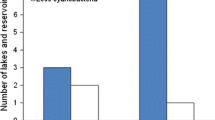
Abstract
Changes in water level and flushing rate directly affect to a large extent the biomass of harmful cyanobacteria, and drive the shift of phytoplankton composition between cyanobacteria dominance/non-dominance in eutrophic waters. Here, we gave a theoretical formula describing the combinational effect of water level and flushing rate on cyanobacterial biomass in eutrophic and well-mixed waters. We also formulated an equation predicting the water level and flushing rate at which cyanobacteria become non-dominating in such water columns. The formulae were confronted with field observations of a low-light adapted cyanobacterium in a large coastal reservoir of southern China. Our formulae demonstrate that water level and flushing rate have an interactive effect on the equilibrium biomass of low-light adapted cyanobacteria in mixed and turbid waters. The formulae were well fitted to the field observation of Raphidiopsis raciborskii population in the reservoir during four dry seasons. In agreement with the theoretical analysis, multiple regression analysis also showed that the interaction between water level and flushing rate is able to interpret the variation of R. raciborskii biomass in the water column. The two formulae are applicable for predicting the response of low-light adapted cyanobacteria to local climate change. Our findings have practical significance in designing measures against the dominance of low light-adapted cyanobacteria in reservoirs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian R, O’Reilly CM, Zagarese H, Baines SB, Hessen DO, Keller W, Winder M (2009) Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnol Oceanogr 54:2283–2297
Antenucci JP, Ghadouani A, Burford MA, Romero JR (2005) The long-term effect of artificial destratification on phytoplankton species composition in a subtropical reservoir. Freshw Biol 50:1081–1093
Bakker ES, Hilt S (2016) Impact of water-level fluctuations on cyanobacterial blooms: options for management. Aquat Ecol 50:485–498
Berger C, Ba N, Gugger M, Bouvy M, Rusconi F, Couté A, Troussellier M, Bernard C (2006) Seasonal dynamics and toxicity of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in lake Guiers (Senegal, West Africa). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 57:355–366
Brauer VS, Stomp M, Huisman J (2012) The nutrient-load hypothesis: patterns of resource limitation and community structure driven by competition for nutrients and light. Am Natur 179:721–740
Briand JF, Leboulanger C, Humbert JF, Bernard C, Dufour P (2004) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) invasion at mid-latitudes: selection, wide physiological tolerance, or global warming? J Phycol 40:231–238
Burford MA, Beardall J, Willis A, Orr PT, Magalhaes VF, Rangel LM, Azevedo SM, Neilan BA (2016) Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 54:44–53
Burford MA, Davis TW (2011) Physical and chemical processes promoting dominance of the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 29:883–891
Diehl S (2002) Phytoplankton, light, and nutrients in a gradient of mixing depths: theory. Ecology 83:386–398
Dobberfuhl DR (2003) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in three central florida lakes: population dynamics, controls, and management implications. Lake Reserv Manag 19:341–348
Elliott JA (2010) The seasonal sensitivity of cyanobacteria and other phytoplankton to changes in flushing rate and water temperature. Global Change Biol 16:864–876
Falconer IR, Humpage AR (2001) Preliminary evidence for in vivo tumour initiation by oral administration of extracts of the blue-green alga Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii containing the toxin cylindrospermopsin. Environ Toxicol 16:192–195
Figueredo CC, Giani A (2009) Phytoplankton community in the tropical lake of Lagoa Santa (Brazil): conditions favoring a persistent bloom of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Limnologica 39:264–272
Gemelgo MCP, Sant’Anna CL, Tucci A, Barbosa HR (2008) Population dynamics of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya & Subba Raju, a cyanobacteria toxic species, in water supply reservoirs in São Paulo, Brazil. Hoehnea 35:297–307
Goldman CR, Jassby A, Powell T (1989) Interannual fluctuations in primary production: meteorological forcing at two subalpine lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 34:310–323
Greenberg AE (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Water Works Association and Water Pollution Control Federation, Washington, DC
Han B-P, Armengol J, Garcia JC, Comerma M, Roura M, Dolz J, Stras̆kraba M (2000) The thermal structure of Sau reservoir (NE: Spain): a simulation approach. Ecol Model 125:109–122
Han B-P, Virtanen M, Koponen J, Koponen J, Stras̆kraba M (1999) Predictors of light-limited growth and competition of phytoplankton in a well-mixed water column. J Theor Biol 197:439–450
Hillebrand H, Dürselen CD, Kirschtel D, Pollingher U, Zohary T (1999) Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J Phycol 35:403–424
Hoff-Risseti C, Dörr FA, Schaker PDC, Pinto E, Werner VR, Fiore MF (2013) Cylindrospermopsin and saxitoxin synthetase genes in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains from Brazilian freshwater. PLoS ONE 8:e74238
Huisman J (1999) Population dynamics of light-limited phytoplankton: microcosm experiments. Ecology 80:202–210
Huisman J, Hulot FD (2005) Population dynamics of harmful cyanobacteria. In: Huisman J, Matthijs HCP, Visser PM (Eds), Harmful cyanobacteria. Springer, Dordrecht, the Netherlands. pp 143–176
Huisman J, Jonker RR, Zonneveld C, Weissing J (1999) Competition for light between phytoplankton species: experimental tests of mechanistic theory. Ecology 80:211–222
Huisman J, Weissing FJ (1994) Light-limited growth and competition for light in well-mixed aquatic environments: an elementary model. Ecology 75:507–520
Janse van Vuuren S, Kriel GP (2008) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, a toxic invasive cyanobacterium in South African fresh waters. Afr J Aquat Sci 33:17–26
Jöhnk KD, Huisman J, Sharples J, Sommeijer B, Visser PM, Stroom JM (2008) Summer heatwaves promote blooms of harmful cyanobacteria. Global Change Biol 14:495–512
King JR, Shuter BJ, Zimmerman AP (1999) Signals of climate trends and extreme events in the thermal stratification pattern of multibasin Lake Opeongo, Ontario. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56:847–852
Kinnear S (2010) Cylindrospermopsin: a decade of progress on bioaccumulation research. Mar Drugs 8:542–564
Lei L, Peng L, Huang X, Han B-P (2014) Occurrence and dominance of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and dissolved cylindrospermopsin in urban reservoirs used for drinking water supply, South China. Environ Monit Assess 186:3079–3090
McGregor GB, Fabbro LD (2000) Dominance of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanoprokaryota) in Queensland tropical and subtropical reservoirs: implications for monitoring and management. Lakes Reserv Res Manag 5:195–205
Mitrovic SM, Hardwick L, Dorani F (2010) Use of flow management to mitigate cyanobacterial blooms in the lower Darling River, Australia. J Plankton Res 33:229–241
Mitrovic SM, Oliver RL, Rees C, Bowling LC, Buckney RT (2003) Critical flow velocities for the growth and dominance of Anabaena circinalis in some turbid freshwater rivers. Freshw Biol 48:164–174
Nielsen A, Trolle D, Bjerring R, Søndergaard M, Olesen JE, Janse JH, Mooij WM, Jeppesen E (2014) Effects of climate and nutrient load on the water quality of shallow lakes assessed through ensemble runs by PCLake. Ecol Appl 24:1926–1944
Ohtani I, Moore RE, Runnegar MTC (1992) Cylindrospermopsin: a potent hepatotoxin from the blue-green alga Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. J Am Chem Soc 114:7941–7942
Padisák J (1997) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptive cyanobacterium: worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Arch Hydrobiol Suppl Monograph Beitr 107:563–593
Paerl HW, Huisman J (2009) Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ Microbiol Rep 1:27–37
Qian SS (2017) Environmental and ecological statistics with R, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Florida
Recknagel F, Orr PT, Cao H (2014) Inductive reasoning and forecasting of population dynamic of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in three sub-tropical reservoirs by evolutionary computation. Harmful Algae 31:26–34
Rigosi A, Hanson P, Hamilton DP, Hipsey M, Rusak JA, Bois J, Brookes JD (2015) Determining the probability of cyanobacterial blooms: the application of Bayesian networks in multiple lake systems. Ecol Appl 25:186–199
Robarts RD, Zohary T (1987) Temperature effects on photosynthetic capacity, respiration, and growth rates of bloom-forming cyanobacteria. N Zeal J Mar Fresh 21:391–399
Saker ML, Thomas AD, Norton JH (1999) Cattle mortality attributed to the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in an outback region of north Queensland. Environ Toxicol 14:179–182
De Souza RCR, Carvalho MC, Truzzi AC (1998) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Wolosz.) Seenaya and Subba Raju (Cyanophyceae) dominance and a contribution to the knowledge of Rio Pequeno Arm, Billings reservoir, Brazil. Environ Toxicol 13:73–81
Stras̆kraba M, Tundisi JG, Duncan A (1993) State-of-the art of reservoir limnology and water quality management. In: Straskraba M, Tundisi JG, Duncan A (Eds), Comparitive resevoir limnology and water quality management. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, the Netherlands, pp 213–288
Stken A, Rcker J, Endrulat T, Preussel K, Hemm M, Nixidorf UK, Wiedner C (2006) Distribution of three alien cyanobacterial species (Nostocales) in northeast Germany: Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, Anabaena bergii and Aphanizomenon aphanizomenoides. Phycologia 45:696–703
Svirčev Z, Obradović V, Codd GA, Marjanović P, Spoof L, Damjana D, Tokodi N, Anđelka P, Nenin T, Simeunović J, Važić T, Meriluoto J (2016) Massive fish mortality and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii bloom in Aleksandrovac Lake. Ecotoxicology 25:1353–1363
Tilzer MM (1987) Light-dependence of photosynthesis and growth in cyanobacteria: implications for their dominance in eutrophic lakes. N Zeal J Mar Fresh 21:401–412
Trenberth KE (2011) Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim Res 47:123–138
Utermöhl H (1958) Zur vervollkommnung der quantitativen phytoplankton-methodik. Int Ver Theor Angew Limnol: Mitt 9:1–38
Verspagen JMH, Passarge J, Jöhnk KD, Visser PR, Peperzak L, Paul B, Laanbroek HJ, Huisman J (2006) Water management strategies against toxic microcystis blooms in the Dutch delta. Ecol Appl 16:313–327
Visser P, Ibelings BW, Van Der Veer B, Koedood J, Mur LR (1996) Artificial mixing prevents nuisance blooms of the cyanobacterium microcystis in Lake Nieuwe Meer, the Netherlands. Freshw Biol 36:435–450
Wagner C, Adrian R (2009) Cyanobacteria dominance: quantifying the effects of climate change. Limnol Oceanogr 54:2460–2468
Webster IT, Sherman BS, Bormans M, Jones J (2000) Management strategies for cyanobacterial blooms in an impounded lowland river. Regul Rivers: Res Manat 16:513–525
Wilhelm S, Adrian R (2008) Impact of summer warming on the thermal characteristics of a polymictic lake and consequences for oxygen, nutrients and phytoplankton. Freshw Biol 53:226–237
Yang J, Lv H, Liu L, Yu X, Chen H (2016) Decline in water level boosts cyanobacteria dominance in subtropical reservoirs. Sci Total Environ 557:445–452
Funding
This work was funded by a National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grant (No. 31770507) and the Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou City (No. 201704020159). Dr. Ken Chen, an ecologist from Australia, commented and revised the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Q., Lei, L., Zhao, L. et al. Interactive effect of water level and flushing rate on population dynamics of a harmful cyanobacterial species: Raphidiopsis raciborskii. Ecotoxicology 30, 936–944 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02351-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02351-3