Abstract
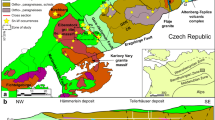
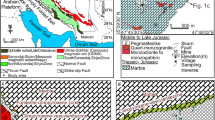
Huangshaping is a world-class skarn deposit hosting abundant W–Sn polymetallic mineralization in the Nanling Range, South China. Although the geochemistry of skarn-hosted mineral deposits has been extensively studied, the role of the prograde-to-retrograde stage transition in the enrichment and precipitation of metallic elements in high-temperature systems has received little study to date. Here, we analyzed garnet, scheelite, and cassiterite in high-temperature granite porphyry-related W–Sn polymetallic system of the Huangshaping deposit to investigate these processes. Three generations of garnet (Grt I, Grt II, and Grt III), two generations of scheelite (Sch I and Sch II), and two types of cassiterite (Cst I and Cst II) were distinguished with regard to their mineral associations, microscopic characteristics, and geochemical features. The results show that grossular–andradite garnet formed from Al-rich andradite (Grt I, Al2O3: 8.18 wt%) in the early prograde stage and pure Fe-andradite (Grt III, Al2O3: 0.15 wt%) in the late prograde stage. Mo-rich scheelite (Sch Ia, MoO3: 19.41 wt%) formed in the prograde stage and coexisted with Grt III, sharing the same REE patterns. A shift from HREE enrichment in Grt I to HREE depletion in Grt III reflects progressive uptake of REEs by secondary mineral phases. Grt III has the highest average contents of W (905 ppm), Mo (19 ppm), and Sn (5610 ppm), suggesting an enrichment of metallic elements at the end of the prograde stage. In contrast, Mo-poor scheelite (Sch II, MoO3: 0.63 wt%) co-crystallized with molybdenite and fluorite in the retrograde stage and shares similar REE patterns with the granite porphyry. Skarn mineralization at Huangshaping was a two-step process controlled by metamorphic stage. The prograde stage was characterized by high temperatures and fO2 and a Cl-rich fluid, and it resulted in enrichment of ore-forming elements with minor scheelite precipitation. The retrograde stage was characterized by lower temperatures and fO2 and a F-rich fluid, and it resulted in major precipitation of ore minerals (scheelite, molybdenite, and cassiterite). Dissolution–reprecipitation reactions played an important role in extraction of metallic elements from decomposing anhydrous skarn minerals and formation of ore minerals. A decrease in the high-field-strength element (HFSE) content of cassiterite from proximal skarn (Cst I) to distal skarn (Cst II) indicates declining temperature accompanied by precipitation of fluorite. This study examines the transition from the prograde stage to the retrograde stage in the Huangshaping deposit, and it provides insights into the genesis of other skarn W–Sn polymetallic deposits in the Nanling magmatic–tectonic–metallogenic belt.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramov SS (2001) Modeling of REE fractionation in the acid melt-fluoride-chloride fluid system. Dokl Earth Sci 377:198–200
Aja SU, Wood SA, Williams-Jones AE (1995) The aqueous geochemistry of Zr and the solubility of some Zr-bearing minerals. Appl Geochem 10:603–620
Amthauer G, McIver JR, Viljoen EA (1979) 57Fe and 119Sn Mössbauer studies of natural tin-bearing garnets. Phys Chem Miner 4:235–244
Bau M (1996) Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib to Mineral Petrol 128:405–408
Bau M, Dulski P (1995) Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids. Contrib to Mineral Petrol 119:213–223
Bea F, Montera P, Garuti G, Zacharini F (1997) Pressure-dependence of rare earth element distribution in amphibolite- and granulite- grade garnets. A LA-ICP-MS study. Geostand Newslett 21:253–270
Bea F, Pereira MD, Stroh A (1994) Mineral/leucosome trace-element partitioning in a peraluminous migmatite (a laser ablation-ICP-MS study). Chem Geol 117:291–312
Bennett JM, Kemp AIS, Roberts MP (2020) Microstructural controls on the chemical heterogeneity of cassiterite revealed by cathodoluminescence and elemental X-ray mapping. Am Mineral 105:58–76
Blevin PL, Chappell BW (1992) The role of magma sources, oxidation states and fractionation in determining the granite metallogeny of eastern Australia. Earth Environ Sci Trans R Soc Edinburgh 83:305–316
Boyd FR, Pearson DG, Hoal KO, Hoal BG, Nixon PH, Kingston MJ, Mertzman SA (2004) Garnet lherzolites from Louwrensia, Namibia: bulk composition and P/T relations. Lithos 77:573–592
Brugger J, Bettiol AA, Costa S, Lahaye Y, Bateman R, Lambert DD, Jamieson DN (2000a) Mapping REE distribution in scheelite using luminescence. Mineral Mag 64:891–903
Brugger J, Lahaye Y, Costa S, Lambert D, Bateman R (2000b) Inhomogeneous distribution of REE in scheelite and dynamics of Archaean hydrothermal systems (Mt. Charlotte and Drysdale gold deposits, Western Australia). Contrib to Mineral Petrol 139:251–264
Brugger J, Maas R, Lahaye Y, McRae C, Ghaderi M, Costa S, Lambert D, Bateman R, Prince K (2002) Origins of Nd–Sr–Pb isotopic variations in single scheelite grains from Archaean gold deposits, Western Australia. Chem Geol 182:203–225
Brugger J, Etschmann B, Pownceby M, Liu W, Grundler P, Brewe D (2008) Oxidation state of europium in scheelite: tracking fluid–rock interaction in gold deposits. Chem Geol 257:26–33
Butler BCM (1978) Tin-rich garnet, pyroxene, and spinel from a slag. Mineral Mag 42:487–492
Cao J, Wu Q, Yang X et al (2018) Geochronology and genesis of the Xitian W-Sn polymetallic deposit in eastern Hunan province, South China: evidence from zircon U-Pb and muscovite Ar-Ar dating, petrochemistry, and wolframite Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes. Minerals 8:15–22
Cao J, Yang X, Lu Y, Fu J, Yang L (2020) Zircon U–Pb and Sm–Nd geochronology and geochemistry of the Sn–W deposits in the northern Guposhan ore field, Nanling Range, southern China. Ore Geol Rev 118:103323
Chang Z, Meinert LD (2008) The empire Cu-Zn mine, Idaho: exploration implications of unusual Skarn features related to high fluorine activity. Econ Geol 103:909–938
Chen J, Wu H (1988) Synthetic analogue experiments on the Shizhuyuan tungsten, tin, molybdenum and bismuth skarn deposit in southeastern Hunan province. Miner Depos 7:32–41
Cheng Y, Spandler C, Kemp A, Mao J, Rusk B, Hu Y, Blake K (2019) Controls on cassiterite (SnO2) crystallization: evidence from cathodoluminescence, trace-element chemistry, and geochronology at the Gejiu Tin District. Am Mineral 104:118–129
Choi W, Park C, Song Y (2020) Multistage W-mineralization and magmatic-hydrothermal fluid evolution : microtextural and geochemical footprints in scheelite from the Weondong W-skarn deposit, South Korea. Ore Geol Rev 116:103219
Cottrant J-F (1981) Cristallochimie et géochimie des terres rares dans la scheelite: application à quelques gisements français. Unpublished PhD thesis, University of Paris, France
Crowe DE, Riciputi LR, Bezenek S, Ignatiev A (2001) Oxygen isotope and trace element zoning in hydrothermal garnets: windows into large-scale fluid-flow behavior. Geology 29:479–482
Ding T, Ma D, Lu J, Zhang R, Zhang S (2016) S, Pb, and Sr isotope geochemistry and genesis of Pb – Zn mineralization in the Huangshaping polymetallic ore deposit of southern Hunan Province, China. Ore Geol Rev 77:117–132
Ding T, Ma D, Lu J, Zhang R (2018a) Magnetite as an indicator of mixed sources for W–Mo–Pb–Zn mineralization in the Huangshaping polymetallic deposit, southern Hunan Province, China. Ore Geol Rev 95:65–78
Ding T, Ma D, Lu J, Zhang R (2018b) Garnet and scheelite as indicators of multi-stage tungsten mineralization in the Huangshaping deposit, southern Hunan province, China. Ore Geol Rev 94:193–211
Dostal J, Kontak DJ, Chatterjee AK (2009) Trace element geochemistry of scheelite and rutile from metaturbidite-hosted quartz vein gold deposits, Meguma Terrane, Nova Scotia, Canada: genetic implications. Mineral Petrol 97:95–109
Douville E, Bienvenu P, Charlou JL, Donval JP, Fouquet Y, Appriou P, Gamo T (1999) Yttrium and rare earth elements in fluids from various deep-sea hydrothermal systems. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:627–643
Eadington PJ, Kinealy K (1983) Some aspects of the hydrothermal reactions of tin during skarn formation. J Geol Soc Aust 30:461–471
Einaudi MT, Meinert LD, Newberry RJ (1981) Skarn deposits. Skarn Depos 76:317–391
Fan D, Kuang Y, Xu J, Li B, Zhou W, Xie H (2017) Thermoelastic properties of grossular–andradite solid solution at high pressures and temperatures. Phys Chem Miner 44:137–147
Feng Z, Wang C, Zhang M, Liang J (2012) Unusually dumbbell-shaped Guposhan–Huashan twin granite plutons in Nanling Range of South China: discussion on their incremental emplacement and growth mechanism. J Asian Earth Sci 48:9–23
Gammons CH, Wood SA, Li Y (2002) Complexation of the rare earth elements with aqueous chloride at 200° and 300°C and saturated water vapor pressure. Geochem Soc Spec Publ 7:191–207
Gaspar LM, Inverno CMC (2000) Mineralogy and metasomatic evolution of distal strata-bound scheelite skarns in the Riba de Alva mine, northeastern Portugal. Econ Geol 95:1259–1275
Gaspar M, Knaack C, Meinert LD, Moretti R (2008) REE in skarn systems: a LA-ICP-MS study of garnets from the Crown Jewel gold deposit. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:185–205
Ghaderi M, Palin JM, Campbell IH, Sylvester PJ (1999) Rare earth element systematics in scheelite from hydrothermal gold deposits in the Kalgoorlie-Norseman region, Western Australia. Econ Geol 94:423–437
Guo J, Zhang R, Li C, Sun W, Hu Y, Kang D, Wu J (2018a) Genesis of the Gaosong Sn–Cu deposit, Gejiu district, SW China: constraints from in situ LA-ICP-MS cassiterite U–Pb dating and trace element fingerprinting. Ore Geol Rev 92:627–642
Guo J, Zhang R, Sun W, Ling M, Hu Y, Wu K, Luo M, Zhang L (2018b) Genesis of tin-dominant polymetallic deposits in the Dachang district, South China: insights from cassiterite U–Pb ages and trace element compositions. Ore Geol Rev 95:863–879
Hall MR, Ribbe PH (1971) An electron microprobe study of luminescence centers in cassiterite. Am Miner 56:31–45
Harris NBW, Gravestock P, Inger S (1992) Ion-microprobe determinations of trace-element concentrations in garnets from anatectic assemblages. Chem Geol 100:41–49
Hennigh QT, Hutchinson RW (1999) Cassiterite at Kidd Creek: an example of volcanogenic massive sulfide-hosted tin mineralization. Econ Geol Monogr v 10:431–440
Hickmott D, Spear FS (1992) Major-and trace-element zoning in garnets from calcareous pelites in the NW shelburne falls Quadrangle, Massachusetts: garnet growth histories in retrograded rocks. J Petrol 33:965–1005
Hsu LC (1977) Effects of oxygen and sulfur fugacities on the scheelite-tungstenite and powellite-molybdenite stability relations. Econ Geol 72:664–670
Hsu LC, Galli PE (1973) Origin of the scheelite-powellite series of minerals. Econ Geol 68:681–696
Hu R-Z, Zhou M-F (2012) Multiple Mesozoic mineralization events in South China—an introduction to the thematic issue. Miner Depos 47:579–588
Hu X, Gong Y, Pi D, Zhang Z, Zeng G, Xiong S, Yao S (2017) Jurassic magmatism related Pb-Zn-W-Mo polymetallic mineralization in the central Nanling Range, South China: Geochronologic, geochemical, and isotopic evidence from the Huangshaping deposit. Ore Geol Rev 91:877–895
Irber W (1999) The lanthanide tetrad effect and its correlation with K/Rb, Eu/Eu∗, Sr/Eu, Y/Ho, and Zr/Hf of evolving peraluminous granite suites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:489–508
Jamtveit B, Wogelius RA, Fraser DG (1993) Zonation patterns of skarn garnets: records of hydrothermal system evolution. Geology 21:113–116
Jiang S-Y (1998) Stable and radiogenic isotope studies of tourmaline: an overview. J Czech Geol Soc 43:75–90
Jiang S-Y, Palmer MR, Slack JF, Shaw DR (1998) Paragenesis and chemistry of multistage tourmaline formation in the sullivan Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, British Columbia. Econ Geol 93:47–67
Jiang W-C, Li H, Evans NJ, Wu J-H (2019a) Zircon records multiple magmatic-hydrothermal processes at the giant Shizhuyuan W–Sn–Mo–Bi polymetallic deposit, South China. Ore Geol Rev 115:103160
Jiang WC, Li H, Mathur R, Wu JH (2019b) Genesis of the giant Shizhuyuan W–Sn–Mo–Bi–Pb–Zn polymetallic deposit, South China: constraints from zircon geochronology and geochemistry in skarns. Ore Geol Rev 111:102980
Jiang WC, Li H, Turner S, Zhu DP, Wang C (2020) Timing and origin of multi-stage magmatism and related W–Mo–Pb–Zn–Fe–Cu mineralization in the Huangshaping deposit, South China: an integrated zircon study. Chem Geol 552:119782
Keankeo W, Hermann J (2002) The oscillatory intergrowth of feldspars in titanian andradite, Little Dromedary, NSW, Australia. Eur J Mineral 14:379–388
Kwak TAP (1987) W-Sn Skarn deposits. Developments in Economic Geology 24, Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kwak TAP, Tan TH (1981) The geochemistry of zoning in skarn minerals at the King Island (dolphin) mine. Econ Geol 76:468–497
Legros H, Harlaux M, Mercadier J, et al. (2020) The world-class Nanling metallogenic belt (Jiangxi, China): W and Sn deposition at 160 Ma followed by 30 m.y. of hydrothermal metal redistribution. Ore Geol Rev 117:103302
Lei ZH, Chen FW, ChenZH, et al. (2010) Petrogenetic and metallogenic age determination of the Huangshaping lead-zinc polymetallic deposit and its geological significance. Acta Geosci Sin 31:532–540 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li C-Y, Zhang H, Wang F-Y, Liu JQ, Sun YL, Hao XL, Li YL, Sun W (2012) The formation of the Dabaoshan porphyry molybdenum deposit induced by slab rollback. Lithos 150:101–110
Li D, Tan C, Miao F, Liu Q, Zhang Y, Sun X (2019a) Initiation of Zn-Pb mineralization in the Pingbao Pb-Zn skarn district, South China: constraints from U-Pb dating of grossular-rich garnet. Ore Geol Rev 107:587–599
Li H, Watanabe K, Yonezu K (2014a) Zircon morphology, geochronology and trace element geochemistry of the granites from the Huangshaping polymetallic deposit, South China: implications for the magmatic evolution and mineralization processes. Ore Geol Rev 60:14–35
Li H, Watanabe K, Yonezu K (2014b) Geochemistry of A-type granites in the Huangshaping polymetallic deposit (South Hunan, China): implications for granite evolution and associated mineralization. J Asian Earth Sci 88:149–167
Li H, Yonezu K, Watanabe K, Tindell T (2017) Fluid origin and migration of the Huangshaping W–Mo polymetallic deposit, South China: geochemistry and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of hydrothermal K-feldspars. Ore Geol Rev 86:117–129
Li H, Palinkaš LA, Watanabe K, Xi X-S (2018) Petrogenesis of Jurassic A-type granites associated with Cu-Mo and W-Sn deposits in the central Nanling region, South China: relation to mantle upwelling and intra-continental extension. Ore Geol Rev 92:449–462
Li H, Palinkaš LA, Evans NJ, Watanabe K (2020) Genesis of the Huangshaping W–Mo–Cu–Pb–Zn deposit, South China: role of magmatic water, metasomatized fluids, and basinal brines during intra-continental extension. Geol J 55:1409–1430
Li J, Li X, Xiao R (2019b) Multiple-stage tungsten mineralization in the Silurian Jiepai W skarn deposit, South China: insights from cathodoluminescence images, trace elements, and fluid inclusions of scheelite. J Asian Earth Sci 181:103898
Li X, McCulloch MT (1996) Secular variation in the Nd isotopic composition of Neoproterozoic sediments from the southern margin of the Yangtze block: evidence for a Proterozoic continental collision in Southeast China. Precambrian Res 76:67–76
Li X, Sasaki M (2007) Hydrothermal alteration and mineralization of Middle Jurassic Dexing Porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, Southeast China. Resour Geol 57:409–426
Li X, Watanabe Y, Yi X (2013) Ages and sources of ore-related porphyries at Yongping Cu-Mo deposit in Jiangxi Province, Southeast China. Resour Geol 63:288–312
Li X, Cheng H, Chunzeng W, Lifa W (2016) Genesis of the Huangshaping W-Mo-Cu-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit in southeastern Hunan Province, China: constraints from fluid inclusions, trace elements, and isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 79:1–25
Liang X, Dong C, Jiang Y, Wu S, Zhou Y, Zhu H, Fu J, Wang C, Shan Y (2016) Zircon U-Pb, molybdenite Re-Os and muscovite Ar-Ar isotopic dating of the Xitian W-Sn polymetallic deposit, eastern Hunan Province, South China and its geological significance. Ore Geol Rev 78:85–100
Liu B, Li H, Wu Q-H, Kong H, Xi XS (2019a) Double-vein (ore-bearing vs. ore-free) structures in the Xitian ore field, South China: implications for fluid evolution and mineral exploration. Ore Geol Rev 115:103181
Liu B, Li H, Wu Q et al (2019b) Fluid evolution of Triassic and Jurassic W mineralization in the Xitian ore field, South China: constraints from scheelite geochemistry and microthermometry. Lithos 330–331:1–15
Liu B, Wu QH, Li H, Wu JH, Cao JY, Jiang JB, Liang W (2020) Fault-controlled fluid evolution in the Xitian W–Sn–Pb–Zn–fluorite mineralization system (South China): insights from fluorite texture, geochemistry and geochronology. Ore Geol Rev 116:103233
Liu Y, Hu Z, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao C, Chen H (2008) In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem Geol 257:34–43
Ma LY, Lu YF, Qu WJ, Fu JM (2007) Re–Os isotopic chronology of molybdenites in Huangshaping lead–zinc deposit, Southeast Hunan, and its geological implications. Min Depos 26:425–431 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Manning DAC (1981) The effect of fluorine on liquidus phase relationships in the system Qz-Ab-Or with excess water at 1 kb. Contrib to Mineral Petrol 76:206–215
Mao JW, Cheng YB, Chen MH, Pirajno F (2012) Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Min Depos 48(3):267–294
McIver JR, Mihalik P (1975) Stannian andradite from “Davib Ost”, south West Africa. Can Miner 13:217–221
Meinert LD (1992) Skarns and skarn deposits. Geosci Canada 19:145–162
Meinert LD, Hedenquist JW, Satoh H, Matsuhisa Y (2003) Formation of anhydrous and hydrous skarn in Cu-Au ore deposits by magmatic fluids. Econ Geol 98:147–156
Meinert LD, Dipple GM, Nicolescu S (2005) World skarn deposits. Econ Geol 100:299–336
Migdisov AA, Williams-Jones AE, Wagner T (2009) An experimental study of the solubility and speciation of the rare earth elements (III) in fluoride- and chloride-bearing aqueous solutions at temperatures up to 300 °C. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73(23):7087–7109
Misra K.C. (2000) Skarn Deposits. In: Understanding Mineral Deposits. Springer, Dordrecht
Möller P, Dulski P, Szacki W, Malow G, Riedel E (1988) Substitution of tin in cassiterite by tantalum, niobium, tungsten, iron and manganese. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:1497–1503
Moretti R, Ottonello G (1998) An appraisal of endmember energy and mixing properties of rare earth garnets. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:1147–1173
Nekrasov IY (1971) Features of tin mineralization in carbonate deposits, as in Eastern Siberia. Int Geol Rev 13:1532–1542
Newberry RJ (1982) Tungsten-bearing skarns of the Sierra Nevada. I. The Pine Creek mine, California. Econ Geol 77:823–844
Newberry RJ (1998) W- and Sn-skarn deposits: a 1998 status report. Miner Intrusion-related Skarn Syst 26:289–335
Orhan A (2017) Evolution of the Mo-rich scheelite skarn mineralization at Kozbudaklar, Western Anatolia, Turkey: evidence from mineral chemistry and fluid inclusions. Ore Geol Rev 80:141–165
Park C, Choi W, Kim H, Park MH, Kang IM, Lee HS, Song Y (2017a) Oscillatory zoning in skarn garnet : implications for tungsten ore exploration. Ore Geol Rev 89:1006–1018
Park C, Song Y, Kang IM, Shim J, Chung D, Park CS (2017b) Metasomatic changes during periodic fluid flux recorded in grandite garnet from the Weondong W-skarn deposit, South Korea. Chem Geol 451:135–153
Park C, Park C, Song Y, Choi S-G (2019) Sequential trace element analysis of zoned skarn garnet: implications for multi-stage fluxing and flow of magmatic fluid into a skarn system. Lithos 350–351:105213
Pavlova GG, Palessky SV, Borisenko AS, Vladimirov AG, Seifert T, Phan LA (2015) Indium in cassiterite and ores of tin deposits. Ore Geol Rev 66:99–113
Peng JT, Zhang DL, Hu RZ et al (2010) Inhomogeneous distribution of rare earth elements (REEs) in scheelite from the Zhazixi W-Sb deposit, western Hunan and its geological implications. Geol Rev 56:810–819
Plimer IR (1984) Malayaite and tin-bearing silicates from a skarn at Doradilla via Bourke, New South Wales. Aust J Earth Sci 31:147–153
Plimer IR, Lu J, Kleeman JD (1991) Trace and rare earth elements in cassiterite - sources of components for the tin deposits of the mole granite, Australia. Miner Depos 26:267–274
Poulin RS (2016) A study of the crystal chemistry, cathodoluminescence, geochemistry and oxygen isotopes in scheelite: application towards discriminating among differing ore-deposit systems. Laurentian University of Sudbury, Canada, Ph.D. dissertation, 301 pp
Putnis A (2002) Mineral replacement reactions: from macroscopic observations to microscopic mechanisms. Mineral Mag 66:689–708
Raimbault L, Baumer A, Dubru M, Benkerrou C, Croze V, Zahm A (1993) REE fractionation between scheelite and apatite in hydrothermal conditions. Am Mineral 78:1275–1285
Ranjbar S, Tabatabaei Manesh SM, Mackizadeh MA, Tabatabaei SH, Parfenova OV (2016) Geochemistry of major and rare earth elements in garnet of the Kal-e Kafi skarn, Anarak area, Central Iran: constraints on processes in a hydrothermal system. Geochem Int 54:423–438
Rempel KU, Williams-Jones AE, Migdisov AA (2009) The partitioning of molybdenum(VI) between aqueous liquid and vapour at temperatures up to 370°C. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:3381–3392
Ren Z (1984) Geochemical characteristics of tin-bearing magnetite-skarns. Geochemistry 3:115–127
Sato K (1980) Tungsten skarn deposit of the Fujigatani mine, Southwest Japan. Econ Geol 75:1066–1082
Shock EL, Sassani DC (1995) Rare earth elements in hydrothermal systems : estimates of standard partial molal thermodynamic properties of aqueous complexes of the rare earth elements at high pressures and temperatures. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59(21):4329–4350
Shore M, Fowler AD (1996) Oscillatory zoning in minerals: a common phenomenon. Can Mineral 34:1111–1126
Slack JF (1996) Tourmaline associations with hydrothermal ore deposits. Boron Mineral Petrol Geochem 33:559–643
Slack JF, Coad PR (1989) Multiple hydrothermal and metamorphic events in the Kidd Creek volcanogenic massive sulphide deposit, Timmins, Ontario: evidence from tourmalines and chlorites. Can J Earth Sci 26:694–715
Soloviev SG, Krivoschekov NN (2011) Petrochemistry of rocks in the Chorukh-Dairon monzonite-syenite-granite pluton, northern Tajikistan. Geochem Int 49:691–710
Song S, Mao J, Xie G et al (2018) The formation of the world-class Zhuxi scheelite skarn deposit: implications from the petrogenesis of scheelite-bearing anorthosite. Lithos 312–313:153–170
Streck MJ (2008) Mineral textures and zoning as evidence for open system processes. Rev Mineral Geochem 69:595–622
Song G, Qin K, Li G, Evans NJ, Chen L (2014) Scheelite elemental and isotopic signatures: implications for the genesis of skarn-type W-Mo deposits in the Chizhou area, Anhui province, eastern China. Am Mineral 99:303–317
Su S, Qin K, Li G et al (2019) Cathodoluminescence and trace elements of scheelite: constraints on ore-forming processes of the Dabaoshan porphyry Mo-W deposit, South China. Ore Geol Rev 115:103183
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt: implications for mantle composition and processes. In Saunders AD and Norry MJ, eds. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins, pp. 313–345
Sylvester PJ, Ghaderi M (1997) Trace element analysis of scheelite by excimer laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ELA-ICP-MS) using a synthetic silicate glass standard. Chem Geol 141:49–65
Tian Z-D, Leng C-B, Zhang X-C, Zafar T, Zhang LJ, Hong W, Lai CK (2019) Chemical composition, genesis and exploration implication of garnet from the Hongshan cu-Mo skarn deposit, SW China. Ore Geol Rev 112:103016
Timon Sanchez SM, Moro Benito MC, Cembranos Pérez ML (2009) Mineralogical and physiochemical evolution of the Los Santos scheelite skarn, Salamanca, NW Spain. Econ Geol 104:961–965
Tindle AG, Breaks FW (1998) Oxide minerals of the separation rapids rare-element granitic pegmatite group, northwestern Ontario. Can Mineral 36:609–635
Wang D, Huang F, Wang Y et al (2019a) Regional metallogeny of tungsten-tin-polymetallic deposits in Nanling region, South China. Ore Geol Rev 120:103305
Wang X-D, Wang X-W, Sun C-M (2010) REE geochemistry of scheelite and Sm-Nd dating for the Houchangchuan scheelite deposit in Gansu. J Mineral Petrol 30:64–68
Wang Y, Fan W, Zhang G, Zhang Y (2013) Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China block: key observations and controversies. Gondwana Res 23:1273–1305
Wang Y, Sun Q, Duan D, Bao X, Liu X (2019b) The study of crystal structure on grossular–andradite solid solution. Minerals 9(11):691
Wang Z, Chen B, Ma X (2014) LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age and geochemical data of cassiterite of the Furong tin deposit, the Nanling Range: implications for the origin and evolution of the ore-forming fluid. Chin Sci Bull 59:2505–2519 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Webster JD, Holloway JR, Hervig RL (1987) Phase equilibria of a be, U and F-enriched vitrophyre from Spor Mountain, Utah. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 51:389–402
Wood SA (1990) The aqueous geochemistry of the rare-earth elements and yttrium: 2. Theoretical predictions of speciation in hydrothermal solutions to 350°C at saturation water vapor pressure. Chem Geol 88:99–125
Wu J-H, Li H, Algeo TJ, Jiang WC, Zhou ZK (2018) Genesis of the Xianghualing Sn–Pb–Zn deposit, South China: a multi-method zircon study. Ore Geol Rev 102:220–239
Wu S, Mao J, Ireland TR, Zhao Z, Yao F, Yang Y, Sun W (2019) Comparative geochemical study of scheelite from the Shizhuyuan and Xianglushan tungsten skarn deposits, South China: implications for scheelite mineralization. Ore Geol Rev 109:448–464
Xiao X, Zhou T, White NC et al (2018) The formation and trace elements of garnet in the skarn zone from the Xinqiao Cu-S-Fe-Au deposit, Tongling ore district, Anhui Province, eastern China. Lithos 302–303:467–479
Xiong DX, Sun XM, Shi GY et al (2006) Trace elements, rare earth elements (REE) and Nd-Sr isotopic compositions in scheelites and their implications for the mineralization in Daping gold mine in Yunnan province, China. Acta Petrol Sin 22:733–741
Xu J, Ciobanu CL, Cook NJ, Slattery A (2019) Crystals from the Powellite-Scheelite series at the Nanoscale: a case study from the Zhibula Cu Skarn, Gangdese Belt, Tibet. Minerals 9:340
Xu X, Reilly SYO, Griffin WL et al (2007) The crust of Cathaysia: age, assembly and reworking of two terranes. Precambrian Res 158:51–78
Yardley BWD, Rochelle CA, Barnicoat AC, Lloyd GE (1991) Oscillatory zoning in metamorphic minerals: an indicator of infiltration metasomatism. Mineral Mag 55:357–365
Yuan L, Chi G, Wang M, Li Z, Xu D, Deng T, Geng J, Hu M, Zhang L (2019) Characteristics of REEs and trace elements in scheelite from the Zhuxi W deposit, South China: implications for the ore-forming conditions and processes. Ore Geol Rev 109:585–597
Zaw K, Singoyi B (2000) Formation of magnetite-scheelite skarn mineralization at Kara, northwestern Tasmania: evidence from mineral chemistry and stable isotopes. Econ Geol 95:1215–1230
Zhai D-G, Liu J-J, Zhang H-Y et al (2014) Origin of oscillatory zoned garnets from the Xieertala Fe–Zn skarn deposit, northern China: in situ LA–ICP-MS evidence. Lithos 190–191:279–291
Zhao P, Yuan S, Mao J, Yuan Y, Zhao H, Zhang D, Shuang Y (2018a) Constraints on the timing and genetic link of the large-scale accumulation of proximal W–Sn–Mo–Bi and distal Pb–Zn–Ag mineralization of the world-class Dongpo orefield, Nanling Range, South China. Ore Geol Rev 95:1140–1160
Zhao WW, Zhou M-F, Williams-Jones AE, Zhao Z (2018b) Constraints on the uptake of REE by scheelite in the Baoshan tungsten skarn deposit, South China. Chem Geol 477:123–136
Zhang H, Zheng J, Pan S et al (2017a) Compositions and processes of lithospheric mantle beneath the west Cathaysia block, Southeast China. Lithos 286–287:241–251
Zhang Y, Yang JH, Chen JY et al (2017b) Petrogenesis of Jurassic tungsten-bearing granites in the Nanling Range, South China: evidence from whole-rock geochemistry and zircon U–Pb and Hf–O isotopes. Lithos 278–281:166–180
Zhou J, Feng C, Li D (2017) Geochemistry of the garnets in the Baiganhu W–Sn orefield, NW China. Ore Geol Rev 82:70–92
Zhu XY, Wang JB, Wang YL et al (2012) Sulfur and lead isotope constraints on ore formation of the Huangshaping W-Mo-Bi-Pb-Zn polymetallic ore deposit, Hunan Province, South China. Acta Petrol Sin 28:3809–3822
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Georges Beaudoin (Editor-in-Chief), Frank Melcher (Associate Editor), and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions that significantly improved this study.
Funding
This work was co-financed by the National Key Research and Development Plan (Grant No. 2018YFC0603902) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41502067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: F. Melcher
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(XLSX 45 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, DP., Li, H., Algeo, T.J. et al. The prograde-to-retrograde evolution of the Huangshaping skarn deposit (Nanling Range, South China). Miner Deposita 56, 1087–1110 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01042-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01042-7