Abstract
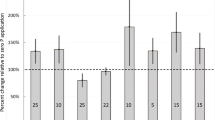
Two soil amendments, biochar and zeolites, were evaluated in their potential for increasing crop productivity and agro-system sustainability. The effect of biochar and zeolites, in combination with four nitrogen (N) rates [0 (N0), 50 (N50), 100 (N100), and 200 (N200) kg ha−1], on crop yield, N use efficiency, and soil properties was evaluated in a cropping system of irrigated forage maize (Zea mays L.) grown in summer and oats (Avena sativa L.) grown in winter as a catch crop. Biochar increased soil organic carbon (C), pH, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and extractable phosphorus (P), but strongly reduced N recovery in the set of the four cropping cycles. In biochar-amended plots, N50 had a negative apparent N recovery (− 21%), indicating that less N was recovered by the plants than in the N0 treatment without biochar. Biochar reduced maize dry matter (DM) yield by 15.6% in comparison to the untreated control, indicating N immobilization by biochar at low N rates (N0 and N50). Zeolites did not influence crop productivity or soil properties, except for the increase in extractable K, probably the result of its initial K content. N application to maize significantly increased the productivity of both crops, including that of the non-fertilized oats. Under the conditions of this experiment, biochar and zeolites did not prove to be useful soil amendments to increase crop DM yield in the short-term. The use of biochar increased soil organic C, which associated to a high N rate can enable the dual objective of maintaining productivity and the sustainability of the agro-system. The results stressed also the important role of oats as a cover crop to reduce the risk of nitrate leaching and denitrification during winter.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agegnehu G, Bass AM, Nelson PN, Bird MI (2016) Benefits of biochar, compost and biochar-compost for soil quality, maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions in a tropical agricultural soil. Sci Total Environ 543:295–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.054
Arif M, Ilyas M, Riaz M, Ali K, Shah K, Haq IU, Fahad S (2017) Biochar improves phosphorus use efficiency of organic-inorganic fertilizers, maize-wheat productivity and soil quality in a low fertility alkaline soil. Field Crop Res 214:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2017.08.018
Assimakopoulou A, Dimitroulia D, Kosmidis S, Doula MK (2020) Growth, yield and nutrient status of pepper plants grown on a soil substrate with olive mill waste sludge and natural zeolite addition. J Plant Nutr 43:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2019.1701030
Baird RB, Eaton AD, Rice EW (2017) Nitrate by ultraviolet spectrophotometric method. In: Baird RB, Eaton AD, Rice EW (eds) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American public health association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC
Balbino LR (1968) La méthode Egner-Riehm et la détermination du phosfore et du potassium «assimilável» des sols du Portugal. II Col. Medit Cont. Fert. Plantas Cultivadas, pp 55–65
Bernardi ACDC, Bezerra M, Monte DM, Renato P, Paiva P, Werneck CG (2010) Dry matter production and nutrient accumulation after successive crops of lettuce, tomato, rice, and andropogon grass in a substrate with zeolite. Rev Bras Cienc Solo 34:435–442. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832010000200017
Bian R, Joseph S, Shi W, Li L, Taherymoosavi S, Pan G (2019) Biochar DOM for plant promotion but not residual biochar for metal immobilization depended on pyrolysis temperature. Sci Total Environ 662:571–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.224
Binford GD, Blackmer AM, El-Hout NM (1990) Tissue test for excess nitrogen during corn production. Agron J 82:124–129. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1990.00021962008200010027x
Blackmer AM, Mallarino AP (1996) Corn stalk testing to evaluate nitrogen management. Iowa State University, University Extension, PM-1584, Iowa
Chen J, Kim H, Yoo G (2015) Effects of biochar addition on CO2 and N2O emissions following fertilizer application to a cultivated grassland soil. PLoS One 10(5):e0126841. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126841
Davies B, Coulter JA, Pagliari PH (2020) Timing and rate of nitrogen fertilization influence maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency. PLoS One 15(5):e0233674. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0233674
FAOSTAT (2020) Fertilizers by nutrient. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/RFN (accessed September 2020)
Ferreira IQ, Arrobas M, Moutinho-Pereira JM, Correia CM, Rodrigues MA (2020) The effect of nitrogen applications on the growth of young olive trees and nitrogen use efficiency. Turk J Agric For 44:278–289. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1905-26
Gao S, DeLuca TH, Cleveland CC (2019) Biochar additions alter phosphorus and nitrogen availability in agricultural ecosystems: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 654:463–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.124
Golia EE, Füleky G, Dimirkou A, Antoniadis V, Tsiropoulos NG, Gizas G (2017) Influence of zeolite and Posidonia oceanica (L.) in the reduction of heavy metal uptake by tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants of Central Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3522-2
González-Cencerrado A, Ranz JP, Jiménez MTL-F, Gajardo BR (2020) Assessing the environmental benefit of a new fertilizer based on activated biochar applied to cereal crops. Sci Total Environ 711:134668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134668
Guaya D, Mendoza A, Valderrama C, Farran A, Sauras-Yera T, Cortina JL (2020) Use of nutrient-enriched zeolite (NEZ) from urban wastewaters in amended soils: evaluation of plant availability of mineral elements. Sci Total Environ 727:138646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138646
Havlin JL, Tisdale SL, Nelson WL, Beaton JD (2014) Soil fertility and fertilizers, an introduction to nutrient management, 8th edn. Boston, USA, Pearson
Isla R, Salmerón M, Cavero J, Yagüe MR, Quílez D (2015) Utility of the end-of-season nitrate test for nitrogen sufficiency of irrigated maize under Mediterranean semi-arid conditions. Span J Agric Res 13(1):e09, 9 pages–e002. https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2015131-6806
Jeffery S, Verheijen FGA, van der Velde M, Bastos AC (2011) A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric Ecosyst Environ 144:175–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.08.015
Jin Z, Chen C, Chen X, Jiang F, Hopkins I, Zhang X, Han Z, Billy G, Benavides J (2019) Soil acidity, available phosphorus content, and optimal biochar and nitrogen fertilizer application rates: a five-year field trial in upland red soil, China. Field Crop Res 232:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.12.013
Jones JB Jr (2001) Laboratory guide for conducting soil tests and plant analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA
Kavitha B, Reddy PVL, Kim B, Lee SS, Pandey SK, Kim K-H (2018) Benefits and limitations of biochar amendment in agricultural soils: a review. J Environ Manag 227:146e154–146e154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.082
Li S, Wang S, Shangguan Z (2019) Combined biochar and nitrogen fertilization at appropriate rates could balance the leaching and availability of soil nitrogen. Agric Ecosyst Environ 276:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2019.02.013
Litaor MI, Katz L, Shenker M (2017) The influence of compost and zeolite co-addition on the nutrients status and plant growth in intensively cultivated Mediterranean soils. Soil Use Manag 33:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12324
Little TM, Hills FJ (1978) Agricultural experimentation: design and analysis. New York, USA, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
Meier U (2001) Growth stages of mono-and dicotyledonous plants. BBCH Monographs. Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry. BBCH Publ, Germany
Noori M, Ahmadi A, Zendehdel M (2007) Comparative study between using natural and synthetic zeolites for the improvement of soil salinity and crop yield. Toxicol Environ Chem 89:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772240601035771
Notaris C, Rasmussen J, Sorensen P, Olesen JE (2018) Nitrogen leaching: a crop rotation perspective on the effect of N surplus, field management and use of catch crops. Agric Ecosyst Environ 255:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2017.12.009
Palanivell P, Ahmed HO, Majid NM (2016) Minimizing ammonia volatilization from urea, improving lowland rice (cv. MR219) seed germination, plant growth variables, nutrient uptake, and nutrient recovery using clinoptilolite zeolite. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:708–724. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2015.1077229
Palansooriya KN, Ok YS, Awad YM, Lee SS, Sung J-K, Koutsospyros A, Moon DH (2019) Impacts of biochar application on upland agriculture: a review. J Environ Manag 234:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.085
Pickering HW, Menzies NW, Hunter MN (2002) Zeolite/rock phosphate—a novel slow release phosphorus fertiliser for potted plant production. Sci Hortic 94:333–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(02)00006-7
Rajkovich S, Enders A, Hanley K, Hyland C, Zimmerman AR, Lehmann J (2012) Corn growth and nitrogen nutrition after additions of biochars with varying properties to a temperate soil. Biol Fertil Soils 48:271–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0624-7
Rodrigues MA, Coutinho J, Martins F (2002) Efficacy and limitations of triticale as nitrogen catch crop in a Mediterranean environment. Eur J Agron 17:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(02)00003-5
Rodrigues MA, Coutinho J, Martins J, Arrobas M (2005) Quantitative sidedress nitrogen recommendations for potatoes based upon crop nutritional indices. Eur J Agron 23:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2004.10.001
Rodrigues MA, Pereira A, Cabanas JE, Dias L, Pires J, Arrobas M (2006) Crops use-efficiency of nitrogen from manures permitted in organic farming. Eur J Agron 25:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2006.07.002
Rodrigues MA, Garmus T, Arrobas M, Gonçalves A, Silva E, Rocha L, Pinto L, Brito C, Martins S, Vargas T, Correia C (2019) Combined biochar and organic waste have little effect on chemical soil properties and plant growth. Span J Soil Sci 9:199–211. https://doi.org/10.3232/SJSS.2019.V9.N3.04
Sadeghpour A, Ketterings QM, Godwin GS, Czymmek KJ (2017) Under- or over-application of nitrogen impact corn yield, quality, soil, and environment. Agron J 109:343–353. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2016.06.0355
Santasnachok C, Kurniawan W, Hinode H (2015) The use of synthesized zeolites from power plant rice husk ash obtained from Thailand as adsorbent for cadmium contamination removal from zinc mining. J Environ Chem Eng 3:2115–2126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.07.016
Shaaban M, Zwieten LV, Bashir S, Younas A, Núñez-Delgado A, Chhajro MA, Kubar KA, Ali U, Rana MS, Mehmood MA, Hu R (2018) A concise review of biochar application to agricultural soils to improve soil conditions and fight pollution. J Environ Manag 228:429–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.09.006
Singh BP, Hatton BJ, Singh B, Cowie AL, Kathuria A (2010) Influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emissions and nitrogen leaching from two contrasting soils. J Environ Qual 39:1224–1235. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2009.0138
Spokas KA, Novak JM, Venterea RT (2012) Biochar’s role as an alternative N-fertilizer: Ammonia capture. Plant Soil 350:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0930-8
Sun H, Lu H, Chu L, Shao H, Shi W (2017) Biochar applied with appropriate rates can reduce N leaching, keep N retention and not increase NH3 volatilization in a coastal saline soil. Sci Total Environ 575:820–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.137
Sun Y, Zhang N, Yan J, Zhang S (2020) Effects of soft rock and biochar applications on millet (Setaria italica L.) crop performance in sandy soil. Agronomy 10(5):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050669
Temminghoff EEJM, Houba VG (2004) Plant analysis procedures. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Aa Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Valkama E, Lemola R, Kankanem H, Turtola E (2015) Meta-analysis of the effects of undersown catch crops on nitrogen leaching loss and grain yields in the Nordic countries. Agric Ecosyst Environ 203:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2015.01.023
Van Reeuwijk LP (2002) Procedures for soil analysis. Technical paper 9. ISRIC FAO, Wageningen, the Netherlands
Villarreal-Núñez JE, Barahona-Amores LA, Castillo-Ortiz AO (2015) Efecto de zeolita sobre la eficiencia de fertilizantes nitrogenados en el cultivo de arroz. Agron Mesoam 26:315–321. https://doi.org/10.15517/am.v26i2.1932
Wei W, Yang H, Fan M, Chen H, Dayong Guo D, Jian Cao J, Kuzyakov Y (2020) Biochar effects on crop yields and nitrogen loss depending on fertilization. Sci Total Environ 702:134423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134423
Werner W (2007) Environmental aspects of fertilizer application. In ‘Ullmann’s agrochemicals, fertilizers, 3 (chap. 9)’. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, Weinheim, Germany, pp 99–111
WRB (2015) World reference base for soil resources 2014, Update 2015. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. World Soil Resources Reports No. 106. FAO, Rome
Yang Z-p, Wang Y-l, Guo C-x, Guo J-l, X-f S, Yost R, X-z Z, Zhang Q (2017) Application of the end-of-season stalk nitrate test for a high-yield maize production system in northwestern China. J Plant Nutr 40:2373–2381. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2017.1346667
Yu H, Zou W, Chen J, Chen H, Yu Z, Huang J, Tang H, Wei X, Gao B (2019) Biochar amendment improves crop production in problem soils: a review. J Environ Manag 232:8–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.117
Zhu Q, Peng X, Huang T (2015) Contrasted effects of biochar on maize growth and N use efficiency depending on soil conditions. Int Agrophys 29:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1515/intag-2015-0023
Zornoza R, Moreno-Barriga F, Acosta JA, Muñoz MA, Faz A (2016) Stability, nutrient availability and hydrophobicity of biochars derived from manure, crop residues, and municipal solid waste for their use as soil amendments. Chemosphere 144:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.046
Funding
The authors are grateful to the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT, Portugal) and European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) under Programme PT2020 for financial support to CIMO (UID/AGR/00690/2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, M.Â., Torres, L.d.D., Damo, L. et al. Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Crop Yield in Four Successive Crops Following Application of Biochar and Zeolites. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21, 1053–1065 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00421-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00421-3