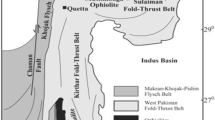
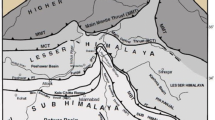
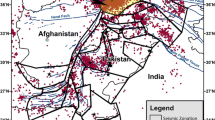
Abstract
The prediction of the earthquake has been a testing investigation field, where a prediction of the impending incidence of destructive calamity is made. In this research, eight seismic features are processed by utilizing seismological notions, such as seismic quiescence, the eminent geophysical specifics of Gutenberg–Richter’s inverse law, and dissemination of typical earthquake extents for earthquake prediction. A classification system based on support vector regressor (SVR) along with hybrid neural network (HNN) is formed to attain the predictions of earthquakes for the Hindukush region. The challenge is expressed as a binary classification undertaking, and for earthquakes of magnitude equal to or more than 5.5, the predictions are generated for 1 month. HNN is a step-by-step amalgamation of three diverse neural networks, and enhanced particle swarm optimization (EPSO) is used to extend weight optimization at an individual layer, thus enhancing the performance of HNN. In amalgamation with the SVR-HNN prediction system, the freshly processed seismic aspects are applied to the Hindukush region. For analyzing the results, another considered performance measure is accuracy. Comparative to earlier prediction investigations, the achieved numerical outcomes demonstrate enhanced prediction implementation for the considered region.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeli H, Panakkat A (2009) A probabilistic neural network for earthquake magnitude prediction. Neural Netw 22(7):1018–1024
Allen CR (1976) Responsibilities in earthquake prediction: to the seismological society of America, delivered in Edmonton, Alberta, may 12, 1976. Bull Seismol Soc Am 66(6):2069–2074
Amjady N, Keynia F (2008) Day-ahead price forecasting of electricity markets by mutual information technique and cascaded neuro-evolutionary algorithm. IEEE Trans Power Syst 24(1):306–318
Amjady N, Keynia F, Zareipour H (2011) Wind power prediction by a new forecast engine composed of modified hybrid neural network and enhanced particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 2(3):265–276
Asim KM, Awais M, Martínez–Álvarez F, Iqbal T (2017) Seismic activity prediction using computational intelligence techniques in northern Pakistan. Acta Geophys 65(5):919–930
Asim KM, Idris A, Iqbal T, Martínez-Álvarez F (2018) Earthquake prediction model using support vector regressor and hybrid neural networks. PLoS One 13(7):e0199004
Båth M (1965) Lateral inhomogeneities of the upper mantle. Tectonophysics 2(6):483–514
Billington S, Isacks BL, Barazangi M (1977) Spatial distribution and focal mechanisms of mantle earthquakes in the Hindu Kush–Pamir region: a contorted Benioff zone. Geology 5(11):699–704
Boore DM (2001) Comparisons of ground motions from the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake with empirical predictions largely based on data from California. Bull Seismol Soc Am 91(5):1212–1217
Chang C-C, Lin C-J (2011) LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 2(3):1–27
Chatelain J-L, Roecker SW, Hatzfeld D, Molnar P (1980) Microearthquake seismicity and fault plane solutions in the Hindu Kush region and their tectonic implications. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 85(B3):1365–1387
Cheng R, Jin Y, Olhofer M, Sendhoff B (2016) A reference vector guided evolutionary algorithm for many-objective optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 20(5):773–791
Cheng R, Li M, Tian Y, Zhang X, Yang S, Jin Y, Yao X (2017) A benchmark test suite for evolutionary many-objective optimization. Compl Intell Syst 3(1):67–81
Christensen K, Olami Z (1992) Variation of the Gutenberg-Richter b values and nontrivial temporal correlations in a spring-block model for earthquakes. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 97(B6):8729–8735
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support vector machine. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Cosma G, Brown D, Archer M, Khan M, Graham Pockley A (2017) A survey on computational intelligence approaches for predictive modeling in prostate cancer. Expert Syst Appl 70:1–19
Dahmen K, Ertaş D, Ben-Zion Y (1998) Gutenberg-Richter and characteristic earthquake behavior in simple mean-field models of heterogeneous faults. Phys Rev E 58(2):1494–1501
Ebel JE, Chambers DW, Kafka AL, Baglivo JA (2007) Non-Poissonian earthquake clustering and the hidden Markov model as bases for earthquake forecasting in California. Seismol Res Lett 78(1):57–65
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. MHS'95. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, Ieee
Farah A, Abbas G, de Jong KA, Lawrence RD (1984) Evolution of the lithosphere in Pakistan. Tectonophysics 105(1-4):207–227
Gutiérrez-Avilés D, Rubio-Escudero C (2015) MSL: a measure to evaluate three-dimensional patterns in gene expression data. Evolutionary Bioinformatics 11:EBO.S25822
Hainzl S, Zöller G, Kurths J, Zschau J (2000) Seismic quiescence as an indicator for large earthquakes in a system of self-organized criticality. Geophys Res Lett 27(5):597–600
Hamburger MW et al (1992) Structural and seismic evidence for intracontinental subduction in the Peter the First Range, central Asia. Geol Soc Am Bull 104(4):397–408
Idris A, Rizwan M, Khan A (2012) Churn prediction in telecom using Random Forest and PSO based data balancing in combination with various feature selection strategies. Comput Electr Eng 38(6):1808–1819
Ikram A, Qamar U (2015) Developing an expert system based on association rules and predicate logic for earthquake prediction. Knowl-Based Syst 75:87–103
Kagan YY, Jackson DD, Rong Y (2007) A testable five-year forecast of moderate and large earthquakes in southern California based on smoothed seismicity. Seismol Res Lett 78(1):94–98
Koulakov I, Sobolev SV (2006) A tomographic image of Indian lithosphere break-off beneath the Pamir–Hindukush region. Geophys J Int 164(2):425–440
Lantada N et al (2009) Vulnerability index and capacity spectrum based methods for urban seismic risk evaluation. A comparison. Nat Hazards 51(3):501
Larsen PE, Field D, Gilbert JA (2012) Predicting bacterial community assemblages using an artificial neural network approach. Nat Methods 9(6):621–625
Liu Y, et al (2004) Earthquake prediction by RBF neural network ensemble. International Symposium on Neural Networks, Springer
McGuire JJ, Boettcher MS, Jordan TH (2005) Foreshock sequences and short-term earthquake predictability on East Pacific Rise transform faults. Nature 434(7032):457–461
Mirrashid M (2014) Earthquake magnitude prediction by adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) based on fuzzy C-means algorithm. Nat Hazards 74(3):1577–1593
Morales-Esteban A, Martínez-Álvarez F, Reyes J (2013) Earthquake prediction in seismogenic areas of the Iberian Peninsula based on computational intelligence. Tectonophysics 593:121–134
Murtza I, Abdullah D, Khan A, Arif M, Mirza SM (2017) Cortex-inspired multilayer hierarchy based object detection system using PHOG descriptors and ensemble classification. Vis Comput 33(1):99–112
Nayak DR et al (2013) A survey on rainfall prediction using artificial neural network. Int J Comput Appl 72(16)
Negarestani A, Setayeshi S, Ghannadi-Maragheh M, Akashe B (2002) Layered neural networks based analysis of radon concentration and environmental parameters in earthquake prediction. J Environ Radioact 62(3):225–233
Panakkat A, Adeli H (2007) Neural network models for earthquake magnitude prediction using multiple seismicity indicators. Int J Neural Syst 17(01):13–33
Partal T (2016) Comparison of wavelet based hybrid models for daily evapotranspiration estimation using meteorological data. KSCE J Civ Eng 20(5):2050–2058
Pavlis GL, Das S (2000) The Pamir-Hindu Kush seismic zone as a strain marker for flow in the upper mantle. Tectonics 19(1):103–115
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1226–1238
Petersen MD, Cao T, Campbell KW, Frankel AD (2007) Time-independent and time-dependent seismic hazard assessment for the State of California: Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast Model 1.0. Seismol Res Lett 78(1):99–109
Rashed T, Weeks J (2003) Assessing vulnerability to earthquake hazards through spatial multicriteria analysis of urban areas. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 17(6):547–576
Reyes J, Morales-Esteban A, Martínez-Álvarez F (2013) Neural networks to predict earthquakes in Chile. Appl Soft Comput 13(2):1314–1328
Romero-Zaliz RC, Rubio-Escudero C, Cobb JP, Herrera F, Cordon O, Zwir I (2008) A multiobjective evolutionary conceptual clustering methodology for gene annotation within structural databases: a case of study on the gene ontology database. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12(6):679–701
Rundle JB (1989) Derivation of the complete Gutenberg-Richter magnitude-frequency relation using the principle of scale invariance. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 94(B9):12337–12342
Searle M, Hacker BR, Bilham R (2001) The Hindu Kush seismic zone as a paradigm for the creation of ultrahigh-pressure diamond-and coesite-bearing continental rocks. J Geol 109(2):143–153
Shen Z-K, Jackson DD, Kagan YY (2007) Implications of geodetic strain rate for future earthquakes, with a five-year forecast of M5 earthquakes in southern California. Seismol Res Lett 78(1):116–120
Tian Y, Wang H, Zhang X, Jin Y (2017) Effectiveness and efficiency of non-dominated sorting for evolutionary multi-and many-objective optimization. Compl Intell Syst 3(4):247–263
Tian Y et al (2017) An indicator-based multiobjective evolutionary algorithm with reference point adaptation for better versatility. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 22(4):609–622
Utsu T, Ogata Y (1995) The centenary of the Omori formula for a decay law of aftershock activity. J Phys Earth 43(1):1–33
Vickers NJ (2017) Animal communication: when i’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr Biol 27(14):R713–R715
Wiemer S, Wyss M (1994) Seismic quiescence before the Landers (M= 7.5) and Big Bear (M= 6.5) 1992 earthquakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84(3):900–916
Wiemer S, Wyss M (2000) Minimum magnitude of completeness in earthquake catalogs: Examples from Alaska, the western United States, and Japan. Bull Seismol Soc Am 90(4):859–869
Yariyan P, Avand M, Soltani F, Ghorbanzadeh O, Blaschke T (2020) Earthquake vulnerability mapping using different hybrid models. Symmetry 12(3):405
Zahur A, et al (2014) Novel ensemble predictor for gram-positive bacterial protein sequences. 2014 12th International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology, IEEE
Zamani A, Sorbi MR, Safavi AA (2013) Application of neural network and ANFIS model for earthquake occurrence in Iran. Earth Sci Inf 6(2):71–85
Zhang X et al (2016) A decision variable clustering-based evolutionary algorithm for large-scale many-objective optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 22(1):97–112
Zhao L, Thorpe CE (2000) Stereo-and neural network-based pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 1(3):148–154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslam, B., Zafar, A., Khalil, U. et al. Seismic activity prediction of the northern part of Pakistan from novel machine learning technique. J Seismol 25, 639–652 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-021-09982-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-021-09982-3