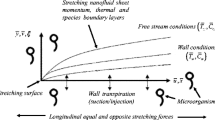
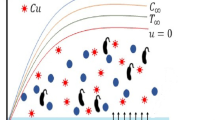
Abstract
This study investigates the mixed convection heat transfer characteristics of micropolar nanofluid containing motile microorganisms as it is passing over a stretching sheet. The governing equations of the fluid flow and boundary conditions are solved via similarity analysis using the fourth-order Runge–Kutta method. To verify the accuracy and validity of the method, the results are compared with those of several previous studies. The results are presented in terms of distribution of the velocity, particle micro-rotation, temperature, nanoparticle concentration, and density of motile microorganisms over the stretching sheet. The skin friction, coupled stress, mass transfer rate, and the rate of microorganism transfer away from the sheet are also examined. It can be concluded that the Nusselt number, coupled stress, friction coefficient, and Sherwood number are independent of the bioconvection Lewis number Lb. On the other hand, the rate of motile microorganism transfer away from the sheet to the fluid increases with Lb.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Eringen, A.C., Simple Microfluids, Int. J. Engin. Sci., 1964, vol. 2, pp. 205–217.
Eringen, A.C., Theory of Thermomicrofluids, J. Math. An. Appl., 1972, vol. 38, pp. 480–496.
Eringen, A.C., Theory of Micropolar Fluids, J. Math. Mech., 1966, pp. 1–18.
Kelson, N.A. and Farrell, T.W., Micropolar Flow over a Porous Stretching Sheet with Strong Suction or Injection, Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transfer, 2001, vol. 28, pp. 479–488.
Lok, Y.Y., Pop, I., and Ingham, D.B., Steady Two-Dimensional Periodic Motion of a Micropolar Fluid near an Infinite Array of Moving Walls, J. Appl. Math. Mech./Z. Angewandte Math. Mech.: Appl. Math. Mech., 2009, vol. 89, pp. 570–586.
Izadi, M., Mehryan, S., and Sheremet, M.A., Natural Convection of CuO–Water Micropolar Nanofluids inside a Porous Enclosure Using Local Thermal Non-Equilibrium Condition, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Engin., 201, vol. 888, pp. 89–103.
Bhargava, R., Kumar, L., and Takhar, H.S., Finite Element Solution of Mixed Convection Micropolar Flow Driven by a Porous Stretching Sheet, Int. J. Engin. Sci., 2003, vol. 41, pp. 2161–2178.
Das, K., Slip Effects on MHD Mixed Convection Stagnation Point Flow of a Micropolar Fluid Towards a Shrinking Vertical Sheet, Comput. Math. Appl., 2012, vol. 63, pp. 255–267.
Gibanov, N.S., Sheremet, M.A., and Pop, I., Free Convection in a Trapezoidal Cavity Filled with a Micropolar Fluid, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2016, vol. 99, pp. 831–838.
Hoyt, J.W. and Fabula, A.G., The Effect of Additives on Fluid Friction, Procs. Fifth Symp. on Naval Hydrodynamics, Bergen, Norway, 1964, p. 947.
Mehryan, S.A., Izadi, M., and Sheremet, M.A., Analysis of Conjugate Natural Convection within a Porous Square Enclosure Occupied with Micropolar Nanofluid Using Local Thermal Non-Equilibrium Model, J. Molec. Liq., 2018, vol. 250, pp. 353–368.
Power, H., Micropolar Fluid Model for the Brain Fluid Dynamics, Int. Conf. Bio-Fluid Mechanics, U.K., 1998.
Sheikholeslami, M., Hatami, M., and Ganji, D.D., Micropolar Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Permeable Channel Using Analytical Method, J. Molec. Liq., 2014, vol. 194, pp. 30–36.
Mosayebidorcheh, S., Analytical Investigation of the Micropolar Flow through a Porous Channel with Changing Walls, J. Molec. Liq., 2014, vol. 196, pp. 113–119.
Izadi, M., Mehryan, S., and Sheremet, M.A., Natural Convection of CuO–Water Micropolar Nanofluids inside a Porous Enclosure Using Local Thermal Non-Equilibrium Condition, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Engin., 2018, vol. 88, pp. 89–103.
Turkyilmazoglu, M., Flow of a Micropolar Fluid due to a Porous Stretching Sheet and Heat Transfer, Int. J. Non-Lin. Mech., 2016, vol. 83, pp. 59–64.
Rosali, H., Ishak, A., and Pop, I., Micropolar Fluid Flow towards a Stretching/Shrinking Sheet in a Porous Medium with Suction, Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transfer, 2012, vol. 39, pp. 826–829.
Tripathy, R.S., Dash, G.C., Mishra, S.R., and Hoque, M.M., Numerical Analysis of Hydromagnetic Micropolar Fluid along a Stretching Sheet Embedded in Porous Medium with Non-Uniform Heat Source and Chemical Reaction, Engin. Sci. Technol., Int. J., 2016, vol. 19, pp. 1573–1581.
Chol, S.U. and Eastman, J.A., Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles, ASME-Publ.-Fed., 1995, vol. 231, pp. 99–106.
Maxwell, J.C., A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, Clarendon, 1881.
Buongiorno, J., Convective Transport in Nanofluids, J. Heat Transfer, 2006, vol. 128, pp. 240–250.
Ghalambaz, M., Behseresht, A., Behseresht, J., and Chamkha, A., Effects of Nanoparticles Diameter and Concentration on Natural Convection of the Al\(_2\)O\(_3\)–Water Nanofluids Considering Variable Thermal Conductivity around a Vertical Cone in Porous Media, Adv. Powder Technol., 2015, vol. 26, pp. 224–235.
Ghalambaz, M., Sabour, M., and Pop, I., Free Convection in a Square Cavity Filled by a Porous Medium Saturated by a Nanofluid: Viscous Dissipation and Radiation Effects, Engin. Sci. Technol., Int. J., 2016, vol. 19, pp. 1244–1253.
Ghalambaz, M., Sheremet, M.A., and Pop, I., Free Convection in a Parallelogrammic Porous Cavity Filled with a Nanofluid Using Tiwari and Das’ Nanofluid Model, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 5, p. e0126486.
Izadi, M., Behzadmehr, A., and Jalali-Vahida, D., Numerical Study of Developing Laminar Forced Convection of a Nanofluid in an Annulus, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2009, vol. 48, pp. 2119–2129.
Izadi, M., Behzadmehr, A., and Shahmardan, M.M., Effects of Inclination Angle on Laminar Mixed Convection of a Nanofluid Flowing through an Annulus, Chem. Engin. Comm., 2015, vol. 202, pp. 1693–1702.
Izadi, M., Behzadmehr, A., and Shahmardan, M.M., Effects of Inclination Angle on Mixed Convection Heat Transfer of a Nanofluid in a Square Cavity, Int. J. Comput. Meth. Engin. Sci. Mech., 2015, vol. 16, pp. 11–21.
Izadi, M., Hossainpour, S., and Jalali, V.D., Effects of Nanolayer Structure and Brownian Motion of Particles in Thermal Conductivity Enhancement of Nanofluids, Int. J. Mech. Industr. Aerospace Engin., 2009, vol. 3, p. 201.
Izadi, M., Shahmardan, M.M., and Am Rashidi, Study on Thermal and Hydrodynamic Indexes of a Nanofluid Flow in a Micro Heat Sink, Transport Phenom. Nano Micro Scales, 2013, vol. 1, pp. 53–63.
Izadi, M., Shahmardan, M.M., and Behzadmehr, A., Richardson Number Ratio Effect on Laminar Mixed Convection of a Nanofluid Flow in an Annulus, Int. J. Comput. Meth. Engin. Sci. Mech., 2013, vol. 14, pp. 304–316.
Izadi, M., Shahmardan, M.M., Behzadmehr, A., Am Rashidi, and Amrollahi, A., Modeling of Effective Thermal Conductivity and Viscosity of Carbon Structured Nanofluid, Transport Phenom. Nano Micro Scales, 2015, vol. 3, pp. 1–13.
Izadi, M., Shahmardan, M.M., Maghrebi, M.J., and Behzadmehr, A., Numerical Study of Developed Laminar Mixed Convection of Al\(_2\)O\(_3\)/Water Nanofluid in an Annulus, Chem. Engin. Comm., 2013, vol. 200, pp. 878–894.
Izadi, M., Shahmardan, M.M., Norouzi, M., Am Rashidi, and Behzadmehr, A., Cooling Performance of a Nanofluid Flow in a Heat Sink Microchannel with Axial Conduction Effect, Appl. Phys. A, 2014, vol. 117, pp. 1821–1833.
Izadi, M., Behzadmehr, A., and Shahmardan, M.M., Effects of Discrete Source-Sink Arrangements on Mixed Convection in a Square Cavity Filled by Nanofluid, Korean J. Chem. Engin., 2014, vol. 31, pp. 12–19.
Izadi, M., Hoghoughi, G., Mohebbi, R., and Sheremet, M., Nanoparticle Migration and Natural Convection Heat Transfer of Cu-Water Nanofluid inside a Porous Undulant-Wall Enclosure Using LTNE and Two-Phase Model, J. Molec. Liq., 2018, vol. 261, pp. 357–372.
Kahveci, K., Buoyancy Driven Heat Transfer of Nanofluids in a Tilted Enclosure, J. Heat Transfer, 2010, vol. 132, p. 62501.
Kandelousi, M.S., KKL Correlation for Simulation of Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Permeable Channel, Phys. Lett. A, 2014, vol. 378, pp. 3331–3339.
Izadi, M., Mohebbi, R., Karimi, D., and Sheremet, M.A., Numerical Simulation of Natural Convection Heat Transfer inside a\(^{\perp}\) Shaped Cavity Filled by a MWCNT-Fe\(_3\)O\(_4\)/Water Hybrid Nanofluids using LBM, Chem. Engin. Proc.-Process Intensif., 2018, vol. 125, pp. 56–66.
Hoghoughi, G., Izadi, M., Oztop, H.F., and Abu-Hamdeh, N., Effect of Geometrical Parameters on Natural Convection in a Porous Undulant-Wall Enclosure Saturated by a Nanofluid Using Buongiorno’s Model, J. Molec. Liq., 2018, vol. 255, pp. 148–159.
Izadi, M., Mohebbi, R., Delouei, A.A., and Sajjadi, H., Natural Convection of a Magnetizable Hybrid Nanofluid Inside a Porous Enclosure Subjected to Two Variable Magnetic Fields, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2019, vol. 151, pp. 154–169.
Mohebbi, R., Izadi, M., and Chamkha, A.J., Heat Source Location and Natural Convection in a C-Shaped Enclosure Saturated by a Nanofluid, Phys. Fluids, 2017, vol. 29, p. 122009.
Bhattacharyya, K. and Layek, G.C., Magnetohydrodynamic Boundary Layer Flow of Nanofluid over an Exponentially Stretching Permeable Sheet, Phys. Res. Int., 2014, no. 1, p. 592536; DOI: 10.1155/2014/592536.
Nield, D.A. and Bejan, A., Convection in Porous Media, Springer, 2006.
Kuznetsov, A.V. and Avramenko, A.A., Effect of Small Particles on the Stability of Bioconvection in a Suspension of Gyrotactic Microorganisms in a Layer of Finite Depth, Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transfer, 2004, vol. 31, pp. 1–10.
Aziz, A., Khan, W.A., and Pop, I., Free Convection Boundary Layer Flow past a Horizontal Flat Plate Embedded in Porous Medium Filled by Nanofluid Containing Gyrotactic Microorganisms, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2012, vol. 56, pp. 48–57.
Khan, W.A. and Makinde, O.D., MHD Nanofluid Bioconvection due to Gyrotactic Microorganisms over a Convectively Heat Stretching Sheet, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2014, vol. 81, pp. 118–124.
Mahdy, A., Natural Convection Boundary Layer Fow due to Gyrotactic Microorganisms about a Vertical Cone in Porous Media Saturated by a Nanofluid, J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Engin., 2016, vol. 38, pp. 67–76.
Sharma, A. and Shandil, R.G., Effect of Magnetic Field Dependent Viscosity on Ferroconvection in the Presence of Dust Particles, J. Appl. Math. Comput., 2008, vol. 27, p. 7.
Wang, L., Wang, Y., Yan, X., Wang, X., and Feng, B., Investigation on Viscosity of Fe\(_3\)O\(_4\) Nanofluid under Magnetic Field, Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transfer, 2016, vol. 72, pp. 23–28.
Bharti, P.K., Sharma, D., and Sharma, R.C., The Effect of a Magnetic Field Dependent Viscosity on the Thermal Convection in a Ferromagnetic Fluid in a Porous Medium, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A, 2004, vol. 59, pp. 397–406.
Gourdin, A. and Boumahrat, M., Applied Numerical Methods, Wiley, 1996.
Mehryan, S.A., Kashkooli, F.M., Soltani, M., and Raahemifar, K., Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Analysis of a Nanofluid Containing Motile Gyrotactic Micro-Organisms Passing a Nonlinear Stretching Vertical Sheet in the Presence of a Non-Uniform Magnetic Field; Numerical Approach, PLoS One, 2016, vol. 11, no. 6, p. e0157598; DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157598.
Hayat, T., Abbas, Z., and Javed, T., Mixed Convection Flow of a Micropolar Fluid over a Non-Linearly Stretching Sheet, Phys. Lett. A, 2008, vol. 372, pp. 637–647.
Salleh, M.Z., Nazar, R., and Pop, I., Boundary Layer Flow and Heat Transfer over a Stretching Sheet with Newtonian Heating, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Engin., 2010, vol. 41, pp. 651–655.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Izadi, M., Shahivand, I., Mehryan, S.A. et al. Magneto-Hydrodynamic Flow of Micropolar Nanofluid Containing Motile Microorganisms Passing over a Vertical Stretching Sheet with Magnetic Field Dependent Viscosity. J. Engin. Thermophys. 29, 632–656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232820040116
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232820040116