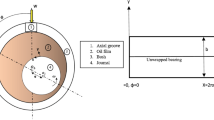
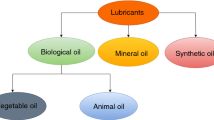
Abstract
The emergence of nanotechnology and existence of computational techniques for measuring the thermophysical properties of nanolubricants has culminated in a substantial number of experimental studies over past two decades. Development of nanoparticles is a field that has more proximity to innovations taking place in the domain of physics and chemistry but their application aspects have attracted the researchers towards the performance analysis of equipments with nanolubricants in diverse engineering fields. This paper presents a state-of-the-art review of various numerical and experimental studies conducted for enhancing the tribological performance of journal bearings with different lubricants. A comprehensive review of previously published studies has been provided as a valuable guide for researchers to choose the correct lubricant(s), nanoparticle(s), and selection of numerical and analytical methods for further exploration in the field of nanolubricants for performance enhancement of journal bearings. Several practical and technical issues with their potential solutions have also been explored in the field of nanolubricants. Despite their exemplary tribological performance, there is a dire need to formulate computational methods for the evaluation of journal bearing performance by taking the effects of nanolubricants into consideration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stachowiak G, Batchelor AW (2013) Engineering tribology, 4th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Dai W, Kheireddin B, Gao H, Liang H (2016) Roles of nanoparticles in oil lubrication. Tribol Int 102:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.05.020
Shahnazar S, Bagheri S, Abd Hamid SB (2016) Enhancing lubricant properties by nanoparticle additives. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:3153–3170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.12.040
Uflyand IE, Zhinzhilo VA, Burlakova VE (2019) Metal-containing nanomaterials as lubricant additives: State-of-the-art and future development. Friction 7:93–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40544-019-0261-y
Wu YY, Kao MJ (2011) Using TiO2/DN nanofluid additive for engine lubrication oil. Ind Lubricat Tribol 63:440–445. https://doi.org/10.1108/00368791111169025
Ghaednia H, Jackson RL, Khodadadi JM (2015) Experimental analysis of stable CuO nanoparticle enhanced lubricants. J Exp Nanosci 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2013.778424
Wu YY, Tsui WC, Liu TC (2007) Experimental analysis of tribological properties of lubricating oils with nanoparticle additives. Wear 262:819–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.08.021
Rapoport L, Leshchinsky V, Lvovsky M et al (2003) Superior tribological properties of powder materials with solid lubricant nanoparticles. Wear 255:794–800
Tarasov S, Kolubaev A, Belyaev S et al (2002) Study of friction reduction by nanocopper additives to motor oil. Wear 252:63–69
Khonsari MM, Booser ER (2017) Applied tribology: bearing design and lubrication. Wiley, Hoboken
Harnoy A (2002) Bearing design in machinery: engineering tribology and lubrication. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Raimondi AA, Boyd J (1958) A solution for the finite journal bearing and its application to analysis and design: I. ASLE Trans 1:159–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/05698195808972330
Raimondi AA, Boyd J (1958) A solution for the finite journal bearing and its application to analysis and design: II. ASLE Trans 1:175–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/05698195808972330
Raimondi AA, Boyd J (1958) A solution for the finite journal bearing and its application to analysis and design: III. ASLE Trans 1:194–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/05698195808972330
Habata K (1961) Theoretical pressure distribution in journal bearings. J Appl Mech 28:497–506
Dowson D (1962) A generalized Reynolds equation for fluid-film lubrication. Int J Mech Sci 4:159–170
Dowson D, Hudson JD, Hunter B, March CN (1966) An experimental investigation of the thermal equilibrium of steadily loaded journal bearings. Proc Inst Mech Eng Conf Proc 181:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1243/pime_conf_1966_181_034_02
Dowson D, March CN (1966) A thermohydrodynamic analysis of journal bearings. Vol 181, pp 117–126
McCallion H, Yousif F, Lloyd T (1970) The analysis of thermal effects in a full journal bearing. J Tribol 92:578–587. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3451479
Conway HD, Lee HC (1975) Analysis of the Lubrication of a Flexible Journal Bearing. American Society of Mechanical Engineers (Paper) 599–604
Suganami T, Szeri AZ (1979) A thermohydrodynamic analysis of journal bearings. J Tribol 101:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3453273
Crosby WA (1980) Thermal considerations in the solution of finite journal bearings. Wear 64:15–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(80)90091-5
Ferron J, Frene J, Boncompain R (1982) A study of the thermohydrodynamic performance of a plain journal bearing comparison between theory and experiments. Vol 105, pp 1–7
Khonsari MM (1987) A review of thermal effects in hydrodynamic bearings. Part II J Bear ASLE Trans 30:26–33
Mistry K, Biswas S, Athre K (1992) Study of thermal profile and cavitation in a circular journal bearing. Wear 159:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(92)90288-J
Banwait SS, Chandrawat HN (1998) Study of thermal boundary conditions for a plain journal bearing. Tribol Int 31:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-679X(98)00029-2
Singh U, Roy L, Sahu M (2008) Steady-state thermo-hydrodynamic analysis of cylindrical fluid film journal bearing with an axial groove. Tribol Int 41:1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.02.009
Brito FP, Miranda AS, Claro JCP, Fillon M (2012) Experimental comparison of the performance of a journal bearing with a single and a twin axial groove configuration. Tribol Int 54:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2012.04.026
Brito FP, Miranda AS, Claro JCP et al (2014) The role of lubricant feeding conditions on the performance improvement and friction reduction of journal bearings. Tribol Int 72:65–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2013.11.016
Manshoor B, Jaat M, Izzuddin Z, Amir K (2013) CFD analysis of thin film lubricated journal bearing. Proc Eng 68:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.12.147
Binu KG, Yathish K, Mallya R et al (2015) Experimental study of hydrodynamic pressure distribution in oil lubricated two-axial groove journal bearing. Mater Today Proc 2:3453–3462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.321
Cristea AF, Bouyer J, Fillon M, Pascovici MD (2017) Transient pressure and temperature field measurements in a lightly loaded circumferential groove journal bearing from startup to steady-state thermal stabilization. Tribol Trans 60:988–1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2016.1241330
Vinh DP, Chatterton S, Pennacchi P (2019) Static and dynamic behaviors of a cylindrical hydrodynamic journal bearing operating at very low Sommerfeld numbers. Mech Machine Sci 73:3835–3844. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20131-9_380
Pinkus O (1956) Analysis of elliptical bearings. Trans ASME 78:965–973
Pinkus O (1956) Power losses in elliptical and three lobe Bearings. Trans ASME 78:899–904
Pinkus O (1956) Experimental investigation of oil whip. Trans ASME 78:975–983
Pinkus O (1959) Analysis and characteristics of the three-lobe bearing. J Basic Eng 81:49–55
Gupta BK (1982) AJEET SINGH and B. K GUPTA Eng 77:159–170
Singh A, Gupta BK (1984) Stability analysis of orthogonally displaced bearings. Wear 97:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(84)90083-8
Malik M (1983) A comparative study of some two-lobed journal bearing configurations. ASLE Trans 26:118–124. https://doi.org/10.1080/05698198308981485
Hashimoto H, Wada S, Tsunoda H (1984) Performance characteristics of elliptical journal bearings in turbulent flow regime. Bulletin of JSME 27:2255–2261
Basri S, Gethin DT (1990) A comparative study of the thermal behaviour of profile bore bearings. Tribol Int 23:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-679X(90)90033-L
Crosby WA (1992) An investigation of the performance of a journal bearing with a slightly irregular bore. Tribol Int 25:199–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-679X(92)90049-S
Hussain A, Mistry K, Biswas S, Athre K (1996) Thermal analysis of noncircular bearings. J Tribol 118:246–254. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2837086
Ma MT, Taylor CM (1996) An experimental investigation of thermal effects in circular and elliptical plain journal bearings. Tribol Int 29:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-679X(95)00029-4
Sehgal R, Swamy KNS, Athre K, Biswas S (2000) A comparative study of the thermal behaviour of circular and non-circular journal bearings. Lubr Sci 12:329–344
Mishra PC, Pandey RK, Athre K (2007) Temperature profile of an elliptic bore journal bearing. Tribol Int 40:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2006.04.009
Strzelecki S, Ghoneam SM (2010) The effect of clearance variation on the maximum temperature of the oil film of cylindrical 3-lobe journal, pp 53–60
Sharma SC, Phalle VM, Jain SC (2012) Performance of a noncircular 2-lobe multirecess hydrostatic journal bearing with wear. Ind Lubricat Tribol 64:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1108/00368791211218704
van Ostayen RAJ, van Beek A (2009) Thermal modelling of the lemon-bore hydrodynamic bearing. Tribol Int 42:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.05.013
Huang B, Wang LQ, Guo J (2014) Performance comparison of circular, two-lobe and elliptical journal bearings based on TEHD analysis. Ind Lubricat Tribol 66:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-11-2011-0086
Mishra PC (2014) Analysis of a rough elliptic bore journal bearing using expectancy model of roughness characterization. Tribol Ind 36:211–219
Chasalevris A (2015) Analytical evaluation of the static and dynamic characteristics of three-lobe journal bearings with finite length. J Tribol. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4030023
Yogaraju R, Ravikumar L, Saravanakumar G et al (2016) Feasibility and performance studies of a semi active journal bearing. Proc Technol 25:1154–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2016.08.233
Singla A, Chauhan A (2016) Experimental study for performance evaluation of steadily loaded true elliptical and orthogonally displaced non-circular journal bearing profiles. Ind Lubricat Tribol 68:702–711. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-10-2015-0155
Tian J, Yang B, Yu L, Zhou J (2018) An investigation on the static performance of the non-circular journal bearing using fourier analysis. Proc ASME Turbo Expo 7A–2018:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1115/GT201877210
Rao TVVLN, Rani AM, Mohamed NM et al (2019) Static and stability analysis of partial slip texture multi-lobe journal bearings. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650119882834
Zhang C, Wang Y, Men R et al (2019) The effect of three-lobed bearing shapes in floating-ring bearings on the nonlinear oscillations of high-speed rotors. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650119873802
Chauhan A (2016) Non-circular journal bearings. Springer, Berlin
Ariman T, Turk MA, Sylvester ND (1973) Microcontinuum fluid mechanics-A review. Int J Eng Sci 11:905–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7225(73)90038-4
Needs SJ (1940) Boundary film investigations. Trans ASME 62:331
Swanson EE, Kirk RG, Mondy RE (1992) An examination and comparison of the maximum film temperature in a journal bearing for 13 synthetic, mineral, and viscosity index enhanced oils. SAE Tech Pap. https://doi.org/10.4271/922343
Del Din M, Kassfeldt E (1999) Wear characteristics with mixed lubrication conditions in a full scale journal bearing. Wear 232:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(99)00145-3
Durak E (2003) Experimental investigation of porous bearings under different lubricant and lubricating conditions. KSME Int J 17:1276–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982469
Brockwell K, Dmochowski W, Decamillo S (2004) An investigation of the steady-state performance of a pivoted shoe journal bearing with ISO VG 32 and VG 68 oils. Tribol Trans 47:480–488. https://doi.org/10.1080/05698190490493382
Dmochowski WM, Webster MN (2005) The effect of lubricant viscosity-temperature characteristics on the performance of plain journal bearings. Proc World Tribol Congress III - WTC 2005:2–3
Durak E, Çetinkaya M, Yenigün B, Karaosmanoǧlu F (2004) Effects of sunflower oil added to base oil on the friction coefficient of statically loaded journal bearings. J Synth Lubr 21:207–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsl.3000210304
Durak E, Karaosmanoǧlu F (2004) Using of cottonseed oil as an environmentally accepted lubricant additive. Energy Sour 26:611–625. https://doi.org/10.1080/00908310490438605
McCarthy DMC, Glavatskih SB, Byheden Å (2009) Influence of oil type on the performance characteristics of a two-axial groove journal bearing. Lubr Sci 21:366–377
Chauhan A, Sehgal R, Sharma RK (2010) Thermohydrodynamic analysis of elliptical journal bearing with different grade oils. Tribol Int 43:1970–1977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.03.017
Simmons GF, Glavatskih SB (2011) Synthetic lubricants in hydrodynamic journal bearings: experimental results. Tribol Lett 42:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9753-2
Nikolakopoulos PG, Bompos DA (2015) Experimental measurements of journal bearing friction using mineral, synthetic, and bio-based lubricants. Lubricants 3:155–163. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3020155
Muzakkir SM, Hirani H, Thakre GD, Tyagi MR (2011) Tribological failure analysis of journal bearings used in sugar mills. Eng Fail Anal 18:2093–2103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2011.06.016
Singla A, Chauhan A (2016) Evaluation of oil film pressure and temperature of an elliptical journal bearing—an experimental study. Tribol Ind 38:74–82
Dadouche A, Conlon MJ (2016) Operational performance of textured journal bearings lubricated with a contaminated fluid. Tribol Int 93:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2015.09.022
Marx N, Fernández L, Barceló F, Spikes H (2018) Shear thinning and hydrodynamic friction of viscosity modifier-containing oils. part i: shear thinning behaviour. Tribol Lett 66:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1039-5
Marx N, Fernández L, Barceló F, Spikes H (2018) Shear thinning and hydrodynamic friction of viscosity modifier-containing oils. part II: impact of shear thinning on journal bearing friction. Tribol Lett 66:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1040-z
Chowdhury MA, Mia MS, Kchaou M et al (2020) Friction coefficient and performance evaluation of plain journal bearing using SAE 5W–30 engine oil. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650120903927
Stunkel BW, Karol TJ, Donnelly SG (2004) Antioxidant, antiwear/extreme pressure additive compositions and lubricating compositions containing the same
Finšgar M, Jackson J (2014) Application of corrosion inhibitors for steels in acidic media for the oil and gas industry: a review. Corros Sci 86:17–41
Bhattacharjee RC, Das NC (1996) Power law fluid model incorporated into elastohydrodynamic lubrication theory of line contact. Tribol Int 29:405–413
Vijaysri M, Chhabra RP, Eswaran V (1999) Power-law fluid flow across an array of infinite circular cylinders: a numerical study. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 87:263–282
Safar ZS (1979) Dynamically loaded bearings operating with non-Newtonian lubricant films. Wear 55:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(79)90161-3
Pinkus O, Sternlicht B (1961) Theory of hydrodynamic lubrication. McGraw-Hill, New York
Tayal SP, Sinhasan R, Singh DV (1981) Analysis of hydrodynamic journal bearings with non-newtonian power law lubricants by the finite element method. Wear 71:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(81)90136-8
Tayal SP, Sinhasan R, Singh DV (1982) Finite element analysis of elliptical bearings lubricated by a non-Newtonian fluid. Wear 80:71–81
Dien IK, Elrod HG (1983) A generalized steady-state reynolds equation for non-newtonian fluids, with application to journal bearings. J Tribol 105:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3254619
Johnson MW, Mangkoesoebroto S (1993) Analysis of lubrication theory for the power law fluid. J Tribol 115:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2920988
Tanner RI (1985) Engineering Rheology. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Buckholz RH (1985) On the role of a non-newtonian fluid in short bearing theory. J Tribol 107:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3261004
Buckholz RH (1986) Effoots of power—law, non-newtonian lubricants on load capacity and friction for plane slider bearings. J Tribol 108:86–91. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3261149
Buckholz RH, Lin JF (1986) The effect of journal bearing misalignment on load and cavitation for non-newtonian lubricants. J Tribol 108:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3261295
Jiin-Yuh J, Chong-Ching C (1988) Adiabatic analysis of finite width journal bearings with non-newtonian lubricants. Wear 122:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(88)90007-5
Zhang C, Cheng HS (2000) Transient non-Newtonian thermohydrodynamic mixed lubrication of dynamically loaded journal bearings. J Tribol 122:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.555338
Sharma SC, Jain SC, Sinhasan R, Sah PL (2001) Static and dynamic performance characteristics of orifice compensated hydrostatic flexible journal bearings with non-newtonian lubricants. Tribol Trans 44:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402000108982454
Garg HC, Kumar V, Sharda HB (2010) Performance of slot-entry hybrid journal bearings considering combined influences of thermal effects and non-Newtonian behavior of lubricant. Tribol Int 43:1518–1531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.02.013
Mongkolwongrojn M, Arunmetta P (2002) Theoretical characteristics of hydrodynamic journal bearings lubricated with soybean-based oil. J Synth Lubr 19:213–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsl.3000190304
Mongkolwongrojn M, Aiumpronsin C (2010) Stability analysis of rough journal bearings under TEHL with non-Newtonian lubricants. Tribol Int 43:1027–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2009.12.039
Khatri CB, Sharma SC (2016) Influence of textured surface on the performance of non-recessed hybrid journal bearing operating with non-Newtonian lubricant. Tribol Int 95:221–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2015.11.017
Lin JR, Chu LM, Hung TC, Wang PY (2016) Derivation of two-dimensional non-Newtonian Reynolds equation and application to power-law film slider bearings: Rabinowitsch fluid model. Appl Math Model 40:8832–8841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2016.04.030
Lin JR, Hung TC, Lin CH (2019) Linear stability analysis of journal bearings lubricated with a non-Newtonian rabinowitsch fluid. J Mech 35:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1017/jmech.2017.48
Yadav SK, Rajput AK, Ram N, Sharma SC (2019) Stability analysis of a rigid rotor supported by two-lobe hydrodynamic journal bearings operating with a non-Newtonian lubricant. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 233:884–898. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650118806377
Das S, Guha SK, Chattopadhyay AK (2002) On the steady-state performance of misaligned hydrodynamic journal bearings lubricated with micropolar fluids. Tribol Int 35:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-679X(01)00065-2
Eringen AC (1964) Simple microfluids. Int J Eng Sci 2:205–217
Eringen A (1966) Theory of micropolar fluids. Indiana Univ Mathe J 16:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1512/iumj.1967.16.16001
Naduvinamani NB, Biradar TV (2007) Effects of surface roughness on porous inclined slider bearings lubricated with micropolar fluids. J Mar Sci Technol 15:278–286
Shukla JB, Isa M (1975) Generalized Reynolds equation for micropolar lubricants and its application to optimum one-dimensional slider bearings: effects of solid-particle additives in solution. J Mech Eng Sci 17:280–284
Zaheeruddin K, Isa M (1978) Micropolar fluid lubrication of one-dimensional journal bearings. Wear 50:211–220
Khonsari MM, Brewe DE (1989) On the performance of finite journal bearings lubricated with micropolar fluids. Tribol Trans 32:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402008908981874
Wang XL, Zhu KQ (2006) Numerical analysis of journal bearings lubricated with micropolar fluids including thermal and cavitating effects. Tribol Int 39:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2005.01.028
Prabhakaran Nair K, Sukumaran Nair VP, Jayadas NH (2007) Static and dynamic analysis of elastohydrodynamic elliptical journal bearing with micropolar lubricant. Tribol Int 40:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2005.09.017
Rahmatabadi AD, Zare Mehrjardi M, Fazel MR (2010) Performance analysis of micropolar lubricated journal bearings using GDQ method. Tribol Int 43:2000–2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.05.002
Rajasekhar Nicodemus E, Sharma SC (2011) Orifice compensated multirecess hydrostatic/hybrid journal bearing system of various geometric shapes of recess operating with micropolar lubricant. Tribol Int 44:284–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.10.026
Sharma SC, Ram N (2011) Influence of micropolar lubricants on the performance of slot-entry hybrid journal bearing. Tribol Int 44:1852–1863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.07.006
Ram N, Sharma SC (2012) Analysis of orifice compensated non-recessed hole-entry hybrid journal bearing operating with micropolar lubricants. Tribol Int 52:132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2012.03.012
Dhawan R, Verma S (2014) Analyzing Micropolar Lubrication in Noncircular Hybrid Journal Bearings. Tribol Trans 57:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2013.859337
Budheeja K, Verma S (2017) A comparative linear and nonlinear stability analysis of hybrid journal bearing operating with micropolar lubricant. Tribol Online 12:203–220. https://doi.org/10.2474/trol.12.203
Khatak P, Garg HC (2018) Investigation of the micropolar lubricant and thermal effects in the slot entry hybrid journal bearings. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 232:2103–2116. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406217713519
Meybodi RR, Shooroki AR, Mehrjardi MZ (2018) Thermo-hydrodynamic performance of tilted non-circular micropolar lubricated journal bearings. Ind Lubricat Tribol 70:711–723
Stokes VK (1966) Couple stresses in fluids. Phys Fluids 9:1709–1715. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1761925
Ariman TTND, Turk MA, Sylvester ND (1974) Applications of microcontinuum fluid mechanics. Int J Eng Sci 12:273–293
Lin JR (1998) Squeeze film characteristics of finite journal bearings: couple stress fluid model. Tribol Int 31:201–207
Mokhiamer UM, Crosby WA, El-Gamal HA (1999) A study of a journal bearing lubricated by fluids with couple stress considering the elasticity of the liner. Wear 224:194–201
Das NC (1998) A study of optimum load-bearing capacity for slider bearings lubricated with couple stress fluids in magnetic field. Tribol Int 31:393–400
Wang XL, Zhu KQ, Wen SZ (2001) Thermohydrodynamic analysis of journal bearings lubricated with couple stress fluids. Tribol Int 34:335–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-679X(01)00022-6
Elsharkawy AA (2005) Effects of lubricant additives on the performance of hydrodynamically lubricated journal bearings. Tribol Lett 18:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-004-1758-7
Jaya Chandra Reddy G, Eswara Reddy C, Rama Krishna Prasad K (2008) Effect of viscosity variation on the squeeze film performance of a narrow hydrodynamic journal bearing operating with couple stress fluids. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 222:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1243/13506501JET327
Crosby WA, Chetti B (2009) The static and dynamic characteristics of a two-lobe journal bearing lubricated with couple-stress fluid. Tribol Trans 52:262–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402000802527773
Chetti B (2011) Static and dynamic analysis of hydrodynamic four-lobe journal bearing with couple stress lubricants. Jordan J Mech Indust Eng 5:23–28
Some S, Guha SK (2018) Effect of slip and percolation of polar additives of coupled-stress lubricant on the steady-state characteristics of double-layered porous journal bearings. J Brazil Soc Mech Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1018-7
Kumar Lambha S, Kumar V, Verma R (2019) Elastohydrodynamic analysis of couple stress lubricated cylindrical journal bearing. J Phys Conf Ser. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1240/1/012165
Rohilla PK, Verma R, Verma S (2019) Performance analysis of couple stress fluid operated elastic hydrodynamic journal bearing. Tribol Online 14:143–154. https://doi.org/10.2474/trol.14.143
Zheng L, Zhu H, Zhu J, Deng Y (2020) Effects of oil film thickness and viscosity on the performance of misaligned journal bearings with couple stress lubricants. Tribol Int 146:106229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106229
Kumar A, Kakoty SK (2019) Effect of couple-stress parameter on the steady state performance parameters of two-lobe journal bearing operating with non- Newtonian lubricant. Mater Today Proc 24:473–482
Ram N (2017) Study of constant flow valve compensated hydrostatic hole-entry journal bearings with couple stress lubricants. Int J Des Eng 7:142. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijde.2017.10010628
Lahmar M (2005) Elastohydrodynamic analysis of double-layered journal bearings lubricated with couple-stress fluids. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 219:145–165
Mahdi MA, Hussein AW (2019) Investigation the combined effects of wear and turbulent on the performance of hydrodynamic journal bearing operating with couple stress fluids. Int J Struct Integrity 10:825–837
Mortier RM, Orszulik ST (1992) Chemistry and technology of lubricants. VCH Publishers Inc., New York
Nagendramma P, Kaul S (2012) Development of ecofriendly/biodegradable lubricants: an overview. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:764–774
Gansheimer J, Holinski R (1973) Molybdenum disulfide in oils and greases under boundary conditions. ASME J Lubricat Technol 95:242–246
Choi Y, Lee C, Hwang Y et al (2009) Tribological behavior of copper nanoparticles as additives in oil. Curr Appl Phys 9:e124-127
Zhou J, Wu Z, Zhang Z et al (2000) Tribological behavior and lubricating mechanism of Cu nanoparticles in oil. Tribol Lett 8:213–218
Luo T, Wei X, Huang X et al (2014) Tribological properties of Al2O3 nanoparticles as lubricating oil additives. Ceram Int 40:7143–7149
Aldana PU, Dassenoy F, Vacher B et al (2016) WS2 nanoparticles anti-wear and friction reducing properties on rough surfaces in the presence of ZDDP additive. Tribol Int 102:213–221
Gupta RN, Harsha AP (2018) Antiwear and extreme pressure performance of castor oil with nano-additives. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 232:1055–1067
Rahmati B, Sarhan AA, Sayuti M (2014) Morphology of surface generated by end milling AL6061-T6 using molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanolubrication in end milling machining. J Cleaner Prod 66:685–691
Azman NF, Samion S (2019) Dispersion stability and lubrication mechanism of nanolubricants: a review. Int J Precision Eng Manuf Green Technol 6:393–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00080-x
Sgroi M, Gili F, Mangherini D et al (2015) Friction reduction benefits in valve-train system using IF-MoS2 added engine oil. Tribol Trans 58:207–214
Chou R, Battez AH, Cabello JJ et al (2010) Tribological behavior of polyalphaolefin with the addition of nickel nanoparticles. Tribol Int 43:2327–2332
Cho Y, Park J, Ku B et al (2012) Synergistic effect of a coating and nano-oil lubricant on the tribological properties of friction surfaces. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0013-7
Chu HY, Hsu WC, Lin JF (2010) Scuffing mechanism during oil-lubricated block-on-ring test with diamond nanoparticles as oil additive. Wear 268:1423–1433
Sia SY, Sarhan AA (2014) Morphology investigation of worn bearing surfaces using SiO2 nanolubrication system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70:1063–1071
Qiu S, Zhou Z, Dong J, Chen G (2001) Preparation of Ni nanoparticles and evaluation of their tribological performance as potential additives in oils. J Tribol 123:441–443. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1286152
Lee J, Cho S, Hwang Y et al (2009) Application of fullerene-added nano-oil for lubrication enhancement in friction surfaces. Tribol Int 42:440–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.08.003
Lee CG, Hwang YJ, Choi YM et al (2009) A study on the tribological characteristics of graphite nano lubricants. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 10:85–90
Lee K, Hwang Y, Cheong S et al (2009) Understanding the role of nanoparticles in nano-oil lubrication. Tribol Lett 35:127–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9441-7
Vadiraj A, Manivasagam G, Kamani K, Sreenivasan VS (2012) Effect of nano oil additive proportions on friction and wear performance of automotive materials. Tribol Ind 34:3–10
Padgurskas J, Rukuiza R, Prosyčevas I, Kreivaitis R (2013) Tribological properties of lubricant additives of Fe, Cu and Co nanoparticles. Tribol Int 60:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2012.10.024
Hu K, Cai Y, Hu X, Xu Y (2013) Synergistic lubrication of MoS2 particles with different morphologies in liquid paraffin. Ind Lubricat Tribol 65:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1108/00368791311311141
Çelik ON, Ay N, Göncü Y (2013) Effect of nano hexagonal boron nitride lubricant additives on the friction and wear properties of AISI 4140 steel. Part Sci Technol 31:501–506. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2013.779336
Jeng YR, Huang YH, Tsai PC, Hwang GL (2014) Tribological properties of carbon nanocapsule particles as lubricant additive. J Tribol 136:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4027994
Baskar S, Sriram G (2014) Tribological behavior of journal bearing material under different lubricants. Tribol Ind 36:127–133
Ghaednia H, Hossain MS, Jackson RL (2016) Tribological performance of silver nanoparticle-enhanced polyethylene glycol lubricants. Tribol Trans 59:585–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2015.1092623
Marko M, Kyle J, Branson B, Terrell E (2015) Tribological improvements of dispersed nanodiamond additives in lubricating mineral oil. J Tribol 137:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4028554
Bhaumik S, Pathak SD (2015) Analysis of anti-wear properties of cuo nanoparticles as friction modifiers in mineral oil (460cst viscosity) using pin-on-disk tribometer. Tribol Ind 37:196–203
Jatti VS, Singh TP (2015) Copper oxide nano-particles as friction-reduction and anti-wear additives in lubricating oil. J Mech Sci Technol 29:793–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-0141-y
Wan Q, Jin Y, Sun P, Ding Y (2015) Tribological behaviour of a lubricant oil containing boron nitride nanoparticles. Proc Eng 102:1038–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.01.226
Laad M, Jatti VKS (2018) Titanium oxide nanoparticles as additives in engine oil. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 30:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2016.01.008
Baskar S, Sriram G, Arumugam S (2016) The use of d-optimal design for modeling and analyzing the tribological characteristics of journal bearing materials lubricated by nano-based biolubricants. Tribol Trans 59:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2015.1063179
Lu Z, Cao Z, Hu E et al (2019) Preparation and tribological properties of WS2 and WS2/TiO2 nanoparticles. Tribol Int 130:308–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.09.030
Ilie F, Covaliu C (2016) Tribological properties of the lubricant containing titanium dioxide nanoparticles as an additive. Lubricants 4:12–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020012
Charoo MS, Wani MF (2016) Tribological properties of IF-MoS2 nanoparticles as lubricant additive on cylinder liner and piston ring tribo-pair. Tribol Ind 38:156–162
Ali MKA, Xianjun H, Elagouz A et al (2016) Minimizing of the boundary friction coefficient in automotive engines using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3679-4
Ali MKA, Fuming P, Younus HA et al (2018) Fuel economy in gasoline engines using Al2O3/TiO2 nanomaterials as nanolubricant additives. Appl Energy 211:461–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.11.013
Ali MKA, Xianjun H, Mai L et al (2016) Reducing frictional power losses and improving the scuffing resistance in automotive engines using hybrid nanomaterials as nano-lubricant additives. Wear 364–365:270–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.08.005
Umer J, Morris N, Leighton M et al (2019) Nano and microscale contact characteristics of tribofilms derived from fully formulated engine oil. Tribol Int 131:620–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.11.007
Guzman Borda FL, Ribeiro de Oliveira SJ, Seabra Monteiro Lazaro LM, Kalab Leiróz AJ (2018) Experimental investigation of the tribological behavior of lubricants with additive containing copper nanoparticles. Tribol Int 117:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.08.012
Saravanakumar N, Jothi Saravanan ML, Barathkumar KE et al (2019) Development and testing of nano particulate lubricant for worm gear application. J Mech Sci Technol 33:1785–1791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0330-1
Saini V, Bijwe J, Seth S, Ramakumar SSV (2020) Role of base oils in developing extreme pressure lubricants by exploring nano-PTFE particles. Tribol Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2019.106071
Kotia A, Ghosh GK, Srivastava I et al (2019) Mechanism for improvement of friction/wear by using Al2O3 and SiO2/Gear oil nanolubricants. J Alloy Compd 782:592–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.215
Mashhadi Keshtiban P, Sheydaei Govarchin Ghaleh S, Alimirzaloo V (2019) Lubrication efficiency of vegetable oil nano-lubricants and solid powder lubricants. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part L J Mater Des Appl 233:1384–1392. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420718754357
Peng DX, Kang Y, Chen CH et al (2009) The tribological behavior of modified diamond nanoparticles in liquid paraffin. Ind Lubricat Tribol 61:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1108/00368790910960057
Shen M, Luo J, Wen S (2001) The tribological properties of oils added with diamond nano-particles. Tribol Trans 44:494–498. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402000108982487
Xu X, Choi Su S, Wang X (1999) Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle - fluid mixture. J Thermophys Heat Transfer 13:474–480
Das SK, Choi SU, Patel HE (2006) Heat transfer in nanofluids—a review. Heat Transfer Eng 27:3–19
Goyal D, Dang RK, Dhami SS, Chauhan A (2017) Effect of nanoparticles based lubricants on static thermal behaviour of journal bearings: a review. Res J Eng Technol 8:149. https://doi.org/10.5958/2321-581x.2017.00023.x
Nicoletti R (2014) The importance of the heat capacity of lubricants with nanoparticles in the static behavior of journal bearings. J Tribol 136:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4027861
Prabhakaran Nair K, Ahmed MS, Al-qahtani ST (2009) Static and dynamic analysis of hydrodynamic journal bearing operating under nano lubricants. Int J Nanoparticles 2:251–262
Solghar AA (2015) Investigation of nanoparticle additive impacts on thermohydrodynamic characteristics of journal bearings. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 229:1176–1186. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650115574734
Gunnuang W, Aiumpornsin C, Mongkolwongrojn M (2015) Effect of nanoparticle additives on journal bearing lubricated with non-Newtonian Carreau fluid. Appl Mech Mater 751:137–142. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.751.137
Kalakada SB, Kumarapillai PNN, Rajendra Kumar PK (2015) Static characteristics of thermohydrodynamic journal bearing operating under lubricants containing nanoparticles. Ind Lubricat Tribol 67:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-01-2013-0015
Prabhakaran Nair K, Rajendra Kumar PK, Sreedhar Babu K (2011) Thermohydrodynamic analysis of journal bearing operating under nanolubricants. Am Soc Mech Eng Tribol Div TRIB. https://doi.org/10.1115/IJTC2011-61244
Kalakada SB, Kumarapillai PN, Perikinalil RK (2012) Analysis of static and dynamic performance characteristics of THD journal bearing operating under lubricants containing nanoparticles. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13:1869–1876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0245-6
Binu KG, Shenoy BS, Rao DS, Pai R (2014) Static characteristics of a fluid film bearing with TiO2 based nanolubricant using the modified Krieger-Dougherty viscosity model and couple stress model. Tribol Int 75:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2014.03.013
Binu KG, Shenoy BS, Rao DS, Pai R (2014) A variable viscosity approach for the evaluation of load carrying capacity of oil lubricated journal bearing with TiO2 nanoparticles as lubricant additives. Proc Mater Sci 6:1051–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.176
Abass BA, Mohammed NF (2017) Thermohydrodynamic characteristics of worn journal bearing lubricated with oil containing nanoparticles additive abstract: keywords: introduction. Al-Nahrain J Eng Sci 20:526–543
Kumar A, Kakoty SK (2017) A variable viscosity approach for the analysis of steady state and dynamic characteristics of two-lobe journal bearing with TiO2 based nanolubricant. In: ASME 2017 Gas Turbine India Conference, GTINDIA 2017, vol 2, pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1115/GTINDIA2017-4661
Kumar A, Kakoty SK (2019) A variable viscosity technique for the analysis of static and dynamic performance parameters of three-lobe fluid film bearing operating with TiO2-based nanolubricant, pp 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6287-3_1
Suryawanshi SR, Pattiwar JT (2018) Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles blended with lubricating oil on the tribological performance of the journal bearing. Tribol Ind 40:370–391. https://doi.org/10.24874/ti.2018.40.03.04
Jamalabadi MYA, Alamian R, Yan WM et al (2019) Effects of nanoparticle enhanced lubricant films in thermal design of plain journal bearings at high reynolds numbers. Symmetry 11:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111353
Shenoy BS, Binu KG, Pai R et al (2012) Effect of nanoparticles additives on the performance of an externally adjustable fluid film bearing. Tribol Int 45:38–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.10.004
Rao TVVLN, Sufian S, Mohamed NM (2013) Analysis of nanoparticle additive couple stress fluids in three-layered journal bearing. J Phys: Conf Ser. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/431/1/012023
Baskar S, Sriram G, Arumugam S (2017) Tribological analysis of a hydrodynamic journal bearing under the influence of synthetic and biolubricants. Tribol Trans 60:428–436. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2016.1176285
Ramaganesh R, Baskar S, Sriram G et al (2020) Finite element analysis of a journal bearing lubricated with nano lubricants. FME Trans 48:476–481. https://doi.org/10.5937/fme2002476R
Baskar S, Sriram G, Arumugam S (2018) Fuzzy logic model to predict oil-film pressure in a hydrodynamic journal bearing lubricated under the influence of nano-based bio-lubricants. Energy Sour Part A Recover Utiliz Environ Effects 40:1583–1590. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2018.1486479
Kornaev A, Savin L, Kornaeva E, Fetisov A (2016) Influence of the ultrafine oil additives on friction and vibration in journal bearings. Tribol Int 101:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.04.014
Katpatal DC, Andhare AB, Padole PM (2020) Performance of nano-bio-lubricants, ISO VG46 oil and its blend with Jatropha oil in statically loaded hydrodynamic plain journal bearing. Proc Instit Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 234:386–400. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650119864242
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, R.K., Goyal, D., Chauhan, A. et al. Numerical and Experimental Studies on Performance Enhancement of Journal Bearings Using Nanoparticles Based Lubricants. Arch Computat Methods Eng 28, 3887–3915 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09538-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09538-1