Abstract
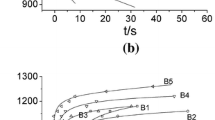
A subsection cooling process is used to selectively precipitate suanite from boron-rich slag, which initially requires a relatively high cooling rate followed by a low cooling rate. The cooling rate and homogeneity affect the crystal growth of the precipitated phase. Different structure intensification approaches, including adding cold slag and applying fins, are effective for improving the reaction. In this work, a numerical simulation of the subsection cooling process was carried out. The temperature distribution and cooling rate distribution were studied. Fast cooling under the conditions of adding cold slag and applying fins yielded centralized cooling rates of 6.3 °C min−1 and 5.3 °C min−1, respectively, with standard deviations of 27.5 and 19.7 °C min−1; the corresponding values of the traditional cooling process are 2.6 °C min−1 and 20.4 °C min−1, respectively. The results show that cold slag is better for increasing the cooling rate than fin slag, but using fins ensures that the cooling process is more homogeneous. Considering the combined effects of different arrangements, applying fins is determined to be the better choice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.X. Zhang, Z.T. Sui, P.X. Zhang, Z.T. Sui, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 26B, 345. (1995).
X.H. Wang, L.Q. Zhang, M.Y. Hou, T. Wang, H.F. Zhou, X.H. Wang, L.Q. Zhang, M.Y. Hou, T. Wang, H.F. Zhou, China J. Process Eng. 7(4), 72. (2007).
J.F. Lang, X.P. Zhang, S.L. Liu, J.F. Lang, X.P. Zhang, S.L. Liu, J Northeast. Univ. (Natural Science) 14(1), 32. (1993).
H.R. Zhan, Z.G. Fan, X.F. Jiang, J. Li, T. Jiang, H.R. Zhan, Z.G. Fan, X.F. Jiang, J. Li, T. Jiang, J. Jiangsu Univ. 32(1), 47. (2011).
T.A. Zhang, Y.L. Wang, H. Yang, C.X. Chen, X.P. Zhang, J.C. He, J.H. Shao, Y.Q. Cui, T.A. Zhang, Y.L. Wang, H. Yang, C.X. Chen, X.P. Zhang, J.C. He, J.H. Shao, Y.Q. Cui, J. Northeast. Univ. (Natural Science) 19(S1), 258. (1998).
Y. Li, Y. Du, J. Gao, Z. Guo, Y. Li, Y. Du, J. Gao, Z. Guo, Miner. Eng. 155, 1. (2020).
Y. Li, Y. Li, J. Gao, Z. Huang, Z. Guo. Ceramics Int. 45, 10961. (2019).
M. Hayashi, H. Ishii, M. Susa, M. Hayashi, H. Ishii, M. Susa,, F. Hiroyuki, K. Nagata. Phys. Chem. Glasses 42, 6. (2001).
J.H. Park, J.H. Park, D.J. Min, H.S. Song. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 35B(2), 269. (2004).
Y. Kang, and K. Morita, Y. Kang, and K. Morita, ISIJ INT 19, 61. (2006).
H.R. Zhan, Z.G. Fan, S.J. Zhou, and S.L. Liu, H.R. Zhan, Z.G. Fan, S.J. Zhou, and S.L. Liu, Mining Metall. 17(6), 34. (2008).
H.R. Zhan, S.L. Liu, and Z.G. Fan, H.R. Zhan, S.L. Liu, and Z.G. Fan, J. Northeast. Univ. (Natural Science) 11, 1604. (2007).
H.J. Hu, D.F. Zhang, and M.B. Yang, H.J. Hu, D.F. Zhang, and M.B. Yang, JMP 10(2), 82. (2008).
W.Q. Tao. Numerical Heat Transfer, 2nd ed. (Xi’an: Xi’an Jiao Tong University Press, 2001), pp. 86.
H.R. Zhan, J. Li, C.F. Gao, T. Jiang, and Z.G. Fan, H.R. Zhan, J. Li, C.F. Gao, T. Jiang, and Z.G. Fan, J. Chinese Rare Earth Soc. 28, 267. (2010).
M. Nitta, H. Nakamura, A. Ishii, Report No. 94, Nippon Steel Technical Report, Tokyo, Japan, July 2008.
F. Moukalled, L. Mangani and M. Darwish: The Finite Volume Method in Computational Fluid Dynamics (Stuttgart: Springer, 2015), pp. 103-135.
T.N. Tan, M. Dou. Chemical engineering principle, 4th ed. (Beijing: Chemical Industry Press), pp. 176.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 51204040); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. N180725023, N2024005-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, X., Zhao, Q., Li, X. et al. Study on the Intensification of the Boron-Rich Slag Subsection Cooling Process. JOM 73, 781–790 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04546-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04546-1