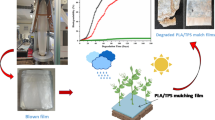
Abstract
The comparative study of biodegradation of various blown films obtained from Poly (lactic) acid (PLA) has been studied via soil burial method. A total of 3-different types of films prepared from neat PLA and the reactive blends containing poly butylenes succinate-co-adipate (PBSA), and thermoplasticized starch (TPS); namely VPLA, PLA/PBSA, PLA/TPS respectively were the subjects of investigation. Several analytical techniques including weight loss method and analysis of mechanical properties were performed in each seven days interval until ninety days to elucidate the biodegradation in soil. The tensile modulus of VPLA and PLA/PBSA blown films were deteriorated to the tune of 60.32% and 71.28% respectively within 28 days, while PLA/TPS blown films recorded a significant reduction of 75.31% in the modulus value within 21 days of soil exposure compared to unexposed blown film samples. Similarly, blown films of PLA/TPS reported the highest rate of weight loss in the order of 40.06% in 90 days of soil burial with an estimated half-life of 103 days in soil environment compared to its counterparts. The depletion in both mechanical properties and weight of the film samples suggesting the occurrence of biodegradation in the real soil environment. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed the formation of coarse morphology for all three types of soil buried samples which trace of microbial action appeared on PLA/TPS films. Fourier transform infrared microscope (FTIR) showed the decrease in carbonyl index and variation in the intensities of carbonyl and hydroxyl peaks irrespective of the film samples after 90 days of soil exposure. Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) documented reduction in molecular weight and variation in polydispersity index (PDI) of post-exposed soil samples. The elemental analysis exhibited that the percentage of organic carbon and hydrogen content of all the films decreased while the oxygen percentage increased after soil burial due to the biodegradation of film specimens. Both Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) reported increase in crystallinity for soil exposed samples indicating the initiation of degradation kinetics preferably at the amorphous region of film composition. It has also been inferred that the biodegradation mechanism of VPLA and PLA/PBSA blown films predominantly driven by hydrolysis of ester bond. Contrastingly, the biodegradation kinetics in case of PLA/TPS film has been proceeded with microbial assimilation of TPS component which further thrived on hydrolysis of PLA component of the blown film system.
Graphic Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palai B, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2020) Synergistic effect of polylactic acid (PLA) and Poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate)(PBSA) based sustainable, reactive, super toughened eco-composite blown films for flexible packaging applications. Polym Testing 83:106130
Palai B, Biswal M, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2019) In situ reactive compatibilization of polylactic acid (PLA) and thermoplastic starch (TPS) blends; synthesis and evaluation of extrusion blown films thereof. Ind Crops Prod 141:111748
Qi X, Ren Y, Wang X (2017) New advances in the biodegradation of Poly(lactic) acid. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 117:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.01.010
Kamm B, Gruber PR, Kamm M (2006) Biorefineries-industrial processes and products. Wiley, Hoboken
Nampoothiri KM, Nair NR, John RP (2010) An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Biores Technol 101(22):8493–8501
Auras R, Harte B, Selke S (2004) An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol Biosci 4(9):835–864
Auras RA, Singh SP, Singh JJ (2005) Evaluation of oriented poly (lactide) polymers vs. existing PET and oriented PS for fresh food service containers. Packag Technol Sci 18(4):207–216
Stloukal P, Kucharczyk P (2017) Acceleration of polylactide degradation under biotic and abiotic conditions through utilization of a new, experimental, highly compatible additive. Polym Degrad Stab 142:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.06.024
Nampoothiri KM, Nair NR, John RP (2010) Biological degradation of plastics: a comprehensive review. Bioresource Technol 101:8493–8501
Gregorova A, Sedlarik V, Pastorek M, Jachandra H, Stelzer F (2011) Effect of compatibilizing agent on the properties of highly crystalline composites based on poly (lactic acid) and wood flour and/or mica. J Polym Environ 19(2):372
Karamanlioglu M, Robson GD (2013) The influence of biotic and abiotic factors on the rate of degradation of poly(lactic) acid (PLA) coupons buried in compost and soil. Polym Degrad Stab 98:2063–2071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.07.004
Lunt J (1998) Large-scale production, properties and commercial applications of polylactic acid polymers. Polym Degrad Stab 59(1–3):145–152
De Andrade MFC, Souza PM, Cavalett O, Morales AR (2016) Life cycle assessment of Poly (Lactic acid)(pla): comparison between chemical recycling, mechanical recycling and composting. J Polym Environ 24(4):372–384
Stloukal P, Verney V, Commereuc S, Rychly J, Matisova-Rychlá L, Pis V, Koutny M (2012) Assessment of the interrelation between photooxidation and biodegradation of selected polyesters after artificial weathering. Chemosphere 88(10):1214–1219
Stloukal P, Pekařová S, Kalendova A, Mattausch H, Laske S, Holzer C, Chitu L, Bodner S, Maier G, Slouf M, Koutny M (2015) Kinetics and mechanism of the biodegradation of PLA/clay nanocomposites during thermophilic phase of composting process. Waste Manage 42:31–40
Karamanlioglu M, Preziosi R, Robson GD (2017) Abiotic and biotic environmental degradation of the bioplastic polymer poly (lactic acid): a review. Polym Degrad Stab 137:122–130
Agarwal M, Koelling KW, Chalmers JJ (1998) Characterization of the degradation of polylactic acid polymer in a solid substrate environment. Biotechnol Prog 14:517–526. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp980015p
Rudnik E, Briassoulis D (2011) Degradation behaviour of poly(lactic acid) films and fibres in soil under Mediterranean field conditions and laboratory simulations testing. Ind Crops Prod 33:648–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.12.031
Weng YX, Jin YJ, Meng QY, Wang L, Zhang M, Wang YZ (2013) Biodegradation behavior of poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)(PBAT), poly (lactic acid)(PLA), and their blend under soil conditions. Polym Testing 32(5):918–926
Shogren RL, Doane WM, Garlotta D, Lawton JW, Willett JL (2003) Biodegradation of starch/polylactic acid/poly(hydroxyester-ether) composite bars in soil. Polym Degrad Stab 79:405–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(02)00356-7
Souza PMS, Coelho FM, Sommaggio LRD, Marin-Morales MA, Morales AR (2019) Disintegration and biodegradation in soil of pbat mulch films: influence of the stabilization systems based on carbon black/hindered amine light stabilizer and carbon black/vitamin E. J Polym Environ 27(7):1584–1594
Copinet A, Copinet-Legin E, Fricoteaux F, Erre D (2011) Degradation in an inert solid medium of poly (lactic acid) polymeric material by Kibdelosporangium aridum. J Polym Environ 19(1):172–176
Tisserat B, Finkenstadt VL (2011) Degradation of poly (l-lactic acid) and bio-composites by alkaline medium under various temperatures. J Polym Environ 19(3):766–775
Balart JF, Montanes N, Fombuena V, Boronat T, Sánchez-Nacher L (2018) Disintegration in compost conditions and water uptake of green composites from poly (lactic acid) and hazelnut shell flour. J Polym Environ 26(2):701–715
Satti SM, Shah AA, Marsh TL, Auras R (2018) Biodegradation of poly (lactic acid) in soil microcosms at ambient temperature: evaluation of natural attenuation, bio-augmentation and bio-stimulation. J Polym Environ 26(9):3848–3857
Morro A, Catalina F, Sanchez-León E, Abrusci C (2019) Photodegradation and biodegradation under thermophile conditions of mulching films based on poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and its blend with poly (lactic acid). J Polym Environ 27(2):352–363
Tai NL, Adhikari R, Shanks R, Adhikari B (2019) Aerobic biodegradation of starch–polyurethane flexible films under soil burial condition: changes in physical structure and chemical composition. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 145:104793
Singh R, Kundu D (2010) Physico-chemical and hydraulic characteristics of soils of major sub-groups of eastern India. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 58:267–278
Ratto JA, Stenhouse PJ, Auerbach M, Mitchell J, Farrell R (1999) Processing, performance and biodegradability of a thermoplastic aliphatic polyester/starch system. Polymer (Guildf) 40:6777–6788. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(99)00014
Kangwanwatthanasiri P, Suppakarn N, Ruksakulpiwat C, Ruksakulpiwat Y (2015) Glycidyl methacrylate grafted polylactic acid: morphological properties and crystallization behavior. Macromol Symp 354(1):237–243
Arruda LC, Magaton M, Bretas RES, Ueki MM (2015) Influence of chain extender on mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of blown films of PLA/PBAT blends. Polym Testing 43:27–37
Ren M, Song J, Song C, Zhang H, Sun X, Chen Q, Zhang H, Mo Z (2005) Crystallization kinetics and morphology of poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate). J Polym Sci Part B 43(22):3231–3241
Babu Valapa R, Pugazhenthi G, Katiyar V (2016) Hydrolytic degradation behaviour of sucrose palmitate reinforced poly (lactic acid) nanocomposites. Int J Biol Macromol 89:70–80
Rogovina SZ, Aleksanyan KV, Loginova AA, Ivanushkina NE, Vladimirov LV, Prut EV, Berlin AA (2018) Influence of PEG on mechanical properties and biodegradability of composites based on PLA and starch. Starch/Staerke. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201700268
Bureepukdee C, Suttiruengwong S, Seadan M (2015) A study on reactive blending of (poly lactic acid) and poly (butylene succinate co adipate). IOP Publishing, Bristol
Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2016) Effect of poly (lactic acid)-graft-glycidyl methacrylate as a compatibilizer on properties of poly (lactic acid)/banana fiber biocomposites. Polym Adv Technol 27(4):515–524
Shirai MA, Grossmann MVE, Mali S, Yamashita F, Garcia PS, Müller CMO (2013) Development of biodegradable flexible films of starch and poly(lactic acid) plasticized with adipate or citrate esters. Carbohydr Polym 92:19–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.038
Lai JC, Rahman WAWA, Averous L, Lim TH (2016) Study and characterisation of the post processing ageing of sago pith waste biocomposites. Sains Malaysiana 45(4):633–641
Mendes JF, Paschoalin RT, Carmona VB, Sena Neto AR, Marques ACP, Marconcini JM, Mattoso LHC, Medeiros ES, Oliveira JE (2016) Biodegradable polymer blends based on corn starch and thermoplastic chitosan processed by extrusion. Carbohydr Polym 137:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.093
Akrami M, Ghasemi I, Azizi H, Karrabi M, Seyedabadi M (2016) A new approach in compatibilization of the poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic starch (PLA/TPS) blends. Carbohydr Polym 144:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.02.035
Moreno DDP, Hirayama D, Saron C (2018) Accelerated aging of pine wood waste/recycled LDPE composite. Polym Degrad Stab 149:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.01.014
Suyama T, Tokiwa Y, Ouichanpagdee P, Kanagawa T, Kamagata Y (1998) Phylogenetic affiliation of soil bacteria that degrade aliphatic polyesters available commercially as biodegradable plastics. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(12):5008–5011
Wilfred O, Tai H, Marriott R, Liu Q, Tverezovskiy V, Curling S, Tai H, Fan Z, Wang W (2018) Biodegradation of polylactic acid and starch composites in compost and soil. Int J Nano Res 1:01–11
Grayson ACR, Cima MJ, Langer R (2005) Size and temperature effects on poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation and microreservoir device performance. Biomaterials 26:2137–2145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.06.033
Puchalski M, Szparaga G, Biela T, Gutowska A, Sztajnowski S, Krucińska I (2018) Molecular and supramolecular changes in polybutylene succinate (PBS) and polybutylene succinate adipate (PBSA) copolymer during degradation in various environmental conditions. Polymers (Basel) 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030251
Salomez M, George M, Fabre P, Touchaleaume F, Cesar G, Lajarrige A, Gastaldi E (2019) A comparative study of degradation mechanisms of PBSA and PHBV under laboratory-scale composting conditions. Polym Degrad Stab 167:102–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.06.025
Malwela T, Ray SS (2015) Enzymatic degradation behavior of nanoclay reinforced biodegradable PLA/PBSA blend composites. Int J Biol Macromol 77:131–142
Feng Zuo Y, Gu J, Qiao Z, Tan H, Cao J, Zhang Y (2015) Effects of dry method esterification of starch on the degradation characteristics of starch/polylactic acid composites. Int J Biol Macromol 72:391–402
Jandas PJ, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2013) Sustainability, compostability, and specific microbial activity on agricultural mulch films prepared from poly(lactic acid). Ind Eng Chem Res 52:17714–17724. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4023429
Way C, Dean K, Wu DY, Palombo E (2012) Biodegradation of sequentially surface treated lignocellulose reinforced polylactic acid composites: Carbon dioxide evolution and morphology. Polym Degrad Stab 97:430–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.11.013
Šerá J, Stloukal P, Jančová P, Verney V, Pekařová S, Koutný M (2016) Accelerated biodegradation of agriculture film based on aromatic-aliphatic copolyester in soil under mesophilic conditions. J Agric Food Chem 64:5653–5661. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b01786
Maharana T, Mohanty B, Negi YS (2009) Melt-solid polycondensation of lactic acid and its biodegradability. Prog Polym Sci 34:99–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.10.001
Lv S, Liu X, Gu J, Jiang Y, Tan H, Zhang Y (2017) Microstructure analysis of polylactic acid-based composites during degradation in soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 122:53–60
Araújo A, Oliveira M, Oliveira R, Botelho G, Machado AV (2014) Biodegradation assessment of PLA and its nanocomposites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9477–9486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2256-y
Rudnik E, Briassoulis D (2011) Comparative biodegradation in soil behaviour of two biodegradable polymers based on renewable resources. J Polym Environ 19:18–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-010-0243-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palai, B., Mohanty, S. & Nayak, S.K. A Comparison on Biodegradation Behaviour of Polylactic Acid (PLA) Based Blown Films by Incorporating Thermoplasticized Starch (TPS) and Poly (Butylene Succinate-co-Adipate) (PBSA) Biopolymer in Soil. J Polym Environ 29, 2772–2788 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02055-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02055-z