Abstract
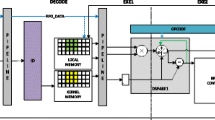
Data stream processors and accelerators, due to the outstanding energy performance, run on hardware more than any time in modern designs. The general model for these processors comprises massive shift register arrays with the largest share in energy dissipation and processing elements (PE). In this paper, a new gated flip-flop is designed and utilized in shift register arrays, to decrease power consumption. Distributed arithmetic (DA) is an efficient method for calculating the inner product and FIR filters. DA-based FIR filter consists of two parts of shift register and PE array. Due to the significant share of power in shift register, in this paper, DA-based FIR filter is employed to show the improvement of the proposed gated flip-flop. Investigation of statistical properties of input in image processing applications, utilization of implicit clock gating, and multi-vdd techniques are three main approaches we used in this study to increase energy efficiency. It is shown that the transition density (TD) in 50% of static images of target databases is lower than 0.5. A set of random data with different TDs is generated, fed to the gated flip-flop in 180 nm technology, and the results show a 62–2% improvement in dynamic power consumption. Further optimization of 29–21% is achieved when the multi-vdd is applied on the wrapper circuit of the gated flip-flop. Likewise, using the proposed flip-flop in the shift register unit of the DA-based FIR filter has improved the power consumption by 15–40% compared to the conventional flip-flop.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
E. Azimi, A. Behrad, M.B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi, A fully pipelined and parallel hardware architecture for real-time BRISK salient point extraction. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 16, 1859–1879 (2019)
G. Bernacchia and M. C. Papaefthymiou, Analytical macromodeling for high-level power estimation, in Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (IEEE Press, 1999), pp. 280–283
A. Bonanno, A. Bocca, A. Macii, E. Macii, and M. Poncino, Data-driven clock gating for digital filters, in International Workshop on Power and Timing Modeling, Optimization and Simulation (Springer, 2009), pp. 96–105
Y.-H. Chen, T.-J. Yang, J. Emer, V. Sze, Eyeriss v2: a flexible accelerator for emerging deep neural networks on mobile devices. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 9(2), 292–308 (2019)
Y.-H. Chen, T. Krishna, J.S. Emer, V. Sze, Eyeriss: an energy-efficient reconfigurable accelerator for deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 52(1), 127–138 (2016)
T.-L. Chou and K. Roy, Statistical estimation of sequential circuit activity, in Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE/ACM International Conference on COMPUTER-AIDED Design (IEEE Computer Society, 1995), pp. 34–37
Y.A. Durrani, T. Riesgo, Power estimation technique for DSP architectures. Digit. Signal Proc. 19(2), 213–219 (2009)
Y. Fan, C.-Y. Tsui, An efficient partial-sum network architecture for semi-parallel polar codes decoder implementation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(12), 3165–3179 (2014)
M. Fons, F. Fons, E. Cantó, M. López, FPGA-based personal authentication using fingerprints. J. Signal Process. Syst. 66(2), 153–189 (2012)
S.F. Ghamkhari, M.B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi, A new low-power architecture design for distributed arithmetic unit in FIR filter implementation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(4), 1245–1259 (2014)
R. Gonzalez, R. Woods, Digital Image Processing, 3rd edn. (Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, 2008)
S. Gupta, F.N. Najm, Power modeling for high-level power estimation. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 8(1), 18–29 (2000)
M. H. Hajkazemi, M. Takapoo, and M. B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi, PABEM: A new power-aware adaptive bus encoding method using Huffman algorithm, in 2011 International Symposium on Computer Networks and Distributed Systems (CNDS) (IEEE, 2011), pp. 23–28
M. Hamada, H. Hara, T. Fujita, A conditional clocking flip-flop for low power H. 264/MPEG-4 audio/visual codec LSI, in Proceedings of the IEEE 2005 Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (IEEE, 2005), pp. 527–530
N. Hassan, S. Gillani, E. Ahmed, I. Yaqoob, M. Imran, The role of edge computing in internet of things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 56(11), 110–115 (2018)
S. Joshi, D. Li, S. Memik, Multi-Vdd design for content addressable memories (CAM): a power-delay optimization analysis. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 8(3), 25 (2018)
J.M. Jung, J.-W. Chong, A low power fir filter design for image processing. VLSI Des. 12(3), 391–397 (2001)
H. Kung, B. McDanel, and S. Q. Zhang, Packing sparse convolutional neural networks for efficient systolic array implementations: Column combining under joint optimization, in Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems (ACM, 2019), pp. 821–834
T. Lang, E. Musoll, J. Cortadella, Individual flip-flops with gated clocks for low power datapaths. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 44(6), 507–516 (1997)
J. Li, A. Chang, and T. T. Kim, An 82% energy-saving change-sensing flip-flop in 40 nm CMOS for ultra-low power applications, in 2017 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC) (IEEE, 2017), pp. 197–200
D. Markovic, B. Nikolic, and R. W. Brodersen, Analysis and design of low-energy flip-flops, in ISLPED’01: Proceedings of the 2001 International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (IEEE Cat. No. 01TH8581) (IEEE, 2001), pp. 52–55
F.N. Najm, A survey of power estimation techniques in VLSI circuits. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2(4), 446–455 (1994)
G. Peng, L. Liu, S. Zhou, Y. Xue, S. Yin, S. Wei, Algorithm and architecture of a low-complexity and high-parallelism preprocessing-based K-best detector for large-scale MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66(7), 1860–1875 (2018)
S. Smets, T. Goedemé, A. Mittal, and M. Verhelst, 2.2 A 978GOPS/W Flexible streaming processor for real-time image processing applications in 22 nm FDSOI, in 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC) (IEEE, 2019), pp. 44–46
A.H. Sodhro, S. Pirbhulal, V.H.C. de Albuquerque, Artificial intelligence driven mechanism for edge computing based industrial applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 15(7), 4235–4243 (2019)
M.R. Stan, W.P. Burleson, Bus-invert coding for low-power I/O. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 3(1), 49–58 (1995)
A. Strollo, E. Napoli, D. De Caro, Low-power flip-flops with reliable clock gating. Microelectron. J. 32(1), 21–28 (2001)
C.-L. Su, C.-Y. Tsui, A.M. Despain, Saving power in the control path of embedded processors. IEEE Des. Test Comput. 11(4), 24–31 (1994)
Y. Wu, New scalable decoder architectures for Reed-Solomon codes. IEEE Trans. Commun. 63(8), 2741–2761 (2015)
X. Xu, Y. Ding, S.X. Hu, Scaling for edge inference of deep neural networks. Nat. Electron. 1(4), 216–222 (2018)
P. Zhao, H. Zhu, H. Li, T. Shibata, A directional-edge-based real-time object tracking system employing multiple candidate-location generation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 23(3), 503–517 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghamkhari, S.F., Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi, M.B. A New Low Power Schema for Stream Processors Front-End with Power-Aware DA-Based FIR Filters by Investigation of Image Transitions Sparsity. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40, 3456–3478 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01632-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01632-2