Abstract
Lignocellulosic materials have huge potential because of their abundance, renewability, and non-edible nature aids to develop it to an eco-friendly bioplastic. These feedstocks can be utilized for extracting lignin and cellulose. Both the materials can easily be tunable by surface modifications and other chemical derivatizations to produce different bioplastics. Common biobased plastics that can be derived from lignin or cellulose include polylactic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoates, bio-polyethylene, polyurethanes and starch based nanocellulosic bioplastics. The present review addresses lignocellulosic compositions, conversion routes for bioplastic production and their applications in various fields. In the nearby future, lignocellulose derived bioplastics will emerge as valuable materials in different fields for a wide range of cutting-edge applications.
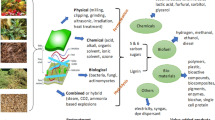
Graphic abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-latif NS, Ong MY, Nomanbhay S (2020) Estimation of carbon dioxide (CO2) reduction by utilization of algal biomass bioplastic in Malaysia using carbon emission pinch analysis ( CEPA ). Bioengineered 11:154–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2020.1718471
Abitbol T, Rivkin A, Cao Y et al (2016) Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 39:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.01.002
Abraham E, Deepa B, Pothan LA et al (2011) Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibres: a novel approach. Carbohydr Polym 86:1468–1475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.034
Achaby M, El MN, El, Aboulkas A et al (2016) Processing and properties of eco-friendly bio-nanocomposite films filled with cellulose nanocrystals from sugarcane bagasse. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.040
Adekunle A, Orsat V, Raghavan V (2016) Lignocellulosic bioethanol: a review and design conceptualization study of production from cassava peels. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 64:518–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.06.064
Agbor VB, Cicek N, Sparling R et al (2011) Biomass pretreatment: fundamentals toward application. Biotechnol Adv 29:675–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.05.005
Ahmad A, Waheed S, Khan SM et al (2015) Effect of silica on the properties of cellulose acetate/polyethylene glycol membranes for reverse osmosis. Desalination 355:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2014.10.004
Ahmed T, Shahid M, Azeem F et al (2018) Biodegradation of plastics: current scenario and future prospects for environmental safety. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:2–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1234-9
Al-ahmed A, Inammudin (2020) Advanced applications of polysaccharides and their composites. Mater Res Found 73:184–197
Al-Battashi SH, Annamalai N, Sivakumar N et al (2019) Lignocellulosic biomass (LCB): a potential alternative biorefinery feedstock for polyhydroxyalkanoates production. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 4:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-018-09488-4
Alemdar A, Sain M (2008) Isolation and characterization of nanofibers from agricultural residues—wheat straw and soy hulls. Biores Technol 99:1664–1671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.029
Anju MS, Lata A (2012) Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic substrates for enhanced delignification and enzymatic digestibility. Indian J Microbiol 52:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-011-0199-x
Arevalo-Gallegos A, Ahmad Z, Asgher M et al (2017) Lignocellulose: a sustainable material to produce value-added products with a zero waste approach—a review. Int J Biol Macromol 99:308–318
Asim M, Saba N, Jawaid M, Nasir M (2018) Potential of natural fiber/biomass filler-reinforced polymer composites in aerospace applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Aswathy US, Sukumaran RK, Devi GL et al (2010) Bio-ethanol from water hyacinth biomass: an evaluation of enzymatic saccharification strategy. Biores Technol 101:925–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.019
Bacakova L, Pajorova J, Bacakova M et al (2019) Versatile application of nanocellulose: from industry to skin tissue engineering and wound healing. Nanomaterials 9:164–183. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020164
Baiya C, Nannuan L, Tassanapukdee Y et al (2018) The synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel from sugarcane bagasse using microwave-assisted irradiation for selective adsorption of copper(II) ions. Environ Progress Sustain Energy 38:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12950
Bari E, Morrell JJ, Sistani A (2019) Durability of natural/synthetic/biomass fiber-based polymeric composites: laboratory and field tests. Durability and life prediction in biocomposites, fibre-reinforced composites hybrid composites, pp 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102290-0.00002-7
Barkalow DG, Rowell RM, Young RA (1989) A new approach for the production of cellulose acetate: acetylation of mechanical pulp with subsequent isolation of cellulose acetate by differential solubility. J Appl Polym Sci 37:1009–1018
Ben M, Kennes C, Veiga MC (2016) Optimization of polyhydroxyalkanoate storage using mixed cultures and brewery wastewater. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4891
Biswas A, Saha BC, Lawton JW et al (2006) Process for obtaining cellulose acetate from agricultural by-products. Carbohydr Polym 64:134–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.11.002
Blanco A, Monte MC, Campano C et al (2018) Nanocellulose for industrial use: cellulose nanofibers (CNF), cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), and bacterial cellulose (BC). Elsevier, Amsterdam
Boneberg BS, Machado GD, Santos DF et al (2016) Biorefinery of lignocellulosic biopolymers. Revista Eletrônica Científica da UERGS 2:79. https://doi.org/10.21674/2448-0479.21.79-100
Brinchi L, Cotana F, Fortunati E, Kenny JM (2013) Production of nanocrystalline cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass: technology and applications. Carbohydr Polym 94:154–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.033
Brodin M, Vallejos M, Opedal MT et al (2017) Lignocellulosics as sustainable resources for production of bioplastics—a review. J Clean Prod 162:646–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.209
Brosse N, Hage REL, Sannigrahi P, Ragauskas A (2010) Dilute sulphuric acid and ethanol organosolv pretreatment of miscanthus x giganteus. In: Cellulose chemistry and technology, pp 71–78
Brylev AN, Adylov DK, Tukhtaeva GG et al (2001) Polysaccharides of rice straw. Chem Nat Compd 37:569–570
Byun Y, Kim YT (2014) Utilization of bioplastics for food packaging industry. Innov Food Packag. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-394601-0.00015-1
Carpenter AW, Lannoy D, Wiesner MR (2015) Cellulose nanomaterials in water treatment technologies. Environ Sci Technol 49:5277–5287. https://doi.org/10.1021/es506351r
Cesario MT, Rodrigo S, Raposo, Almeida MCMD de et al (2014) Enhanced bioproduction of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate from wheat straw lignocellulosic hydrolysates. New Biotechnol 31:104–113
Chandel AK (2018) Advances in sugarcane biorefinery technologies. Policy issues and paradigm shift for bioethanol and by-products, commercialization
Chen H, Chen H (2014) Chemical composition and structure of natural lignocellulose. In: Biotechnology of lignocellulose. Springer, Amsterdam, pp 25–71
Chen L, Fu S (2013) Enhanced cellulase hydrolysis of eucalyptus waste fibers from pulp mill by tween80-assisted ferric chloride pretreatment. J Agric Food Chem 61:3293–3300. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf400062e
Chen YW, Lee HV (2018) Revalorization of selected municipal solid wastes as new precursors of “green” nanocellulose via a novel one-pot isolation system: a source perspective. Int J Biol Macromol 107:78–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.143
Davis R, Kataria R, Cerrone F et al (2013) Conversion of grass biomass into fermentable sugars and its utilization for medium chain length polyhydroxyalkanoate (mcl-PHA) production by Pseudomonas strains. Biores Technol 150:202–209
Deepa B, Abraham E, Cordeiro N et al (2015) Utilization of various lignocellulosic biomass for the production of nanocellulose: a comparative study. Cellulose 22:1075–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0554-x
Deepa B, Abraham E, Mathew B et al (2011) Structure, morphology and thermal characteristics of banana nano fibers obtained by steam explosion. Biores Technol 102:1988–1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.030
Deepa B, Chirayil CJ, Pothan LA, Thomas S (2019) Lignocellulose-based nanoparticles and nanocomposites: preparation, properties, and applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Demirbaş A (2005) Thermochemical conversion of biomass to liquid products in the aqueous medium. Energy Sources 27:1235–1243
Deshavath NN, Veeranki VD, Goud VV (2019) Lignocellulosic feedstocks for the production of bioethanol: availability, structure, and composition. In: Sustainable bioenergy: advances and impacts. Elsevier, pp 1–19
Dharmaraja J, Shobana S, Arvindnarayan S et al (2020) Biobutanol from lignocellulosic biomass: bioprocess strategies. In: Lignocellulosic biomass to liquid biofuels, pp 169–193
Di Blasi C, Branca C, Galgano A (2010) Biomass screening for the production of furfural via thermal decomposition. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:2658–2671. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie901731u
Dietrich K, Dumont M, Del LF, Orsat V (2016) Producing PHAs in the bioeconomy—towards a sustainable bioplastic producing PHAs in the bioeconomy—towards a sustainable bioplastic. Sustain Prod Consump. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2016.09.001
Dutt A, Ajay T (2012) Utilizing of sugar refinery waste (Cane Molasses) for production of bio-plastic under submerged fermentation process. J Polym Environ 20:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-011-0394-1
Fatma S, Hameed A, Noman M et al (2018) Lignocellulosic biomass: a sustainable bioenergy source for the future. Protein Peptide Lett 25:148–163. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929866525666180122144504
Fei Z, Huang S, Yin J et al (2015) Preparation and characterization of bio-based degradable plastic films composed of cellulose acetate and starch acetate. J Polym Environ 23:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-015-0711-1
Fitzpatrick M, Champagne P, Cunningham MF, Whitney RA (2010) A biorefinery processing perspective: treatment of lignocellulosic materials for the production of value-added products. Biores Technol 101:8915–8922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.125
Galbe M, Wallberg O (2019) Pretreatment for biorefineries: a review of common methods for efficient utilisation of lignocellulosic materials. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:1–26
Gomes ME, Ribeiro AS, Malafaya PB et al (2001) A new approach based on injection moulding to produce biodegradable starch-based polymeric scaffolds: morphology, mechanical and degradation behaviour. Biomaterials 22:883–889
Gonz Y, Grieve J, Meza-contreras JC et al (2019) Tequila agave bagasse hydrolysate for the production of polyhydroxybutyrate by burkholderia sacchari. Bioengineering 6:115–128
Gopakumar DA, Pasquini D, Henrique MA et al (2017) Meldrum’s acid modified cellulose nano fiber-based polyvinylidene fluoride microfiltration membrane for dye water treatment and nanoparticle removal. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:2026–2033. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02952
Goriparthi BK, Suman KNS, Nalluri MR (2012) Processing and characterization of jute fiber reinforced hybrid biocomposites based on polylactide/polycaprolactone blends. Polym Compos 33:237–244
Govil T, Wang J, Samanta D et al (2020) Lignocellulosic feedstock: a review of a sustainable platform for cleaner production of nature’s plastics. J Clean Prod 8:122521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122521
Gumel AM, Annuar MSM (2015) Nanocomposites of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs). In: RSC green chemistry, pp 98–118
Gupta VK, Potumarthi R, O’Donovan A et al (2014) Bioenergy research: an overview on technological developments and bioresources. In: Bioenergy research: advances and applications. Elsevier, pp 23–47
Guzman-puyol S, Ceseracciu L, Tedeschi G et al (2019) Transparent and robust all-cellulose nanocomposite packaging materials prepared in a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic anhydride. Nanomaterials 9:368–387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030368
Habibi Y, Lucia LA, Rojas OJ (2010) Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem Rev 110:3479–3500
Harding KGG, Gounden T, Pretorius S (2017) “Biodegradable” plastics: a myth of marketing? Proc Manuf 7:106–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2016.12.027
Haro P, Ollero P, Trippe F (2013) Technoeconomic assessment of potential processes for bio-ethylene production. Fuel Process Technol 114:35–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2013.03.024
Hassan ML, Mathew AP, Hassan EA et al (2012) Nanofibres from bagasse and rice straw: process optimization and properties. Wood Sci Technol 46:193–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0373-z
Hasunuma T, Okazaki F, Okai N et al (2012) A review of enzymes and microbes for lignocellulosic biorefinery and the possibility of their application to consolidated bioprocessing technology. Biores Technol 47:2–21
He W, Benson R (2014) Polymeric biomaterials. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hoeng F, Denneulin A, Bras J (2016) Use of nanocellulose in printed electronics. Nanoscale 8:13131–13154. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR03054H
Hubbe MA, Ferrer A, Tyagi P et al (2017) Nanocellulose in thin films, coatings, and plies for packaging applications: a review. Bioresources 12:2143–2233
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0nr00583e
Ivanov V, Ahmed Z (2015) Production and applications of crude polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing bioplastic from the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:725–738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0505-3
Ivanov V, Christopher L (2016) Biore finery-derived bioplastics as promising low-embodied energy building materials. In: Nano and biotech based materials, pp 375–389
Jawaid M, Kumar S (2018) Bionanocomposites for packaging applications
Jonoobi M, Harun J, Mathew AP, Oksman K (2010) Mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) prepared by twin screw extrusion. Compos Sci Technol 70:1742–1747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.07.005
Kabir SMF, Sikdar PP, Rahman BHMA, Ali BA (2018) Cellulose-based hydrogel materials: chemistry, properties and their prospective applications. Prog Biomater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40204-018-0095-0
Kargarzadeh H, Ioelovich M, Ahmad I et al (2017) Methods for extraction of nanocellulose from various sources
Kaur L, Khajuria R, Parihar L, Singh GD (2017) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: biosynthesis to commercial production: a review. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci 6:1098–1106. https://doi.org/10.15414/jmbfs.2017.6.4.1098-1106
Khalil HPSA, Bhat AH, Yusra AFI (2012) Green composites from sustainable cellulose nanofibrils: a review. Carbohydr Polym 87:963–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.08.078
Khalil HPSA, Davoudpour Y, Islam N et al (2014) Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: a review. Carbohydr Polym 99:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.069
Khalil HPSA, Davoudpour Y, Saurabh CK et al (2016) A review on nanocellulosic fibres as new material for sustainable packaging: process and applications. 64:823–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.06.072
Kim DH, Kwon OJ, Yang SR, Park JS (2007) Preparation of starch-based polyurethane films and their mechanical properties. Fibers Polym 8:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877266
Kim H, Lee S, Ahn Y et al (2020) Sustainable Production of Bioplastics from Lignocellulosic Biomass: Technoeconomic Analysis and Life-Cycle Assessment. ACS Sustainable Chemistry Engineering 8:12419–12429. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02872
Kim J, Lee J, Kim KH et al (2017) Pyrolysis of wastes generated through saccharification of oak tree by using CO2 as reaction medium. Appl Therm Eng 110:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.08.200
Kim KH, Hong J (2001) Supercritical CO2 pretreatment of lignocellulose enhances enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis. Biores Technol 77:139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00147-4
Klemm D, Klemm D, Kramer F et al (2011) Reviews nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials Angewandte. Green Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201001273
Koh JJ, Zhang X, He C (2018) Fully biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/starch blends: a review of toughening strategies. Int J Biol Macromol 109:99–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.048
Kolybaba M, Tabil LG, Panigrahi S et al (2003) Biodegradable Polym Past Present Future. The society for engineering in agricultural food biological systems 0300:1–15
Köse K, Mavlan M, Youngblood JP (2020) Applications and impact of nanocellulose based adsorbents. Cellulose 27:2967–2990
Kuhad RC, Singh A (1993) Lignocellulose biotechnology: current and future prospects. Crit Rev Biotechnol 13:151–172. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388559309040630
Kumar A, Gautam A, Dutt D (2016) Biotechnological transformation of lignocellulosic biomass in to industrial products: an overview. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 07:149–168. https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2016.73014
Kumar A, Lee Y, Kim D et al (2017) Effect of crosslinking functionality on microstructure, mechanical properties, and in vitro cytocompatibility of cellulose nanocrystals reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hybrid scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol 95:962–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.085
Kurańska M, Aleksander P, Mikelis K, Ugis C (2013) Porous polyurethane composites based on bio-components. Compos Sci Technol 75:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.11.014
Laadila MA, Hegde K, Rouissi T et al (2017) Green synthesis of novel biocomposites from treated cellulosic fibers and recycled bio-plastic polylactic acid. J Clean Prod 235:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.235
Lee WS, Chen IC, Chang CH, Yang SS (2012) Bioethanol production from sweet potato by co-immobilization of saccharolytic molds and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Renew Energy 39:216–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2011.08.024
Li F, Mascheroni E, Piergiovanni L (2015) The potential of nanocellulose in the packaging field: a review. https://doi.org/10.1002/pts.2121
Liu G, Zhao X, Chen C et al (2020) Robust production of pigment-free pullulan from lignocellulosic hydrolysate by a new fungus co-utilizing glucose and xylose. Carbohydr Polym 241:116400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116400
Ludwicka K, Jedrzejczak-krzepkowska M, Kubiak K et al (2016) Medical and cosmetic applications of bacterial nanocellulose. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Machado G, Santos F, Lourega R et al (2020) Biopolymers from lignocellulosic biomass feedstocks, production processes and applications. In: Lignocellulosic biorefining technologies, pp 125–140
Madhavan A, Arun KB, Sindhu R et al (2019) Tailoring of microbes for the production of high value plant-derived compounds: from pathway engineering to fermentative production. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Proteins Proteomics 1867:140262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2019.140262
Maheshwari NV (2018) Agro-industrial lignocellulosic waste: an alternative to unravel the future bioenergy. In: Biofuels: greenhouse gas mitigation and global warming: next generation biofuels and role of biotechnology. Springer, India, pp 291–305
Maity J, Ray SK (2017) Removal of Cu (II) ion from water using sugar cane bagasse cellulose and gelatin based composite hydrogels. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Malladi R, Nagalakshmaiah M, Robert M, Elkoun S (2018) Importance of agriculture and industrial waste in the field of nanocellulose and its recent industrial developments: a review. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:2807–2828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03437
Mathew B, Lopes A, Ferreira S et al (2010) Isolation of nanocellulose from pineapple leaf fibres by steam explosion. Carbohydr Polym 81:720–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.03.046
Maulida SM, Tarigan P (2016) Production of starch based bioplastic from cassava peel reinforced with microcrystalline celllulose avicel PH101 using sorbitol as plasticizer. J Phys Conf Ser 710:012012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/710/1/012012
McKendry P (2002) Energy production from biomass (part 1): overview of biomass. Biores Technol 83:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00118-3
Mendes J, Paschoalin R, Carmona V et al (2016) Biodegradable polymer blends based on corn starch and thermoplastic chitosan processed by extrusion. Carbohydr Polym 137:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.093
Miron J, Yosef E, Ben-Ghedalia D (2001) Composition and in vitro digestibility of monosaccharide constituents of selected byproduct feeds. J Agric Food Chem 49:2322–2326. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0008700
Mishra R, Sabu A, Tiwari SK (2018) Materials chemistry and the futurist eco-friendly applications of nanocellulose: status and prospect. J Saudi Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2018.02.005
Mishra S, Unnikrishnan L, Nayak SK, Mohanty S (2019) Advances in piezoelectric polymer composites for energy harvesting applications: a systematic review. Macromol Mater Eng 1800463:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201800463
Mohammed L, Ansari MNM, Pua G et al (2015) A review on natural fiber reinforced polymer composite and its applications. Int J Polym Sci 2015:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/243947
Mohanty AK, Khan MA, Hinrichsen G (2000) Influence of chemical surface modification on the properties of biodegradable jute fabrics - polyester amide composites. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 31:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(99)00057-3
Mondal S (2016) Preparation, properties and applications of nanocellulosic materials. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.050
Moreno-Bayona DA, Gomez-Mendez LD, Blanco-vargas A et al (2019) Simultaneous bioconversion of lignocellulosic residues and oxodegradable polyethylene by Pleurotus ostreatus for biochar production, enriched with phosphate solubilizing bacteria for agricultural use. PLoS ONE 10:1–25
Mostafa NA, Farag AA, Abo-dief HM, Tayeb AM (2018) Production of biodegradable plastic from agricultural wastes. Arab J Chem 11:546–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.04.008
Moura IG, De SAV, De, Sofia A et al (2017) Bioplastics from agro-wastes for food packaging applications. In: Food packaging. Elsevier, pp 223–263
Moustakas K, Loizidou M, Rehan M, Nizami AS (2020) A review of recent developments in renewable and sustainable energy systems: key challenges and future perspective. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 119:109418
Naeimi A, Honarmand M, Jawhid O (2018) Iron porphyrin immobilized on cellulose extracted from sesbania sesban plant: a novel eco-friendly and cost- effective catalyst for green oxidation of organic compounds. Cellul Chem Technol 52:343–351
Nechyporchuk O, Belgacem MN, Bras J (2016) Production of cellulose nanofibrils: a review of recent advances. Ind Crops Prod 93:2–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.02.016
Okolie JA, Nanda S, Dalai AK, Kozinski JA (2020) Chemistry and specialty industrial applications of lignocellulosic biomass. Waste Biomass Valoriz 20:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01123-0
Oliveira De Moraes J, Scheibe AS, Sereno A, Borges Laurindo J (2013) Scale-up of the production of cassava starch based films using tape-casting. J Food Eng 119:800–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.07.009
Oliveira J, Luiza Martins A, Komesu JMN (2017) Nanotechnology applications on lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment
Padmaja NSPG (2015) Enhancing the enzymatic saccharification of agricultural and processing residues of cassava through pretreatment techniques. Waste Biomass Valoriz. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9345-8
Pan W, Perrotta JA, Stipanovic AJ et al (2012) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates by Burkholderia cepacia ATCC 17759 using a detoxi W ed sugar maple hemicellulosic hydrolysate. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:459–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-011-1040-6
Patel M, Bastioli C, Würd-Marini L (2002) Environmental assessment of bio-based polymers and natural fibres. Utrecht University, Amsterdam, pp 1–59
Paula C, De, De CBC, Paula BC, De, Contiero J (2018) Prospective biodegradable plastics from biomass conversion processes. In: Biofuels-state of development, pp 246–274
Pei L, Schmidt M, Wei W (2011) Conversion of biomass into bioplastics and their potential environmental impacts. In: Biotechnology of biopolymers
Peng BL, Dhar N, Liu HL, Tam KC (2011) Chemistry and applications of nanocrystalline cellulose and its derivatives: a nanotechnology perspective. 89:1191–1206. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.20554
Petersson A, Thomsen MH, Hauggaard-Nielsen H, Thomsen AB (2007) Potential bioethanol and biogas production using lignocellulosic biomass from winter rye, oilseed rape and faba bean. Biomass Bioenerg 31:812–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2007.06.001
Pilla S (2011) Handbook of bioplastics and biocomposites engineering applications. Wiley, New York
Plackett DV, Letchford K, Jackson JK et al (2014) A review of nanocellulose as a novel vehicle for drug delivery. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 29:105–118
Ponnusamy VK, Nguyen DD, Dharmaraja J et al (2018) A review on lignin structure, pretreatments, fermentation reactions and biorefinery potential. Biores Technol 271:462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.070
Rabemanolontsoa H, Saka S (2013) Comparative study on chemical composition of various biomass species. RSC Adv 3:3946–3956. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra22958k
Ragauskas AJ, Nagy M, Kim DH et al (2006) From wood to fuels. Ind Biotechnol 2:55–65
Ragauskas AJ, Nagy M, Kim DH et al (2005) From wood to fuels integrating biofuels and pulp production. Ind Biotechnol 2:55–65
Raghavendra GM, Varaprasad K, Jayaramudu T (2015) Biomaterials design, development and biomedical applications, vol 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Rahman R, Zhafer Putra S (2019) Tensile properties of natural and synthetic fiber-reinforced polymer composites. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Rosentrater KA, Otieno AW (2006) Considerations for manufacturing bio-based plastic products. J Polym Environ 14:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-006-0036-1
Sabo R, Yermakov A, Law CT et al (2016) Nanocellulose-enabled electronics, energy harvesting devices, smart materials and sensors: a review. J Renew Mater 4:297–312. https://doi.org/10.7569/JRM.2016.634114
Sagnelli D, Hebelstrup KH, Leroy E, Rolland-sabaté A (2017) Plant-crafted starches for bioplastics production. Carbohydr Polym 152:398–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.039
Sahari J, Sapuan SM (2011) Natural fibre reinforced biodegradable polymer composites. Rev Adv Mater Sci 30:166–174
Saini JK, Saini R, Tewari L (2015) Lignocellulosic agriculture wastes as biomass feedstocks for second-generation bioethanol production: concepts and recent developments. Biotechnology 5:337–353
Salama A, El-Sakhawy M, Kamel S (2016) Carboxymethyl cellulose based hybrid material for sustained release of protein drugs. Int J Biol Macromol 93:1647–1652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.04.029
Sánchez ÓJ, Cardona CA (2008) Trends in biotechnological production of fuel ethanol from different feedstocks. Biores Technol 99:5270–5295
Sanyang ML, Sapuan SM, Jawaid M et al (2016) Effect of plasticizer type and concentration on physical properties of biodegradable films based on sugar palm (Arenga pinnata) starch for food packaging. J Food Sci Technol 53:326–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2009-7
Schreiner M, Lopes G (2014) Polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis and simultaneous remotion of organic inhibitors from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate by Burkholderia sp. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:1353–1363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1485-5
Schutyser W, Renders T, Van Den Bosch S et al (2018) Chemicals from lignin: an interplay of lignocellulose fractionation, depolymerisation, and upgrading. Chem Soc Rev 47:852–908
Sharma KH, Xu C, Qin W (2017) Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and bioproducts: an overview. Waste Biomass Valoriz 59:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0059-y
Shirai MA, Grossmann MVE, Mali S et al (2013) Development of biodegradable flexible films of starch and poly(lactic acid) plasticized with adipate or citrate esters. Carbohyd Polym 92:19–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.038
Silverstein RA, Chen Y, Sharma-Shivappa RR et al (2007) A comparison of chemical pretreatment methods for improving saccharification of cotton stalks. Biores Technol 98:3000–3011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.10.022
Simangunsong DI, Hutapea THA, Lee HW, Ahn JO (2018) The effect of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) filler on polylactic acid (PLA) nanocomposite properties. J Eng Technol Sci 50:578–587. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2018.50.4.9
Sindhu R, Gnansounou E, Binod P, Pandey A (2016) Bioconversion of sugarcane crop residue for value added products: an overview. Renew Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.02.057
Sindhu R, Kuttiraja M, Binod P et al (2014) Physicochemical characterization of alkali pretreated sugarcane tops and optimization of enzymatic sacchari fi cation using response surface methodology. Renew Energy 62:362–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2013.07.041
Sindhu R, Silviya N, Binod P, Pandey A (2013) Pentose-rich hydrolysate from acid pretreated rice straw as a carbon source for the production of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. Biochem Eng J 78:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2012.12.015
Singh P, Sulaiman O, Hashim R (2010) Biopulping of lignocellulosic material using different fungal species: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 9:141–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-010-9200-0
Sinner M, Puls J, Dietrichs H (1979) Carbohydrate composition of nut shells and some other agricultural residues. Starch Stärke 31:267–269. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.19790310807
Siracusa V, Rocculi P, Romani S, Rosa MD (2008) Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 19:634–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2008.07.003
Song H, Li H, Seo J et al (2009) Pilot-scale production of bacterial cellulose by a spherical type bubble column bioreactor using saccharified food wastes. Korean J Chem Eng 26:141–146
Takeda Y, Tobimatsu Y, Yamamura M et al (2019) Comparative evaluations of lignocellulose reactivity and usability in transgenic rice plants with altered lignin composition. J Wood Sci 65:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10086-019-1784-6
Tandon G (2016) Bioproducts from residual lignocellulosic biomass. In: Bioproducts from agrowastes, pp 52–76
Taraballi F, Wang S, Li J et al (2012) Understanding the nano-topography changes and cellular influences resulting from the surface adsorption of human hair keratins. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201200043
Teresa CM, Manuela MR, M MM DDAMCM (2018) Marine algal carbohydrates as carbon sources for the production of biochemicals and biomaterials. Biotechnol Adv 36:798–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.02.006
Thomas MS, Koshy RR, Mary SK et al (2019) Starch, chitin and chitosan based composites and nanocomposites
Thompson RC, Moore CJ, vom Saal FS, Swan SH (2009) Plastics, the environment and human health: current consensus and future trends. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 364:2153–2166. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0053
Tran MH, Lee EY (2019) Green preparation of bioplastics based on degradation and chemical modification of lignin residue. J Wood Chem Technol 38:460–478. https://doi.org/10.1080/02773813.2018.1533978
Tsang YF, Kumar V, Samadar P et al (2019) Production of bioplastic through food waste valorization. Environ Int 127:625–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.076
Vilarinho F, Sanches-silva A, Vaz MF, Farinha JP (2017) Nanocellulose: a benefit for green food packaging. 8398. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1270254
Wan C, Zhou Y, Li Y (2011) Liquid hot water and alkaline pretreatment of soybean straw for improving cellulose digestibility. Biores Technol 102:6254–6259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.02.075
Wang S, Lin H, Zhang L et al (2016) Structural characterization and pyrolysis behavior of cellulose and hemicellulose isolated from softwood Pinus armandii Franch. Energy Fuels 30:5721–5728. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00650
Wang YS, Byrd CS, Barlaz MA (1994) Anaerobic biodegradability of cellulose and hemicellulose in excavated refuse samples using a biochemical methane potential assay. J Ind Microbiol 13:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01583999
Wischral D, Arias JM, Modesto LF et al (2019) Lactic acid production from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysates by Lactobacillus pentosus: integrating xylose and glucose fermentation. Biotechnol Prog 35:2718. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2718
Wu C, Huang X, Wang G et al (2012) Hyperbranched-polymer functionalization of graphene sheets for enhanced mechanical and dielectric properties of polyurethane composites. J Mater Chem 22:7010–7019. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm16901k
Wypych G (2018) Functional fillers–renewable and recycling. In: Functional fillers. Elsevier, pp 181–195
Xiao C, Anderson CT (2013) Roles of pectin in biomass yield and processing for biofuels. Front Plant Sci 4
Xue Y, Mou Z, Xiao H (2017) Nanocellulose as sustainable biomass material: structure, properties, present status and future prospects in biomedical applications. Nanoscale 9:14758–14781. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR04994C
Yang H, Yan R, Chen H et al (2007) Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 86:1781–1788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.12.013
Yang J, Ching YC, Chuah CH (2019a) Applications of lignocellulosic fibers and lignin in bioplastics: a review. Polymers 11:751–777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050751
Yang J, Ching YC, Chuah CH (2019b) Applications of lignocellulosic fibers and lignin in bioplastics: a review. Polymers 11:751–277
Yang S (2007) Bioprocessing for value-added products from renewable resources. New technologies and applications
Ying Y, Teong K, Nadiah W et al (2016) The world availability of non-wood lignocellulosic biomass for the production of cellulosic ethanol and potential pretreatments for the enhancement of enzymatic saccharification. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:155–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.01.072
Yoo Y, Youngblood JP (2016) Green one-pot synthesis of surface hydrophobized cellulose nanocrystals in aqueous medium green one-pot synthesis of surface hydrophobized cellulose nanocrystals in aqueous medium. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:1–48. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00781
Yue Y, Wang X, Han J et al (2019) Effects of nanocellulose on sodium alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogel: mechanical properties and adsorption-desorption capacities. Carbohydr Polym 206:289–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.105
Zhang BT, Wang W, Zhang D et al (2010) Biotemplated synthesis of gold nanoparticle- bacteria cellulose nanofiber nanocomposites and their application. Biosensing. 1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200902104
Zhang Y, Kumar A, Hardwidge PR et al (2016) D-lactic acid production from renewable lignocellulosic biomass via genetically modified Lactobacillus plantarum. Biotechnol Prog 32:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2212
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wang X et al (2014) Porous graphene oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose monoliths, with high metal ion adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 101:392–400
Zhang Y, Sun W, Wang H, Geng A (2013) Bioresource technology polyhydroxybutyrate production from oil palm empty fruit bunch using Bacillus megaterium R11. Biores Technol 147:307–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.029
Zhu H, Jia S, Wan T et al (2011) Biosynthesis of spherical Fe3O4/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites as adsorbents for heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 86:1558–1564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.061
Acknowledgements
Reshmy R and Raveendran Sindhu acknowledge Department of Science and Technology for sanctioning a project under DST WOS B scheme. Aravind Madhavan acknowledges Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare for sanctioning a project under Young Scientist Scheme. Ranjna Sirohi acknowledges CSIR for providing fellowship under direct SRF scheme bearing the Grant No. 09/171(0136)/19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reshmy, R., Thomas, D., Philip, E. et al. Bioplastic production from renewable lignocellulosic feedstocks: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 20, 167–187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-021-09565-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-021-09565-1