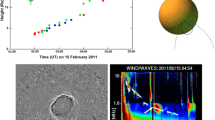
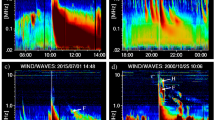
Abstract
Solar radio bursts are often early indicators of space weather events such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs). In this study, we determined the properties of a sample of 40 high-starting-frequency (≥ 150 MHz) type II radio bursts and the characteristics of the associated CMEs such as width, location and speed during 2010–2016. The high starting frequency implies shock formation closer to the solar surface, which has important ramifications for the analysis of particle acceleration near the Sun. We found the CME heliocentric distances at the onset time of metric type II bursts range from 1.16 to 1.90 solar radii (Rs). The study was also extended to 128 metric type II bursts to include lower-starting-frequency events for further analysis. The projected CME heights range from 1.15 to 2.85 Rs. The lower starting frequency correspond to shocks forming at larger heights. A weak correlation was found between the type-II starting frequency and CME heights, which is consistent with the density decline in the inner corona. The analysis confirmed a good correlation between the drift rate and the starting frequency of type II bursts (correlation coefficient ∼ 0.8). Taking into account the radial variation of CMEs speeds from the inner corona to the interplanetary medium, we observed the deviations from the universal drift-rate spectrum of type II bursts and confirmed the previous results relating type II bursts to CMEs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., Gopalswamy, N., MacDowall, R., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.I.: 2005, A study of the drift rate of type II radio bursts at different wavelengths. In: Solar Wind 11/SOHO 16. Connecting Sun and Heliosphere 592, 393. ADS.
Allen, C.W.: 1947, Interpretation of electron densities from corona brightness. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 107, 426. DOI. ADS.
Bougeret, J.-L., Kaiser, M.L., Kellogg, P.J., Manning, R., Goetz, K., Monson, S.J., Monge, N., Friel, L., Meetre, C.A., Perche, C., Sitruk, L., Hoang, S.: 1995, WAVES: the radio and plasma wave investigation on the wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 231. DOI. ADS.
Cho, K.-S., Gopalswamy, N., Kwon, R.-Y., Kim, R.-S., Yashiro, S.: 2013, A high-frequency type II solar radio burst associated with the 2011 February 13 Coronal Mass Ejection. Astrophys. J. 765, 148. DOI. ADS.
Cliver, E.W., Nitta, N.V., Thompson, B.J., Zhang, J.: 2004, Coronal shocks of November 1997 revisited: the CME type II timing problem. Solar Phys. 225, 105. DOI. ADS.
Ginzburg, V.L., Zheleznyakov, V.V.: 1958, On the possible mechanisms of sporadic solar radio emission (radiation in an isotropic plasma). Soviet Astron. 2, 653. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2000, Type II solar radio bursts. Radio astronomy at long wavelengths. In: Geophysical Monograph 119, AGU, Washington DC, 123.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006a, Coronal mass ejections and type II radio bursts. In: Gopalswamy, N., Mewaldt, R., Torsti, J. (eds.) Solar Eruptions and Energetic Particles, American Geophysical Union (Geophysical Monograph Series) 165, 207. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006b, Coronal mass ejections of Solar Cycle 23. J. Astrophys. Astron. 27, 243. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2011, Coronal mass ejections and solar radio emissions. In: Planetary, Solar and Heliospheric Radio Emissions (PRE VII), 325.
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001a, Near-Sun and near-Earth manifestations of solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25261. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001b, Characteristics of coronal mass ejections associated with long-wavelength type II radio bursts. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 29219. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Krucker, S., Stenborg, G., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2004, Intensity variation of large solar energetic particle events associated with coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 109, 12105. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., Yashiro, S., Nunes, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2005, Type II radio bursts and energetic solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12S07. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Thompson, W.T., Davila, J.M., Kaiser, M.L., Yashiro, S., Mäkelä, P., Michalek, G., Bougeret, J.-L., Howard, R.A.: 2009a, Relation between type II bursts and CMEs inferred from STEREO observations. Solar Phys. 259, 227. DOI. ADS
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Freeland, S., Howard, R.: 2009b, The SOHO/LASCO CME catalog. Earth Moon Planets 104, 295. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Nariaki, N., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P., Yashiro, S.: 2012, Coronal magnetic field measurement from EUV images made by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. Astrophys. J. 744, 72. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Uddin, W., Srivastava, A.K., Joshi, N.C., Chandra, R., Manoharan, P.K., Mahalakshmi, K., Dwivedi, V.C., Jain, R., Awasthi, A.K., Nitta, N.V., Aschwanden, M.J., Choudhary, D.P.: 2013, Height of shock formation in the solar corona inferred from observations of type II radio bursts and coronal mass ejections. Adv. Space Res. 51, 1981. DOI. ADS.
Leblanc, Y., Dulk, G.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 1998, Tracing the electron density from the corona to 1 au. Solar Phys. 183(165), 180. DOI. ADS.
Lemen, R.J., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., Boerner, P.F., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., Duncan, D.W., Edwards, C.G., Friedlaender, F.M., Heyman, G.F., Hurlburt, N.E., Katz, N.L., Kushner, G.D., Levay, M., Lindgren, R.W., Mathur, D.P., McFeaters, E.L., Mitchell, S., Rehse, R.A., Schrijver, C.J., Springer, L.A., Stern, R.A., Tarbell, T.D., Wuelser, J.-P., Jacob Wolfson, C., Yanari, C., Bookbinder, J.A., Cheimets, P.N., Caldwell, D., Deluca, E.E., Gates, R., Golub, L., Park, S., Podgorski, W.A., Bush, R.I., Scherrer, P.H., Gummin, M.A., Smith, P., Auker, G., Jerram, P., Pool, P., Soufli, R., Windt, D.L., Beardsley, S., Clapp, M., Lang, J., Waltham, N.: 2012, The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamic Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 17. DOI. ADS.
Lengyel-Frey, D., Stone, R.G.: 1989, Characteristics of interplanetary type II radio emission and the relationship to shock and plasma properties. J. Geophys. Res. 94(159), 167. DOI. ADS.
Mann, G., Classen, T., Aurass, H.: 1995, Characteristics of coronal shock waves and solar type II radio bursts. Astron. Astrophys. 295, 775. ADS.
Mann, G., Klassen, A.: 2005, Electron beams generated by shock waves in the solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 441, 319. DOI. ADS.
Mann, G., Klassen, A., Classen, H.F.T., Aurass, H., Scholz, D., MacDowall, R.J., Stone, R.G.: 1996, Catalogue of solar type II radio bursts observed from September 1990 to December 1993 and their statistical analysis. Astron. Astrophys. 119, 489. ADS.
Nelson, G.J., Melrose, D.B.: 1985, Coronal Loops, Magnetohydrodynamic Waves, Shock Wave Propagation, Type 2 Bursts, Electron Acceleration, H Alpha Line, Interplanetary Medium, Plasma Radiation, Solar Flares. Solar Radiophysics: Studies of Emission from the Sun at Metre Wavelengths, 333–359. ADS.
Newkirk, G. Jr.: 1967, Structure of the solar corona. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 5, 213. DOI. ADS.
Pohjolainen, S., Pomoell, J., Vainio, R.: 2008, CME liftoff with high-frequency fragmented type II burst emission. Astron. Astrophys. 490(357), 363. DOI. ADS.
Saito, K.: 1970, Ann. Tokyo Astron. Obs. Ser. 2 12, 53.
Schmidt, J.M., Cairns, I.H., Lobzin, V.V.: 2014, The solar type II radio bursts of 7 March 2012: detailed simulation analyses. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 6042. DOI. ADS.
Vršnak, B., Aurass, J., Magdalenic, J., Gopalswamy, N.: 2001, Band-splitting of coronal and interplanetary type II bursts. I. Basic properties. Astron. Astrophys. 377, 321. DOI. ADS.
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Michalek, G., St. Cyr, O.C., Plunkett, S.P., Rich, N.B., Howard, R.A.: 2004, A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07105. DOI. ADS.
Zlotnik, E.Y., Klassen, A., Aurass, H., Klein, K.-L., Mann, G.: 1998, Interpretation of harmonic structure in solar type II radio bursts. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 41, 39. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge NASA’s open data policy in using SDO, SOHO, STEREO, and Wind data. ACU acknowledges financial support from NASA-GSFC and SCOSTEP visiting scholarship program and administrative support from the Catholic University of America. ACU also acknowledges the partial financial support from the Swedish International Development cooperation Agency (SIDA) through the International Science Program (ISP) to University of Rwanda (UR-Swedish program) through the Rwanda Astrophysics, Space and Climate Science Research Group (RASCSRG). This work was primarily supported by NASA’s Living with a Star and GI programs. This work was initiated during the COSPAR Capacity Building workshop “Coronal and Interplanetary Shocks” held in Mekelle, Ethiopia, during May 21–June 1, 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umuhire, A.C., Gopalswamy, N., Uwamahoro, J. et al. Properties of High-Frequency Type II Radio Bursts and Their Relation to the Associated Coronal Mass Ejections. Sol Phys 296, 27 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01743-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01743-8