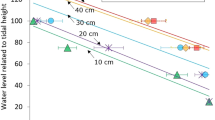
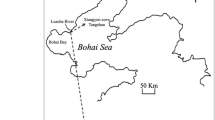
Abstract
Oyster reef habitats in estuarine areas are an important marine ecosystem globally. Due to the destruction of oyster reef habitats within the Luanhe River estuarine area, Bohai Sea, China, a local fisheries company created 2 km2 of artificial oyster reef habitats by deploying artificial reef blocks that provided a settling surface for a natural oyster population and conducted sea cucumber aquaculture. The aims of this study are to help fisheries managers to understand whether the ecosystem function of created oyster reef habitat is consistent throughout the seasons and to assess if the current fishing production policy which varies with seasons is reasonable. We presented steady-state trophic models in different seasons of a newly created artificial coastal oyster reef within the Luanhe River estuary to address the above issues. We concluded that seasonality is an important factor that needs to be carefully considered in the fisheries management of oyster reef ecosystems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlstrom EH, Thrailkill JR (1963) Plankton volume loss with time of preservation. Calif Coop Ocean Fish Invest Rep 9:57–73
Allen RK (1971) Relation between production and biomass. J Fish Res Bd Canada 28(10):1573–1581
Beck MW, Brumbaugh DR, Airoldi L, Carranza A, Coen LD, Crawford C, Defeo O, Edgar GJ, Hancock B, Kay M, Lenihan HS, Luckenbach MW, Toropova CL, Zhang G (2009) Shellfish reefs at risk: a global analysis of problems and solutions. The Nature Conservancy, Arlington
Beck MW, Brumbaugh RD, Airoldi L, Carranza A, Coen LD, Crawford C, Defeo O, Edgar GJ, Hancock B, Kay MC, Lenihan HS, Luckenbach MW, Toropova CL, Zhang G, Guo X (2011) Oyster reefs at risk and recommendations for conservation, restoration, and management. Bioscience 61(2):107–116
Castilla JC, Gelcich S, Defeo O (2007) Successes, lessons, and projections from experience in marine benthic invertebrate artisanal fisheries in Chile. Pages 25–42 in McClanahan TR, Castilla JC, eds. Fisheries Management: Progress towards Sustainability. Blackwell
Cheng BP, Wang BL, Gao XX (1982) Full exploitation of garfish resource through drift net. Marine Fish 5:218–219 (In Chinese)
Christensen V (1995) Ecosystem maturity - towards quantification. Ecol Model 77(1):3–32
Christensen V, Pauly D (1992) Ecopath-II–a software for balancing steady-state ecosystem models and calculating network characteristics. Ecol Model 61(3-4):169–185
Christensen V, Walters CJ (2004) Ecopath with Ecosim: methods, capabilities, capabilities and limitations. Ecol Model 172:109–139
Christensen V, Walters CJ and Pauly D (2005) Ecopath with Ecosim: a user’s guide., 154 p. Vancouver: University of British Columbia
Coen LD, Brumbaugh RD, Bushek D, Grizzle R, Luckenbach MW, Posey MH, Powers SP, Tolley SG (2007) Ecosystem services related to oyster restoration. Marine Ecol Prog 341:303–307
Duan LJ, Li SY, Liu Y, Jiang T, Failler P (2009) A trophic model of the Pearl River Delta coastal ecosystem. Ocean Coast Manag 52(7):359–367
Finn JT (1976) Measures of ecosystem structure and function derived from analysis of flows. J Theor Biol 56:363–380
Fulford RS, Breitburg DL, Luckenbach M (2010) Evaluating ecosystem response to oyster restoration and nutrient load reduction with a multispecies bioenergetics model. Ecol Appl 20(4):915–934
Goldman RL, Tallis H (2009) A critical analysis of ecosystem services as a tool in conservation projects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1162:63–78
Heymans JJ, Coll M, Link JS, Mackinson S, Steenbeek J, Walters C, Christensen V (2016) Best practice in Ecopath with Ecosim food-web models for ecosystem-based management. Ecol Model 331:173–184
Hu GS, Zhang ZW (1983) The preliminary research of growth characteristics of the autumn shrimp in the coastal sea areas of Hebei province. Hebei Fish 3:1–7 (In Chinese)
Kremer JN, Nixon SW (1978) A coastal marine ecosystem: simulation and analysis. Springer, New York, p 217
Li YG, Wang ZH, Zhang SY (2007) A preliminary approach on the ecosystem model of the artificial reef in Shengsi. Marine Fish 29(3):227–234 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Libralato S, Christensen V, Pauly D (2006) A method for identifying keystone species in food web models. Ecol Model 195(3):153–171
Link JS (2010) Adding rigor to ecological network models by evaluating a set of pre-balance diagnostics: a plea for PREBAL. Ecol Model 221:1580–1591
Ma QY, Han DY, Liu H, Xue Y, Ji YP, Ren YP (2015) Construction of a continuous trophic spectrum for the food web in Jiaozhou Bay using stable isotope analyses. Acta Ecol Sin 35(21):7207–7218 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Mu FH, Zhang ZN (2001) Abundance and biomass of the benthic meiofauna in the Bohai Sea. J Ocean Univ China 31(6):897–905 (In Chinese with English abstract)
National Research Council (2010) Ecosystem Concepts for Sustainable Bivalve Mariculture. National Academy Press
Nawratil M (2009) Seasonal change of trophic guilds of the fish fauna of the Sylt-Romo Bight (Wadden Sea, Germany). Radiobiologiia 20(1):127–130
Odum EP (1969) The strategy of ecosystem development. Science 104:262–270
Odum HT (1988) Self-organization, transformity and information. Science 242:1132–1139
Ortiz M, Wolff M (2002) Trophic models of four benthic communities in Tongoy Bay (Chile): comparative analysis and preliminary assessment of management strategies. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 268(2):205–235
Parsons TR, Maita Y, Lalli CM (1984) A manual of chemical ad biological methods for seawater analysis. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Pauly D (1980) On the interrelationships between natural mortality, growth parameters, and mean environmental temperature in 175 fish stocks. ICES J Mar Sci 39(2):175–192
Pauly D, Christensen V, Walters C (2000) Ecopath, Ecosim, and Ecospace as tools for evaluating ecosystem impact of fisheries. ICES J Mar Sci 57(3):697–706
Prins TC, Smaal AC, Dame RF (1997) A review of the feedbacks between bivalve grazing and ecosystem processes. Aquat Ecol 31:349–359
Quan WM, Shen XQ, Luo MB, Chen YQ (2006) Ecological function and restoration measures of oyster reef in Estuaries. Chin J Ecol 25(10):1234–1239 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Reubens JT, Braeckman U, Vanaverbeke J, Colen CV, Degraer S, Vincx M (2013) Aggregation at windmill artificial reefs: CPUE of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) and pouting (Trisopterus luscus) at different habitats in the Belgian part of the North Sea. Fish Res 139(1):28–34
Reum JCP, Essington TE (2008) Seasonal variation in guild structure of the Puget Sound bottom fish community. Estuar Coasts 31(4):790–801
Russell BC, Talbot FH, Domm S (1974) Patterns of colonization of artificial reefs by coral reef fishes. Proc. 2nd Intern. Coral Reef Symp 1:207–215
Shen XQ, Quan WM, Yuan Q (2011) Restoration and assessment of carbon sink potential for a intertidal oyster reef in the Yangtze river estuary, China. J Agro-Environ Sci 30(10):2119–2123 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Talbot FY, Russel BC, Anderson GRV (1978) Coral reef fish communities: unstable, high-diversity systems? Ecol Monogr 48:425–440
Tong L, Tanga Q (1999) Preliminary mass-balance Ecopath model in the Bohai Sea. Mar Fish Res 1-12
Vegacendejas ME, Arregunsanchez F (2001) Energy fluxes in a mangrove ecosystem from a coastal Lagoon in Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Ecol Modell 137(2):119–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00421-X
Wackernagel M, and Rees W (1996) Our ecological footprint: reducing the human impact on the Earth. In: New Society Publishers. Gabriela Island. 160 p
Walker B, Henderson K, Spieler B, Richard E (2002) Fish assemblages associated with artificial reefs of concrete aggregates or quarry stone offshore Miami beach, Florida, USA. Aquat Living Resour 15(2):95–105
Wang H, Fan CF, Li JF, Li FL, Yan YZ, Wang YS (2006) Holocene oyster reefs on the northwest coast of the Bohai Bay, China. Geol Bull China 25(3):315–331 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Watson W, Leis JJ (1974) Ichthyoplankton in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. A one-year study of fish eggs and larvae. Univ Hawaii Sea Grant Tech Rep 75(01):1–178
Wilberg MJ, Livings ME, Barkman JS, Morris BT, Robinson JM (2011) Overfishing, habitat loss, and potential extirpation of oysters in upper Chesapeake Bay. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 436:131–144
Wu YG (1980) Current status and future development suggestions of marine fisheries resources in Hebei Province. Hebei Fish 3:1–12 (In Chinese)
Wu ZX, Zhang XM, Zhang L, Tong F, Liu HJ (2012) Structure and function of Lidao artificial reef ecosystem in Rongcheng of Shandong Procince, East China: an evaluation based on Ecopath model. Chin J Appl Ecol 23(10):2878–2886 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Xu BC, Zhou EM, Song WX (1986) Distribution characteristics of surface temperature, salinity in the mouth of Luanhe River. J Oceanogr Huanghai Bohai Seas 3:126–133 (In Chinese)
Xu M, Qi L, Zhang LB, Zhang T, Yang HS, Zhang YL (2019) Ecosystem attributes of trophic models before and after construction of artificial oyster reefs using Ecopath. Aquac Environ Interact 11:111–127
Yang CJ, Wu ZX, Liu HY, Zhang PD, Li WT, Zeng XQ et al (2016) The fishing strategy of Charybdis japonica and Rapana venosa and the carrying capacity of Apostichopus japonucus in Zhuwang, Laizhou artificial reef ecosystem based on Ecopath model. Periodi Ocean Univ China 46(11):168–177 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Yuan H, Chen P, Qin C, Xiao LI, Zhou Y, Feng X et al (2017) Seasonal variation of fish community structure in Zhelin bay, the South China Sea. South China Fish Sci 2:17–20 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang P, Jiao JH, Sun WS, Li D, Ye HM (2016) Community structure and secondary production of macrobenthos in Tianjin coastal seawaters in Bohai Bay. J Dalian Ocean Univ 31(3):324–330 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao J, Zhang SY, Xu M (2010) The primary research of the energy flow in Gouqi kelp bed ecosystem. J Shanghai Ocean Univ 19(1):99–104 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mr Chun Li and the members of Tangshan Marine Ranching Ltd. for their help with field sampling, as well as members from the CAS Key Laboratory of Marine Ecology and Environmental Sciences, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for constructive discussions and encouragement. We thank anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments.
Funding
The research was supported by Tangshan Talent Project (no. A201905009), Qingdao Postdoctoral Applied Basic Research (no. Y7KY02106N), a Postdoctoral International Exchange Program Introduction Project (no. Y8KY02102L), Hebei Province Modern Agricultural Industry Technical System “Special seafood innovation team” (no. HBCT2018170204), and the special fund for the Key R&D Project of Zhejiang Province (no. 2019C02056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Yang, X., Song, X. et al. Seasonal analysis of artificial oyster reef ecosystems: implications for sustainable fisheries management. Aquacult Int 29, 167–192 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00617-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00617-x