Abstract
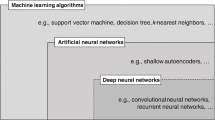
Deep learning is associate degree future field of machine learning (ML) analysis. It consists of variety of numerous concealed layers of artificial neural networks ANN). Deep learning methods applies nonlinear transformation and high-level model abstraction to giant databases. Recent advances in deep learning design among several fields have already contributed considerably to computer science. This text present class study on commitments and novel uses of escalated instruction of intensive education. The subsequent examination presents however and during which key application intensive algorithms for learning are used. Additionally, deep learning methodology is given with enhancements and its hierarchy in linear and non-linear functions and compared with a lot of ancient algorithms in widespread applications. The status of the survey of art provides a common rundown on the novel thought and therefore rising learning and deep learning quality.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fourie C (2003) Deep learning? What deep learning? South Afr J High Educ. https://doi.org/10.4314/sajhe.v17i1.25201
Pandey H (2017) Genetic algorithm for grammar induction and rules verification through a PDA simulator. IAES Int J Artif Intell (IJ-AI) 6(3):100. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v6.i3.pp100-111
Ordonez C, Zhang Y, Johnsson S (2018) Scalable machine learning computing a data summarization matrix with a parallel array DBMS. Distrib Parallel Databases 37(3):329–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-018-7229-1
Criminisi A (2016) Machine learning for medical images analysis. Med Image Anal 33:91–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2016.06.002
Goel A (2017) Editorial: expository AI applications. AI Mag 38(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1609/aimag.v38i1.2739
Alonso E (2002) AI and agents: state of the art. AI Mag 23(3):25–25
Shapiro, S. C. (1971). The MIND system: a data structure for semantic information processing (Vol. 837, No. PR). Rand Corp Santa Monica Califsss
Beck J, Stern M, Haugsjaa E (1996) Applications of AI in education. XRDS Crossroads ACM Mag Stud 3(1):11–15
Faught WS (1986) Applications of AI in engineering. Computer 7:17–27
Zhenan S, Zhaoxiang Z, Wei W, Fei L, Tieniu T (2020) Artificial intelligence: developments and advances in 2019. Front Data Comput 1(2):1–16
Li XH, Cao CC, Shi Y, Bai W, Gao H, Qiu L, Chen L (2020) A survey of data-driven and Knowledge-aware eXplainable AI. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2020.2983930
Maxwell AE, Warner TA, Fang F (2018) Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: an applied review. Int J Remote Sens 39(9):2784–2817
Usama M, Qadir J, Raza A, Arif H, Yau KLA, Elkhatib Y, Al-Fuqaha A (2019) Unsupervised machine learning for networking: techniques, applications and research challenges. IEEE Access 7:65579–65615
Osband, I., Doron, Y., Hessel, M., Aslanides, J., Sezener, E., Saraiva, A., & Van Roy, B. (2019). Behaviour suite for reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint
Mnih, V., Badia, A. P., Graves, A. B., Harley, T.J . A., Silver, D., & Kavukcuoglu, K. (2019). U.S. Patent Application No. 16/403,388.
Mnih, V., Czarnecki, W., Jaderberg, M. E., Schaul, T., Silver, D., & Kavukcuoglu, K. (2019). U.S. Patent Application No. 16/403,385.
Mnih, V., Czarnecki, W., Jaderberg, M. E., Schaul, T., Silver, D., & Kavukcuoglu, K. (2019). U.S. Patent Application No. 16/403,385
Zhai, X., Oliver, A., Kolesnikov, A., & Beyer, L. (2019). S4l: self-supervised semi-supervised learning. In: proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1476–1485)
Souza JTD, Francisco ACD, Piekarski CM, Prado GFD (2019) Data mining and machine learning to promote smart cities: a systematic review from 2000 to 2018. Sustainability 11(4):1077
Niculescu V (2019) High performance computing in big data analytics. Appl Med Inform 41:2–21
Zhao ZQ, Zheng P, Xu ST, Wu X (2019) Object detection with deep learning: a review. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(11):3212–3232
Huang, S. L., Xu, X., Zheng, L., & Wornell, G. W. (2019). An information theoretic interpretation to deep neural networks. In: 2019 IEEE international symposium on information theory (ISIT) (pp. 1984–1988). IEEE
Elfwing S, Uchibe E, Doya K (2018) Sigmoid-weighted linear units for neural network function approximation in reinforcementlearning. Neural Netw 107:3–11
Szegedy, C., Erhan, D., & Toshev, A. T. (2016). U.S. Patent No. 9,275,308. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
Kombrink, Stefan & Mikolov, Tomas & Karafiát, Martin & Burget, Lukas. (2011). Recurrent neural network based language modeling in meeting recognition. In: proceedings of the annual conference of the international speech communication association, INTERSPEECH. 2877–2880
Hinton G (2012) Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: the shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process Mag 29(6):82–97
Chung, J., Ahn, S., & Bengio, Y. (2016). Hierarchical multiscale recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint
Li, B., & Sainath, T. N. (2018). U.S. Patent No. 9,984,683. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
Martin, L. J., Ammanabrolu, P., Wang, X., Hancock, W., Singh, S., Harrison, B., & Riedl, M.O. (2018). Event representations for automated story generation with deep neuralnets. In: thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Zhang X, Sun J (2016) Object detection networks on convolutional feature maps. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(7):1476–1481
Miyato T, Maeda SI, Koyama M, Ishii S (2018) Virtual adversarial training: a regularization method for supervised and semi-supervised learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(8):1979–1993
Wang M, Fu W, Hao S, Tao D, Wu X (2016) Scalable semi-supervised learning by efficient anchor graph regularization. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28(7):1864–1877
Gong C, Tao D, Maybank SJ, Liu W, Kang G, Yang J (2016) Multi-modal curriculum learning for semi-supervised image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(7):3249–3260
Tang, H., Xu, D., Yan, Y., Corso, J. J., Torr, P. H., & Sebe, N. (2020). Multi-channel attention selection GANs for guided image-to-image translation. arXiv preprint
Royer A, Bousmalis K, Gouws S, Bertsch F, Mosseri I, Cole F, Murphy K (2020) Xgan: unsupervised image-to-image translation for many-to-many mappings. In Domain adaptation for visual understanding. Springer, Cham, pp. 33–49
French, G., Mackiewicz, M., & Fisher, M. (2017). Self-ensembling for visual domain adaptation. arXiv preprint
Saito, K., Ushiku, Y., & Harada, T. (2017). Asymmetric tri-training for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: proceedings of the 34th international conference on machine learning-volume 70 (pp. 2988–2997). JMLR. org
Hung, W. C., Tsai, Y. H., Liou, Y. T., Lin, Y. Y., & Yang, M. H. (2018). Adversarial learning for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint
Van Hasselt, H., Guez, A., & Silver, D. (2016). Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning. In: thirtieth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
M. Hausknecht and P. Stone (2015). Deep recurrent q-learning for partially observable mdps. AAAI
Hessel, M., Modayil, J., Van Hasselt, H., Schaul, T., Ostrovski, G., Dabney, W., & Silver, D. (2018). Rainbow: combining improvements in deep reinforcement learning. In thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Wu, Y., Mansimov, E., Grosse, R. B., Liao, S., & Ba, J. (2017). Scalable trust-region method for deep reinforcement learning using kronecker-factored approximation. In: advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 5279–5288)
Dabney, W., Rowland, M., Bellemare, M. G., & Munos, R. (2018, April). Distributional reinforcement learning with quantile regression. In: thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Marcus, G. (2018). Deep learning: a critical appraisal. arXiv preprint
Shu, M. (2019). Deep learning for image classification on very small datasets using transfer learning
Jin L, Li S, La HM, Luo X (2017) Manipulability optimization of redundant manipulators using dynamic neural networks. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(6):4710–4720
Bertinetto, L., Henriques, J. F., Valmadre, J., Torr, P., & Vedaldi, A. (2016). Learning feed-forward one-shot learners. In: advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 523–531)
SaishanmugaRaja V, Rajagopalan SP (2013) IRIS recognition system using neural network and genetic algorithm. Int J Comput Appl 68(20):49–53. https://doi.org/10.5120/11699-7431
Tran, D. T., Kanniainen, J., Gabbouj, M., & Iosifidis, A. (2019). Data-driven neural architecture learning for financial time-series forecasting. arXiv preprint
Qi H, Shi Y, Tian Y, Mayhew C, Yu DL, Gomm JB, Zhang Q (2019) A new fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control method for mechanical and aeronautical systems with neural estimators. Adv Mech Eng 11(11):1687814019891659
Huang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Yan, C. (2019). Automatic sleep staging based on deep neural network using single channel EEG. In: international conference on knowledge management in organizations (pp. 63–73). Springer: Cham
Martens J, & Sutskever I (2011). Learning recurrent neural networks with hessian-free optimization. In: proceedings of the 28th international conference on machine learning (ICML-11) (pp. 1033–1040)
Tolosana R, Vera-Rodriguez R, Fierrez J, Ortega-Garcia J (2018) Exploring recurrent neural networks for on-line handwritten signature biometrics. IEEE Access 6:5128–5138
Kasongo SM, Sun Y (2019) A deep long short-term memory based classifier for wireless intrusion detection system. ICT Express 6(2):98–103
Bouktif S, Fiaz A, Ouni A, Serhani MA (2020) Multi-sequence LSTM-RNN deep learning and metaheuristics for electric load forecasting. Energies 13(2):391
Zhang YF, Fitch P, Thorburn PJ (2020) Predicting the trend of dissolved oxygen based on the kPCA-RNN model. Water 12(2):585
Razzak, F., Yi, F., Yang, Y., & Xiong, H. (2019). An integrated multimodal attention-based approach for bank stress test prediction. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM) (pp. 1282–1287). IEEE
Kumar, P., Gupta, M., Gupta, M., & Sharma, A. (2019). Profession Identification Using Handwritten Text Images. In: international conference on computer vision and image processing (pp. 25–35). Springer: Singapore
Yan LC, Bengio YS, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436–444
Tong W, Li L, Zhou X, Hamilton A, Zhang K (2019) Deep learning PM 2.5 concentrations with bidirectional LSTM RNN. Air Qual Atmos Health 12(4):411–423
Vedaldi A, & Lenc K (2015). Matconvnet: Convolutional neural networks for matlab. In: proceedings of the 23rd ACM international conference on multimedia (pp. 689–692)
Aloysius N, Geetha M (2017). A review on deep convolutional neural networks. In: 2017 international conference on communication and signal processing (ICCSP) (pp. 0588–0592). IEEE
Chi YS, Kamarulzaman SF (2020) Intelligent gender recognition system for classification of gender in malaysian demographic. In: Nasir ANK, Ahmad MA, Najib MS (eds) In ECCE 2019. Springer, Singapore, pp 283–295
Wang C, Zhang Z, Zhou X (2018) An image copy-move forgery detection scheme based on A-KAZE and SURF features. Symmetry 10(12):706
Gan W, Wang S, Lei X, Lee MS, Kuo CCJ (2018) Online CNN-based multiple object tracking with enhanced model updates and identity association. Signal Process Image Commun 66:95–102
Kong X, Gong S, Su L, Howard N, Kong Y (2018) Automatic detection of acromegaly from facial photographs using machine learning methods. EBioMedicine 27:94–102
Telgarsky, M. (2015). Representation benefits of deep feedforward networks. arXiv preprint
Liu W, Wang Z, Liu X, Zeng N, Liu Y, Alsaadi FE (2017) A survey of deep neural network architectures and their applications. Neurocomputing 234:11–26
Yan, R., Song, Y., & Wu, H. (2016) Learning to respond with deep neural networks for retrieval-based human-computer conversation system. In: proceedings of the 39th international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval (pp. 55–64)
Hatcher WG, Yu W (2018) A survey of deep learning: platforms, applications and emerging research trends. IEEE Access 6:24411–24432
Milz, S., Arbeiter, G., Witt, C., Abdallah, B., & Yogamani, S. (2018). Visual slam for automated driving: Exploring the applications of deep learning. In: proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (pp. 247–257)
Najafabadi MM, Villanustre F, Khoshgoftaar TM, Seliya N, Wald R, Muharemagic E (2015) Deep learning applications and challenges in big data analytics. J Big Data 2(1):1
Shen D, Wu G, Suk HI (2017) Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 19:221–248
Zhang K, Zhu Y, Leng S, He Y, Maharjan S, Zhang Y (2019) Deep learning empowered task offloading for mobile edge computing in urban informatics. IEEE Internet Things J 6(5):7635–7647
Lemley J, Bazrafkan S, Corcoran P (2017) Deep learning for consumer devices and services: pushing the limits for machine learning, artificial intelligence, and computer vision. IEEE Consum Electron Mag 6(2):48–56
Wu, R., Yan, S., Shan, Y., Dang, Q., & Sun, G. (2015). Deep image: Scaling up image recognition. arXiv preprint
Noda K, Yamaguchi Y, Nakadai K, Okuno HG, Ogata T (2015) Audio-visual speech recognition using deep learning. Appl Intell 42(4):722–737
Deng L, Liu Y (eds) (2018) Deep learning in natural language processing. Springer, Singapore
Sun S, Luo C, Chen J (2017) A review of natural language processing techniques for opinion mining systems. Inf Fusion 36:10–25
Min S, Lee B, Yoon S (2017) Deep learning in bioinformatics. Brief Bioinform 18(5):851–869
Ker J, Wang L, Rao J, Lim T (2017) Deep learning applications in medical image analysis. IEEE Access 6:9375–9389
Nakao A, Du P (2018) Toward in-network deep machine learning for identifying mobile applications and enabling application specific network slicing. IEICE Trans Commun. https://doi.org/10.1587/transcom.2017CQI0002
Kumar, D., Kumar, C., & Shao, M. (2017). Cross-database mammographic image analysis through unsupervised domain adaptation. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on big data (Big Data) (pp. 4035–4042). IEEE
Wang Y, Xu W (2018) Leveraging deep learning with LDA-based text analytics to detect automobile insurance fraud. Decis Support Syst 105:87–95
Zhang, C., Vinyals, O., Munos, R., & Bengio, S. (2018). A study on overfitting in deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint
Graves, A. (2016). Adaptive computation time for recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint
Molchanov, D., Ashukha, A., & Vetrov, D. (2017). Variational dropout sparsifies deep neural networks. In: proceedings of the 34th international conference on machine learning-volume 70: (pp. 2498–2507). JMLR. org
Garcia-Garcia, A., Orts-Escolano, S., Oprea, S., Villena-Martinez, V., & Garcia-Rodriguez, J. (2017). A review on deep learning techniques applied to semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint
Cui, H., Zhang, H., Ganger, G. R., Gibbons, P. B., & Xing, E. P. (2016, April). Geeps: Scalable deep learning on distributed gpus with a gpu-specialized parameter server. In: proceedings of the eleventh European conference on computer systems (pp. 1–16)
Wang, D., & Shang, Y. (2014). A new active labeling method for deep learning. In: 2014 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN) (pp. 112–119). IEEE
Xiao, T., Xia, T., Yang, Y., Huang, C., & Wang, X. (2015). Learning from massive noisy labeled data for image classification. In: proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2691–2699)
Larsson, G., Maire, M., & Shakhnarovich, G. (2016). Learning representations for automatic colorization. In: European conference on computer vision (pp. 577–593). Springer: Cham
Ghose, S., & Prevost, J. J. (2020). AutoFoley: artificial synthesis of synchronized soundtracks for silent videos with deep learning. arXiv preprint
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 60(6):1097–1105
Bai S, An S (2018) A survey on automatic image caption generation. Neurocomputing 311:291–304
Hossain MZ, Sohel F, Shiratuddin MF, Laga H (2019) A comprehensive survey of deep learning for image captioning. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 51(6):1–36
Wang, H., Qin, Z., & Wan, T. (2018). Text generation based on generative adversarial nets with latent variables. In: Pacific-Asia conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 92–103). Springer: Cham
Jaderberg M, Simonyan K, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A (2016) Reading text in the wild with convolutional neural networks. Int J Comput Vision 116(1):1–20
Guo, J., Lu, S., Cai, H., Zhang, W., Yu, Y., & Wang, J. (2018). Long text generation via adversarial training with leaked information. In: thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Wiseman, S., Shieber, S. M., & Rush, A. M. (2017). Challenges in data-to-document generation. arXiv preprint
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittal, R., Arora, S., Bansal, V. et al. An Extensive Study on Deep Learning: Techniques, Applications. Arch Computat Methods Eng 28, 4471–4485 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09542-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09542-5