Abstract
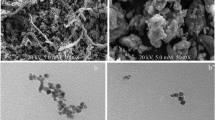
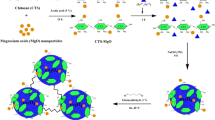
Reactive Blue 19 (RB19) removal from synthetic textile wastewater was investigated by using a CoFe2O4@methylcellulose (MC) activated with peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and the ultrasound process. CoFe2O4@MC as a new magnetic nano-biocomposite was prepared using a convenient and rapid microwave-assisted technique in presence of MC as a green biopolymer, and characterized by FESEM, EDS, Mapping, TEM, FTIR, XRD, TGA, VSM, and BET techniques. Then, the effective parameters including pH (4–10), reaction time (0–30 min), CoFe2O4@MC (0.2–1 g/L), and PMS concentration (0.5–10 mM) in the sonocatalytic degradation of RB19 were investigated. The maximum removal efficiency of RB19 was achieved as 97% for synthetic wastewater under the optimal conditions of pH 4, CoFe2O4@MC dosage (0.6 g/L), reaction time = 30 min, and PMS (5 mM) in the presence of ultrasonic waves (60 kHz) at the ambient room temperature of 22 °C. The CoFe2O4@MC catalyst was simply isolated using a magnet and recycled with no remarkable loss of catalytic activity following usage in four runs. The results showed that the CoFe2O4@MC sonocatalysis process is practical, and effective for degrading complex and resistant dyes such as RB19.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daneshvar N, Aber S, Vatanpour V, Rasoulifard MH (2008) Electro-Fenton treatment of dye solution containing Orange II: influence of operational parameters. J Electroanal Chem 615(2):165–174
Al-Kdasi A, Idris A, Saed K, Guan CT (2004) Treatment of textile wastewater by advanced oxidation processes—a review. Glob nest Int J 6(3):222–230
Kurt U, Apaydin O, Gonullu MT (2007) Reduction of COD in wastewater from an organized tannery industrial region by Electro-Fenton process. J Hazard Mater 143(1–2):33–40
Alinsafi A, Khemis M, Pons M-N, Leclerc J-P, Yaacoubi A, Benhammou A et al (2005) Electro-coagulation of reactive textile dyes and textile wastewater. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 44(4):461–470
Bellakhal N, Dachraoui M, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2006) Degradation of tartrazine in water by electro-Fenton process. J-Soc Chim Tunisie 8(2):223
Ventura A, Jacquet G, Bermond A, Camel V (2002) Electrochemical generation of the Fenton’s reagent: application to atrazine degradation. Water Res 36(14):3517–3522
Oturan MA, Sirés I, Oturan N, Pérocheau S, Laborde J-L, Trévin S (2008) Sonoelectro-Fenton process: a novel hybrid technique for the destruction of organic pollutants in water. J Electroanal Chem 624(1–2):329–332
Hammami S, Oturan N, Bellakhal N, Dachraoui M, Oturan MA (2007) Oxidative degradation of direct orange 61 by electro-Fenton process using a carbon felt electrode: application of the experimental design methodology. J Electroanal Chem 610(1):75–84
Amirmahani N, Mahdizadeh H, Malakootian M, Pardakhty A, Mahmoodi NO (2020) Evaluating nanoparticles decorated on Fe3O4@SiO2-Schiff Base (Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS-HBA) in adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous environments. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater [Internet] 30(9):3540–3551
Malakootian M, Nasiri A, Mahdizadeh H (2019) Metronidazole adsorption on CoFe2O4/activated carbon@chitosan as a new magnetic biocomposite: modelling, analysis, and optimization by response surface methodology. Desalin Water Treat [Internet] 164:215–227
Javid N, Nasiri A, Malakootian M (2019) Removal of nonylphenol from aqueous solutions using carbonized date pits modified with ZnO nanoparticles. Desalin Water Treat 141:140–148
Chiou C-S, Chang C-F, Chang C-T, Shie J-L, Chen Y-H (2006) Mineralization of Reactive Black 5 in aqueous solution by basic oxygen furnace slag in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere 62(5):788–795
Mahdizadeh H, Nasiri A, Gharaghani MA, Yazdanpanah G (2020) Hybrid UV/COP advanced oxidation process using ZnO as a catalyst immobilized on a stone surface for degradation of acid red 18 dye. MethodsX 7:101118
Malakootian M, Smith AJ, Gharaghani MA, Mahdizadeh H, Nasiri A, Yazdanpanah G (2020) Decoloration of textile Acid Red 18 dye by hybrid UV/COP advanced oxidation process using ZnO as a catalyst immobilized on a stone surface. Desalin Water Treat [Internet] 182:385–394
Rajabizadeh K, Yazdanpanah G, Dowlatshahi S, Malakootian M (2020) Photooxidation process efficiency (UV/O3) for P-nitroaniline removal from aqueous solutions. Ozone Sci Eng [Internet] 42(5):420–427
Malakootiana M, Asadzadehc SN (2020) Oxidative removal of tetracycline by sono Fenton-like oxidation process in aqueous media. Desalin Water Treat 193:392–401
Malakootian M, Asadzadeh SN (2020) Removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by ultrasound and ultraviolet enhanced persulfate oxidation. Desalin Water Treat 197:191–199
Malakootian M, Khatami M, Ahmadian M, Asadzadeh SN (2019) Biogenic silver nanoparticles/hydrogen peroxide/ozone: efficient degradation of reactive blue 19. Bionanoscience 1–8.
Malakootian M, Kannan K, Gharaghani MA, Dehdarirad A, Nasiri A, Shahamat YD et al (2019) Removal of metronidazole from wastewater by Fe/charcoal micro electrolysis fluidized bed reactor. J Environ Chem Eng 7(6):103457
Malakootian M, Nasiri A, Asadipour A, Faraji M, Kargar E (2019) A facile and green method for synthesis of ZnFe2O4@CMC as a new magnetic nanophotocatalyst for ciprofloxacin removal from aqueous media. MethodsX [Internet] 6:1575–1580
Tamaddon F, Nasiri A, Yazdanpanah G (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin using CuFe2O4@methyl cellulose based magnetic nanobiocomposite. MethodsX [Internet] 7:74–81
Malakootian M, Khatami M, Mahdizadeh H, Nasiri A, Amiri GM (2020) A study on the photocatalytic degradation of p-nitroaniline on glass plates by thermo-immobilized ZnO nanoparticle. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem [Internet] 50(3):124–135
Jangam K, Patil K, Balgude S, Patange S, More P (2020) Synthesis and characterization of magnetically separable Zn1-xCoxFeMnO4 nanoferrites as highly efficient photocatalyst for degradation of dye under solar light irradiation. J Phys Chem Solids 148:109700
Jangam K, Patil K, Balgude S, Patange S, More P (2020) Magnetically separable Zn1–xCo0.5xMg0.5xFe2O4 ferrites: stable and efficient sunlight-driven photocatalyst for environmental remediation. RSC Adv 10(70):42766–76
Oh W-D, Dong Z, Lim T-T (2016) Generation of sulfate radical through heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: current development, challenges and prospects. Appl Catal B Environ 194:169–201
Feng M, Cizmas L, Wang Z, Sharma VK (2017) Synergistic effect of aqueous removal of fluoroquinolones by a combined use of peroxymonosulfate and ferrate (VI). Chemosphere 177:144–148
Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang Q, Pan J, Zhang J (2018) Simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 using vacuum ultraviolet light (VUV)/heat/peroxymonosulfate (PMS). Chemosphere 190:431–441
Yin R, Guo W, Wang H, Du J, Zhou X, Wu Q et al (2018) Enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation for sulfamethazine degradation by ultrasound irradiation: performances and mechanisms. Chem Eng J 335:145–153
Sharma J, Mishra IM, Dionysiou DD, Kumar V (2015) Oxidative removal of Bisphenol A by UV-C/peroxymonosulfate (PMS): kinetics, influence of co-existing chemicals and degradation pathway. Chem Eng J 276:193–204
Ren Y, Lin L, Ma J, Yang J, Feng J, Fan Z (2015) Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M= Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water. Appl Catal B Environ 165:572–578
Lashkaryani EB, Kakavandi B, Kalantary RR, Jafari AJ, Gholami M (2019) Activation of peroxymonosulfate into amoxicillin degradation using cobalt ferrite nanoparticles anchored on graphene (CoFe2O4@ Gr). Toxin Rev 1–10
Li J, Xu M, Yao G, Lai B (2018) Enhancement of the degradation of atrazine through CoFe2O4 activated peroxymonosulfate (PMS) process: kinetic, degradation intermediates, and toxicity evaluation. Chem Eng J 348:1012–1024
Heidari MR, Varma RS, Ahmadian M, Pourkhosravani M, Asadzadeh SN, Karimi P et al (2019) Photo-fenton like catalyst system: activated carbon/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite for reactive dye removal from textile wastewater. Appl Sci 9(5):963
Tan C, Gao N, Fu D, Deng J, Deng L (2017) Efficient degradation of paracetamol with nanoscaled magnetic CoFe2O4 and MnFe2O4 as a heterogeneous catalyst of peroxymonosulfate. Sep Purif Technol 175:47–57
Liu Z, Yang S, Yuan Y, Xu J, Zhu Y, Li J et al (2017) A novel heterogeneous system for sulfate radical generation through sulfite activation on a CoFe2O4 nanocatalyst surface. J Hazard Mater 324:583–592
Farhadi S, Siadatnasab F, Khataee A (2017) Ultrasound-assisted degradation of organic dyes over magnetic CoFe2O4@ ZnS core-shell nanocomposite. Ultrason Sonochem 37:298–309
Siadatnasab F, Farhadi S, Khataee A (2018) Sonocatalytic performance of magnetically separable CuS/CoFe2O4 nanohybrid for efficient degradation of organic dyes. Ultrason Sonochem 44:359–367
Baird RB, Eaton AD, Rice EW, Bridgewater L (2017) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Ahmadi S, Mohammadi L, Igwegbe CA, Rahdar S, Banach AM (2018) Application of response surface methodology in the degradation of Reactive Blue 19 using H2O2/MgO nanoparticles advanced oxidation process. Int J Ind Chem 9(3):241–253
Amirmahani N, Rashidi M, Mahmoodi NO (2020) Synthetic application of gold complexes on magnetic supports. Appl Organomet Chem 34(5):e5626
Nguyen VA, Ramanathan M (2020) Application of Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) theory and the Guggenheim–Anderson–de Boer (GAB) equation for concentration-dependent, non-saturable cell–cell interaction dose-responses. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn [Internet] 47(6):561–572
Li X, Wang Z, Zhang B, Rykov AI, Ahmed MA, Wang J (2016) FexCo3−xO4 nanocages derived from nanoscale metal–organic frameworks for removal of bisphenol A by activation of peroxymonosulfate. Appl Catal B Environ 181:788–799
Antoniou MG, Armah A, Dionysiou DD (2010) Degradation of microcystin-LR using sulfate radicals generated through photolysis, thermolysis and e-transfer mechanisms. Appl Catal B Environ 96(3–4):290–298
Gong C, Chen F, Yang Q, Luo K, Yao F, Wang S et al (2017) Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by Fe-Co layered doubled hydroxide for efficient catalytic degradation of Rhoadmine B. Chem Eng J 321:222–232
Deng J, Shao Y, Gao N, Tan C, Zhou S, Hu X (2013) CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst of oxone for the degradation of diclofenac in water. J Hazard Mater 262:836–844
Xie M, Tang J, Kong L, Lu W, Natarajan V, Zhu F et al (2019) Cobalt doped g-C3N4 activation of peroxymonosulfate for monochlorophenols degradation. Chem Eng J 360:1213–1222
Tan C, Gao N, Deng Y, Deng J, Zhou S, Li J et al (2014) Radical induced degradation of acetaminophen with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as heterogeneous activator of peroxymonosulfate. J Hazard Mater 276:452–460
Wang Q, Shao Y, Gao N, Chu W, Chen J, Lu X et al (2017) Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Al2O3-based CoFe2O4 for the degradation of sulfachloropyridazine sodium: kinetics and mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 189:176–185
Yao Y, Xu C, Yu S, Zhang D, Wang S (2013) Facile synthesis of Mn3O4-reduced graphene oxide hybrids for catalytic decomposition of aqueous organics. Ind Eng Chem Res. 52(10):3637–45
Zhang B, Zhang Y, Xiang W, Teng Y, Wang Y (2017) Comparison of the catalytic performances of different commercial cobalt oxides for peroxymonosulfate activation during dye degradation. Chem Res Chin Univ 33(5):822–827
Du Y, Ma W, Liu P, Zou B, Ma J (2016) Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants. J Hazard Mater 308:58–66
Hassani A, Çelikdağ G, Eghbali P, Sevim M, Karaca S, Metin Ö (2018) Heterogeneous sono-Fenton-like process using magnetic cobalt ferrite-reduced graphene oxide (CoFe2O4-rGO) nanocomposite for the removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution. Ultrason Sonochem 40:841–852
Khan MA, Alam MM, Naushad M, Alothman ZA, Kumar M, Ahamad T (2015) Sol–gel assisted synthesis of porous nano-crystalline CoFe2O4 composite and its application in the removal of brilliant blue-R from aqueous phase: an ecofriendly and economical approach. Chem Eng J 279:416–424
Li X, Lu H, Zhang Y, He F (2017) Efficient removal of organic pollutants from aqueous media using newly synthesized polypyrrole/CNTs-CoFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 316:893–902
Ahmadi M, Ghanbari F (2018) Combination of UVC-LEDs and ultrasound for peroxymonosulfate activation to degrade synthetic dye: influence of promotional and inhibitory agents and application for real wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(6):6003–6014
Oh W-D, Dong Z, Hu Z-T, Lim T-T (2015) A novel quasi-cubic CuFe2O4–Fe2O3 catalyst prepared at low temperature for enhanced oxidation of bisphenol A via peroxymonosulfate activation. J Mater Chem A 3(44):22208–22217
Huang R, Fang Z, Yan X, Cheng W (2012) Heterogeneous sono-Fenton catalytic degradation of bisphenol A by Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles under neutral condition. Chem Eng J 197:242–249
Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD, Gonzalez MA (2006) Cobalt-mediated activation of peroxymonosulfate and sulfate radical attack on phenolic compounds. Implications of chloride ions. Environ Sci Technol 40(3):1000–7
Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD (2004) Transition metal/UV-based advanced oxidation technologies for water decontamination. Appl Catal B Environ 54(3):155–163
Xu LJ, Chu W, Gan L (2015) Environmental application of graphene-based CoFe2O4 as an activator of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of a plasticizer. Chem Eng J 263:435–443
Gupta VK, Fakhri A, Azad M, Agarwal S (2017) Synthesis of CdSe quantum dots decorated SnO2 nanotubes as anode for photo-assisted electrochemical degradation of hydrochlorothiazide: Kinetic process. J Colloid Interface Sci 508:575–582
Hu L, Zhang G, Liu M, Wang Q, Wang P (2018) Optimization of the catalytic activity of a ZnCo2O4 catalyst in peroxymonosulfate activation for bisphenol A removal using response surface methodology. Chemosphere 212:152–161
Kamal S, Pan G-T, Chong S, Yang TC-K (2020) Ultrasonically induced sulfur-doped carbon nitride/cobalt ferrite nanocomposite for efficient sonocatalytic removal of organic dyes. Processes. 8(1):104
Tsitonaki A, Petri B, Crimi M, Mosbæk H, Siegrist RL, Bjerg PL (2010) In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 40(1):55–91
Guan Y-H, Ma J, Ren Y-M, Liu Y-L, Xiao J-Y, Lin L et al (2013) Efficient degradation of atrazine by magnetic porous copper ferrite catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation via the formation of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals. Water Res 47(14):5431–5438
Siddique M, Farooq R, Shaheen A (2011) Removal of Reactive Blue 19 from wastewaters by physicochemical and biological processes-a review. J Chem Soc Pakistan 33(2):284–285
Esmaeili S, Dehvari M, Babaei A (2019) Degradation of acid orange 7 dye with PMS and H2O2 activated by CoFe2O4/PAC nanocomposite. Arch Hyg Sci 8(1):35–45
Parhizkar J, Habibi MH, Mosavian SY (2019) Synthesis and characterization of nano CoFe2O4 prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion with ultrasonic irradiation and evaluation of photocatalytic removal and degradation kinetic of reactive red 195. Silicon 11(2):1119–1129
Huang Y, Wang Y, Meng X, Liu X (2020) Highly efficient Co-OMS-2 catalyst for the degradation of reactive blue 19 in aqueous solution. Inorg Chem Commun 112:107757
Singh P, Vishnu MC, Sharma KK, Singh R, Madhav S, Tiwary D et al (2016) Comparative study of dye degradation using TiO2-activated carbon nanocomposites as catalysts in photocatalytic, sonocatalytic, and photosonocatalytic reactor. Desalin Water Treat 57(43):20552–20564
Kaur S, Singh V (2007) Visible light induced sonophotocatalytic degradation of Reactive Red dye 198 using dye sensitized TiO2. Ultrason Sonochem 14(5):531–537
Acknowledgements
This research with Project Number 98000528 and IR.KMU.REC.1398.507 ethic approval cod was conducted in the Student Research Committee of Kerman University of Medical Sciences. This research was supported by the Vice-Chancellor for Research and Technology of Kerman University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasiri, A., Malakootian, M., Heidari, M.R. et al. CoFe2O4@Methylcelloluse as a New Magnetic Nano Biocomposite for Sonocatalytic Degradation of Reactive Blue 19. J Polym Environ 29, 2660–2675 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02074-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02074-w