Dong L, Wang Y (2013) Enhanced thermoelectric properties of WO3 by adding SnO2. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24:4494
Ferreira M, Loureiro J, Nogueira A, Rodrigues A, Martins R, Ferreira I (2015) SnO2 thin film oxides produced by RF sputtering for transparent thermoelectric devices. Mater Today Proc 2:647
Tervo J, Manninen A, Ilola R, Hanninen H (2009) State-of-the-art of thermoelectric materials processing, properties and applications. VTT, Finland 124:1
Uyar T, Besenbacher F (2008) Electrospinning of uniform polystyrene fibers: the effect of solvent conductivity. Polymer 49:5336–5343
Morad M, Fadlallah MM, Hassan MA, Sheha E (2016) Evaluation of the effect of V2O5on the electrical and thermoelectric properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene nanoplatelets nanocomposite. Mater Res Express 3:035015
Acknowledgements
MPS delightedly acknowledges Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India, New Delhi, India for financial support through [CSIR-HRDG No. 09/1045 (0019) 2K18 EMR I]. BJC acknowledges a research grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (NRF-2015R1A5A1036133). We also thank sincerely to SRM IST, Kattankulathur and gratefully acknowledge Prof. C. Muthamizhchelvan, Director E&T, Prof. D. John Thiruvadigal, Dean Sciences and Dr. C. Preferencial Kala, Head, Physics and Nanotechnology, SRM IST for the extended facilities created under (DST-FIST SR/FST/PSI-155/2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that thay have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramaniam, M.P., Veluswamy, P., Satheesh, A. et al. Electrospun SnO2 and its composite V2O5 nanofibers for thermoelectric power generator. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 98, 183–192 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05443-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05443-4